- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-CBS3125G-S Switch
- What is Optical Ethernet?
- All Cisco CWDM-GBIC-1490's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- What is 1000BASE Transceiver?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF112-24-UK Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960XR-24PS-I Switch
- The New Easy-to-Use Managed Switches-Cisco 350 Series
- The difference between QSFP+ and CSFP
- The difference between TDM and WDM
- What is a Laser Diode?

PCI-Express is the new bus and interface standard, which original name for the "3GIO and was made by Intel, it means that it represents the next generation of I / O interface standard. It was renamed "PCI-Express after certification by PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Group). This new standard will completely replace the PCI and AGP, and ultimately realize the unity of the bus standard.
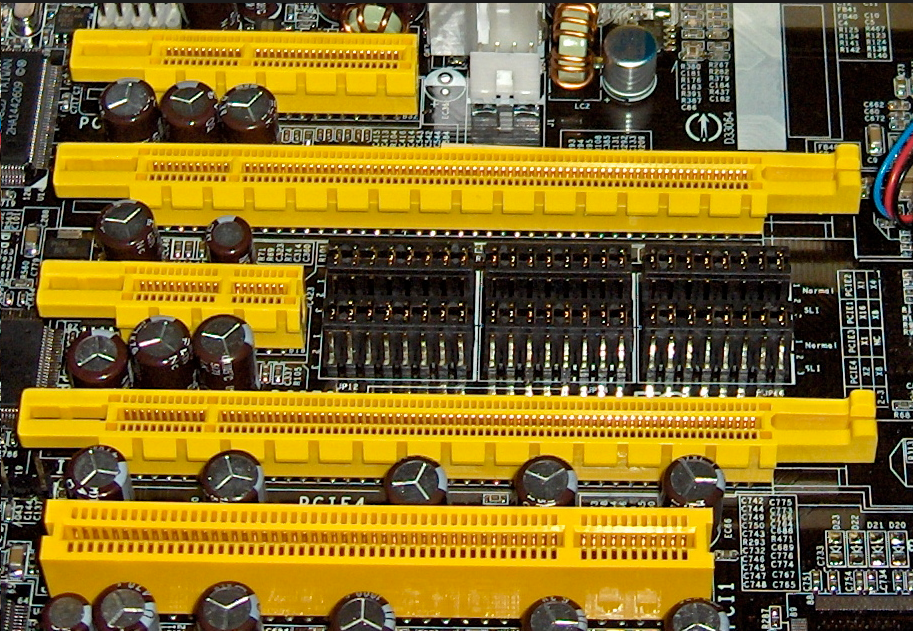
The main advantage of PCI Express is that it has high data transfer rate, currently, the highest rate is up to 10GB / s, and there is considerable potential for development. There are a variety of specifications for PCI Express, from PCI Express 1 x to 16 x, can meet the present and the future of low-speed devices and the demand for high-speed equipment.
Intel's i915 and i925 series chipset is mainly support for PCI Express. However, it will take a long time to replace PCI and AGP completely.
PCI Express uses the point-to-point serial connection which is very popular in the industry. Each device has its own dedicated connection rather than the shared parallel architecture of the PCI and earlier computer buses, which does not require bandwidth to the entire bus and improve the data transfer rate to a high frequency that PCI cannot provide. Compared to traditional PCI bus, which is only achieve one-way transmission in a single period of time, the duplex and simplex connection of PCI-E can provide higher transmission rate and quality, The differences between them are similar to half-duplex and full-duplex.
The differences of PCI-E interface depending on the bus width, including X1, X4, X8, and X16, and the X2 mode is used for the internal interface instead of the slot mode. PCI-E specifications from one channel connection to 32-channel, there is a very strong scalability to meet the different systems and equipment of different needs for data transmission bandwidth. In addition, the shorter PCI-E card can be inserted into a longer PCI-E slot, PCI-E interface can also support hot-swappable, and this is a great improvement. The transfer speed of PCI-E X1 is up to 250MB / S has been able to meet the mainstream sound chip, network card chip and storage equipment for data transmission bandwidth needs, but cannot meet graphics chip’s demand for data transmission bandwidth. As a result, the PCI-E interface, which is used for replacing the AGP interface, has a bit-width of X16, providing 8GB / s bandwidth, far exceeding the 2.1GB / s bandwidth of the AGP 8X.
Although the PCI-E allows achieve X1 (250MB / s), X2, X4, X8, X12, X16 and X32 channel specifications. But now, PCI-E X1 and PCI-E X16 has become the PCI-E mainstream specifications, while many chipset manufacturers add support for PCI-E X1 in the South Bridge chip, and add to the PCI- E X16 support in Northbridge chip. In addition to providing extremely high data transfer bandwidth, the PCI-E interface provides more bandwidth per pin than traditional I / O standards due to the use of serial data packets. This reduces PCI- E equipment production costs and volume. In addition, PCI-E also supports high-end power management, hot-swappable, data synchronous transmission, bandwidth optimization for the priority transmission of data.
PCI-E 1.0 Specification:
PCI-E 1X (1.0 standard) uses a one-way 2.5G baud rate for transmission, since each byte is 10 bits (1 start bit, 8 data bits, 1 end bit), so the transmission rate 2.5G / 10 = 250MB / S (250 megabytes per second), which can be calculated PCI-E16X unidirectional transmission rate of 250MB / S * 16 = 4GB / S, bidirectional transfer rate of 8GB / S. Currently the motherboard of P43 and below (excluding P43) using PCI-E 16X (1.0 standard), PCIe-104 Express and PCIe-104 adopts PCI-E 1.0 specification.
PCI-E 2.0 Specification:
PCI-E 1X (2.0 standard) uses a unidirectional 5G baud rate for transmission, since each byte is 10 bits (1 bit start bit, 8 data bits, 1 bit stop bit), so the unidirectional transmission rate (500 MB / s), which can be calculated PCI-E 16X (2.0 standard) unidirectional transfer rate of 500MB / S * 16 = 8GB / S, bidirectional transmission rate of 16GB / S, PCI-E 32X (2.0 standard) speed rate of 32GB / S, the motherboard of P43, P45, P55 and above come with PCI-E 16X (2.0 standard) slot.
PCI-E 3.0 Specification:
PCI-E 1X (3.0 standard) uses a one-way 10G baud rate for transmission, since each byte is 10 bits (1 start bit, 8 data bits, 1 bit stop bit), so unidirectional transmission rate (1000 MB / s), which can be calculated PCI-E16X (3.0 standard) unidirectional transfer rate of 1000MB / S * 16 = 16GB / S, bidirectional transmission rate of 10G / 10 = 1000MB / 32GB / S, PCI-E 32X (3.0 standard) bidirectional transfer rate up to 64GB / S, the specification was officially released in 2010.





































































