- Related articles
- What Is GYXS Optical Fiber Cable?
- All Cisco SFP-10GE-SR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matri
- Difference between transponder and muxponder
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560V2-48TS-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750V2-48PS-S Switch
- Not confused! How to choose PCI-E and SATA SSD
- What can PCI-E 3.0 bring us?
- The difference between GBIC and CSFP
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG300-52MP-K9-UK Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SRW248G4-K9-UK Switch

Tight-buffered trunk optical cable is composed of multiple sets of fibers, usually used in the trunk (vertical) wiring subsystem to connect devices and telecommunications. Now there are a variety of optional tight-buffered trunk optical cables on the market, applicable to different application environments. This tutorial will introduce the factors when we consider purchasing tight-buffered trunk optical cable.
Application Environment
In general, tight-buffered trunk optical cable is ideal for use in indoor environments, but can also be used in indoor/outdoor applications (shown in the third section below). If you want to select tight-buffered trunk optical cable for the indoor application, the first consideration is the cable fire-proof rating, which has been specified in detail in the National Electrical Specification. In general, there are three main categories of tight-buffered trunk optical cable’s fire-proof rating: versatile rate, rise rate (Riser) and booster rate (Plenum), of which, booster (Plenum) cable has the highest level of fire proof. The use ranges of tight-buffered trunk optical cable with different fire-proof ratings are as follows:
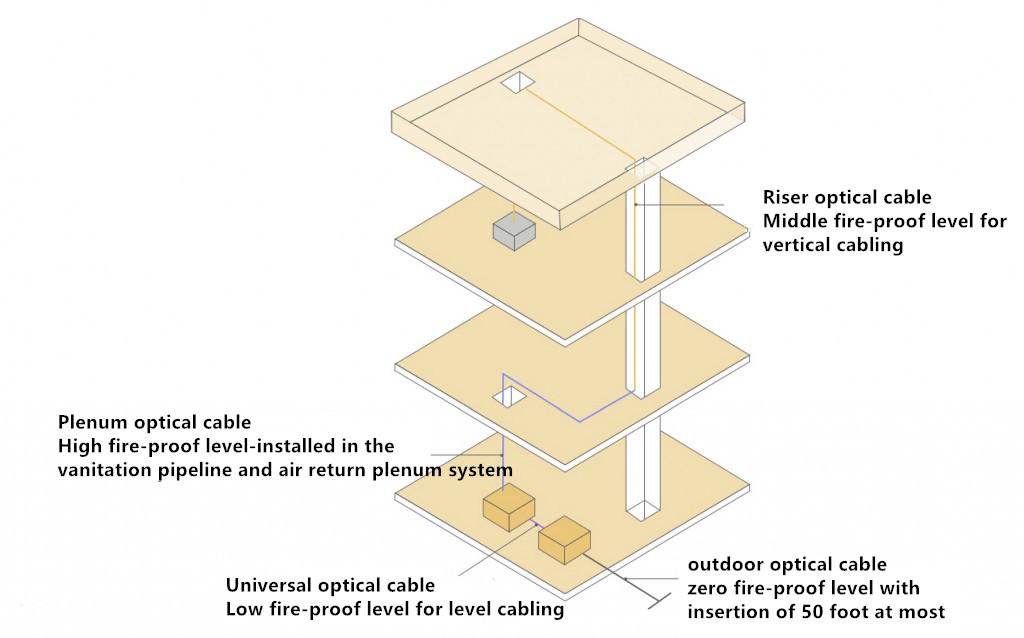
It should be noted that the Plenum cable can also be used in the riser and general application environment while trunk (Riser) cable can be used in general application environment. However, the higher fire-proof rating determines the higher cable prices. In order to save cost, we should select the appropriate fire-proof level of the trunk-buffered cable based on the specific application environment.
