- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF500-48P-K9-G5 Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750V2-24TS-S Switch
- What is DWDM in networking?
- How to install NIC card?
- Difference between GLC-LH-SM and GLC-LH-SMD
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-48TD-L Switch
- All Cisco ONS-SI-155-L2's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-60.61's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- What is network adapter?
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-40.56's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma

The fiber network is gradually replacing the copper network because of its high speed, high density, high bandwidth and other advantages. Compared with traditional coaxial cable or twisted pair cable, fiber can support further transmission distance. But in fact, the optical fiber transmission distance is affected by many factors. In the field of ultra-high-speed optical communication, transmission distance has become an urgent problem to be solved. With the continuous development of optical fiber networks, optical fiber transmission distance has been extended from a few meters to 100 meters or even thousands of meters. However, the optical signal becomes weak during long-distance transmission. Many optical devices are used to solve the problem of limited optical signal transmission distance. This article will focus on several major factors limiting the optical transmission distance.
Type of fiber
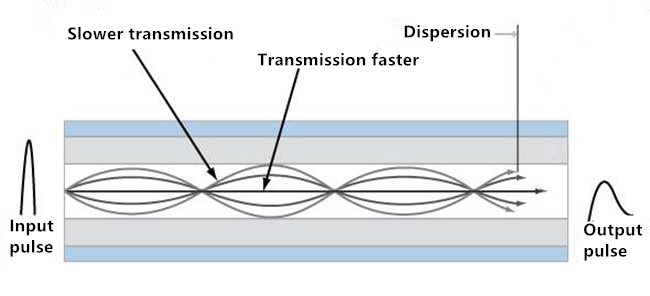
In general, the maximum transmission distance of the optical signal in the fiber will be affected by the dispersion of the fiber. There are two types of fiber dispersion, one is the waveguide dispersion, that is, the process of transmission of different wavelengths of light at different wavelengths caused by the expansion of the signal pulse; the other is the mode of dispersion, referring to each mode to reach the fiber Terminal time differently, resulting in the phenomenon of pulse broadening.
In multimode fiber, mode dispersion is the main factor affecting the transmission distance. Due to the large diameter of the multimode core, the optical signal cannot be transmitted at the same time, the delay between the highest secondary mode and the lowest secondary mode occurs, and the dispersion occurs and the performance of the multimode fiber is affected, as shown in the following figure. In the single-mode fiber, the waveguide dispersion is the main constraint. This is because the core of a single-mode fiber is much smaller than a multimode fiber. This is also the reason why single-mode fiber can travel more than multimode fiber.
Light module light source
The transmission of optical signals depends on fiber optic cables. Since our various terminal devices are based on electricity. So the conversion between the photoelectric signals is essential in the optical network. The quality of the optical module to convert the optical signal is largely dependent on its internal light source. Optical modules in the light source will generally use LED (light-emitting diode) or laser diode. Their quality is good or bad will directly affect the optical signal transmission distance.
Light-emitting diode-based optical modules can only support short-range, low data rate transmission. So they cannot meet the growing demand for higher transmission rates and further transmission distances. In general, the use of laser diode optical module supports the high-speed long-distance transmission. The most common laser sources are Fab laser, DFB laser, and VCSEL laser. The following diagram shows the main features of these light sources.
|
Light Source |
Light Emitting Diode (LED) |
FP Laser |
Distributed Feedback Laser (DFB) |
Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) |
|
Transmission distance |
short distance |
medium distance |
long distance |
medium distance |
|
Transmission rate |
low rate |
high rate |
high speed |
high rate |
|
Transmission frequency |
Wide spectral bandwidth |
Medium spectral bandwidth |
Narrow spectral bandwidth |
Narrow spectral bandwidth |
|
Cost |
Low Cost |
Medium Cost |
High Cost |
Low Cost |
Transmission frequency
As shown in the graph above, different laser sources support different frequencies. The optical signal frequency will affect the optical transmission system transmission distance. In general, the higher the frequency, the farther the transmissions distance. Therefore, selecting the appropriate frequency is critical for the transmission of optical signals. Multimode fibers typically operate at 850 nm and 1300 nm wavelengths, and single-mode fibers operate at 1300 nm and 1550 nm wavelengths.
Bandwidth is another important factor that can affect the transmission distance. In most cases, as the bandwidth increases, the transmission distance is inversely proportional. For example, within a kilometer of fiber can only support 500 MHz bandwidth, and in the distance of 2 km can only support 250 MHz, 5 km is only 100 MHz. Single-mode fiber is more suitable for long-range high-speed propagation of optical signals because of the different transmission modes of optical signals in single-mode and multimode fiber.
Fiber connection point
In the optical network, optical fiber connection is essential, generally, will use the thermal connection, that is, fiber splicing, or cold connection, and fiber optic connectors or cold connectors, these two ways to complete the fiber connection. And the signal through the optical fiber connection point is prone to light loss, which will affect the optical signal transmission distance.
Conclusion
Optical transmission distance is affected by a variety of factors, such as fiber type, light source, transmission frequency, bandwidth, welding and fiber optic connectors and so on. In deploying fiber-optic networks, we should consider these factors to reduce their impact on the transmission distance. At the same time, such as repeaters and optical amplifiers and other optical devices can also effectively extend the optical signal transmission distance. In the future, we will continue to study with great concentration, and strive to solve these restrictions.





































