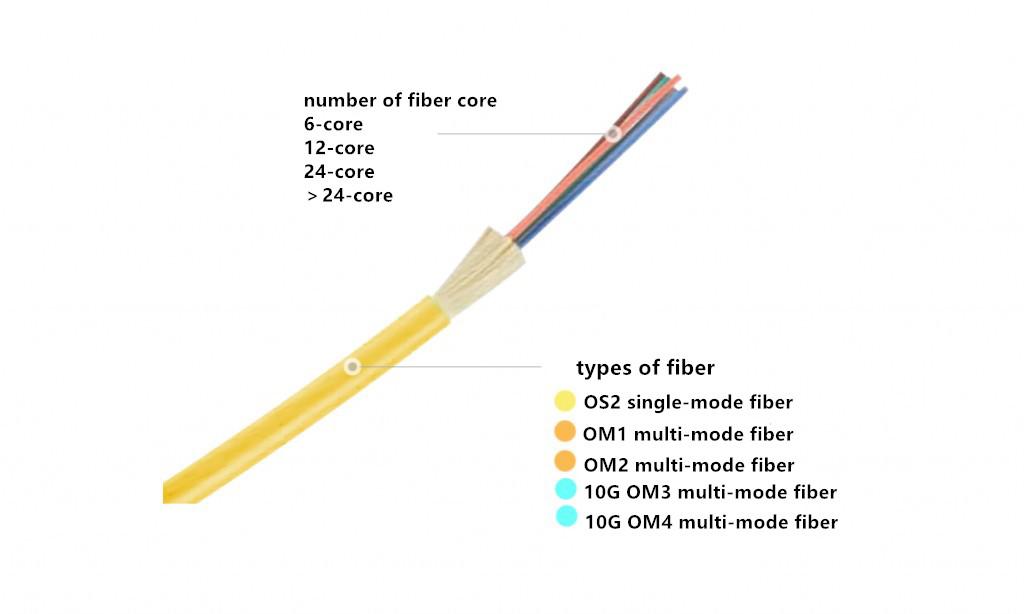
Fiber Type and Core Number
We know that different types of fiber performance are also different; in addition, the number of fiber optic cable core should be chosen according to the size of the network. The fiber types of the trunk-buffered cable are OS2 single mode fiber, OM1 multimode fiber, OM2 multimode fiber, 10G OM3 multimode fiber and 10G OM4 multimode fiber. Single mode fiber is often used for long distance transmission and multimode fiber for short distance transmission. After determining the type of fiber, it is necessary to start to select the number of cores. Common tight-buffered trunk cable’s core number is between 2 to 24 in which 2-core, 6-core, 12-core, 24-core tight-buffered trunk cable are most widely used in trunk (vertical) cabling; the number of cores in the tight-buffered trunk cable should meet the needs of current and future network expansion.
Optical Cable Structure
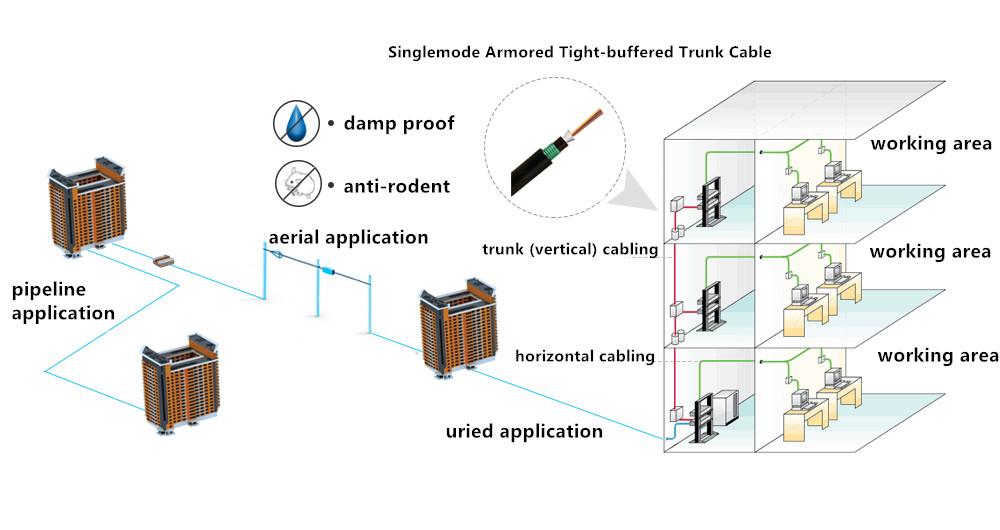
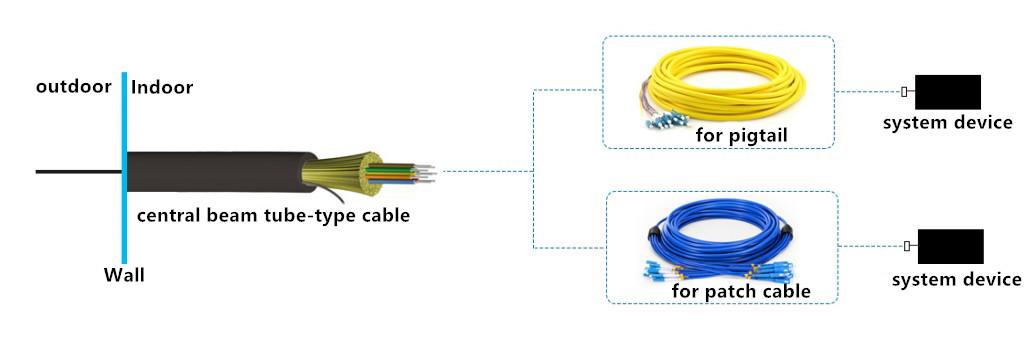
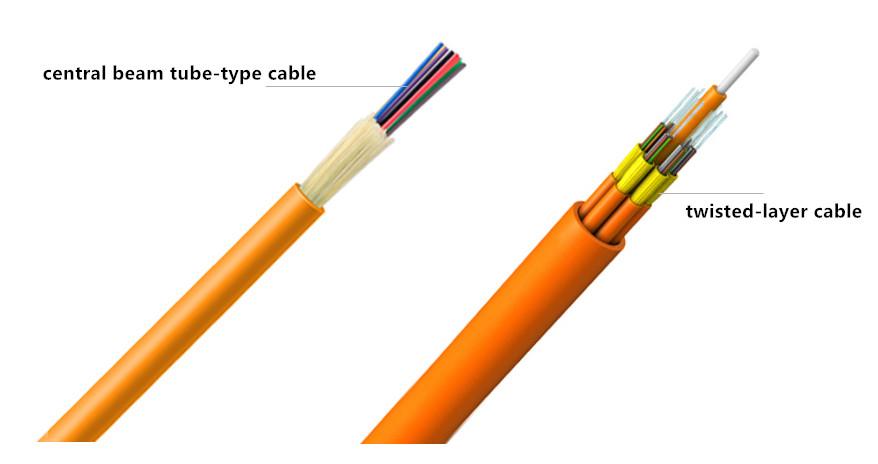
It is mentioned that the trunk cable can also be used in indoor/outdoor applications, but the outer jacket of the tight-buffered trunk cable is not enough to resist the outdoor harsh environment, therefore, in order to protect the cable, people add the design of armor layer on the basis of tight-buffered trunk cable to prevent the rat and insects; the armored design of tight-buffered trunk cable can be divided into interlocking armor and corrugated steel armor. In addition, the tight-buffered trunk cable can also be designed as the central beam tube-type cable and twisted-layer cable (as shown below). The installation and management of the former are more convenient, and more widely used.
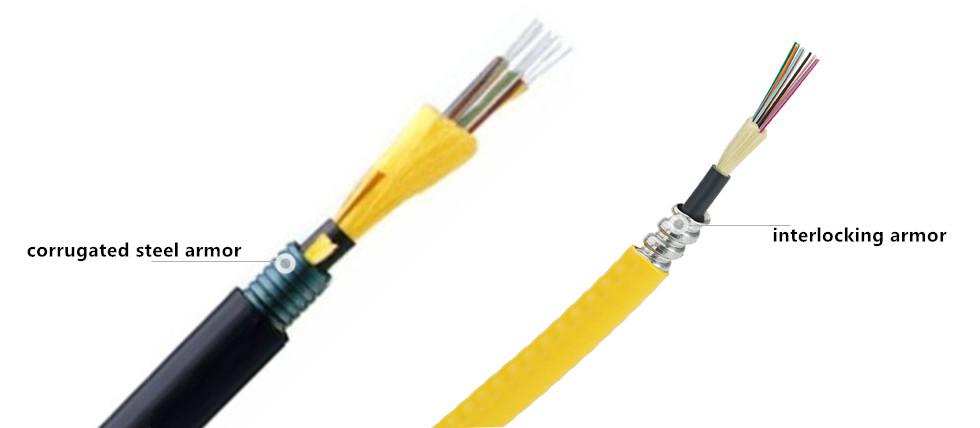

Tight-buffered Trunk Cable Solutions
Here are some examples of the applications of the tight-buffered trunk cable:
Application Example of Central beam Tube-type Tight-buffered Trunk Cable
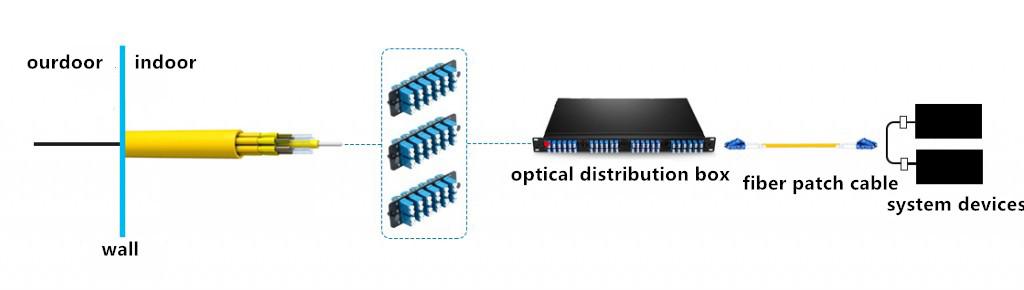
Application Example of Twisted-Layer Tight-buffered Trunk Cable
Application Example of Armored Tight-buffered Trunk Cable