Why SSD use PCI-E interface?
In the 60 years of computer development, storage media has undergone enormous changes from the initial punch cards to SSD. In recent years, SSD is developing rapidly, and with SSD production process and the user's pursuit of read and write speed, more and more high-end SSD began to choose PCI-E interface to connect SSD with motherboard. In this article I will detailed introduce the pros and cons of SATA channel and PCI-E channel SSD, so that allow people to choose the best one when purchase.
Why adopt PCI-E channel?
Why SSD use PCI-E interface instead of using SATA 3.0 interface? First of all, we need to understand the working principle of two interface hard drive: In the traditional SATA SSD, when we operate the data, it will be read from the hard disk to memory, and then extract the data to the CPU internal calculation, and then write into Memory, storage to the hard disk; but the PCI-E is quite different, , the data connected with the CPU directly through the bus, close to the maximum transmission speed, the maximum amount of data, eliminating the need to call the hard disk memory process. In short, we can compare the two channels as two cars, PCI-E-channel car is like driving at high speed, and SATA channel car is like driving at a rugged mountain road, it is clear that which is faster.
Speed table of different SSD interface
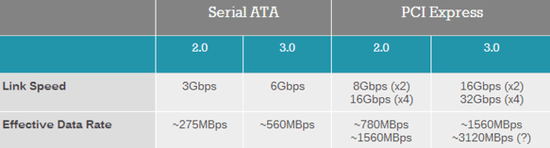
From the above table we can easily see that the maximum transmission speed of SATA 3.0 channel is 6Gbps, the actual speed of up to 560MB / s, SATA channel has been unable to meet the growing needs of read and write speed, so PCI-E SSD came into being.
But some readers may have a doubt: why my SSD is M.2 interface, but the speed is not fast? M.2 was originally called NGFF, which full name is Next Generation Form Factor. This interface is very special, while supporting SATA and PCI-E two channels, it is easy to mislead. In fact, not all of the M.2 SSD has a fast speed of reading and writing, the speed of reading and writing will not more than 550MB / s if it is using SATA channel M.2 interface SSD. It is worth noting that some of the motherboard manufacturers with M.2 interface to select the CPU native PCI-E channel, some extended through the PCH South Bridge, which may have an impact on the speed of SSD.
PCI-E protocol and the advantage of speed
AHCI and NVMe protocols
After discussing interface, we are going to talk about the protocol of two kinds of SSD. As if the IDE will come to the end, AHCI seems to have a bottleneck, the SATA interface and AHCI standard we used now is designed for high-delay mechanical hard drive, the most of SSD drive still continue to use them. In the early days, SSDs may not have a big problem with performance, but as SSDs the growing demand in performance, these standards have become a bottleneck in limiting SSDs, and the AHCI standard designed for mechanical hard drives is not well suited for low Delay of the SSD.
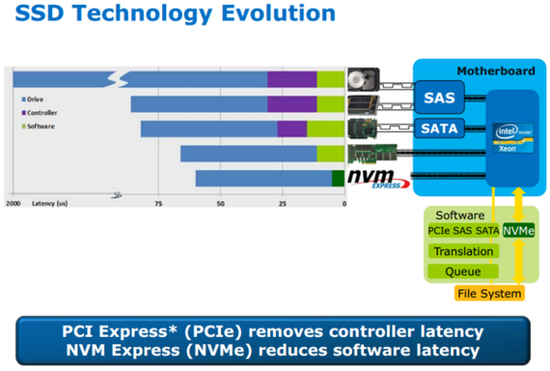
One advantage of NVMe is low latency. This is mainly because of streamlined storage stack, NVMe no need to read the register to issue commands, each command of AHCI requires reading four non-cacheable registers, so that resulting in an additional delay of approximately 2.5 μs. The advantage of low latency and good parallelism is that the random performance of the SSD can be greatly improved and can play an excellent speed at any queue depth.
The performance of IOPS is also improving greatly for NVMe on SSDs. Because of the idea of parallelism was not fully incorporated into the specification when the AHCI specification was developed, and the function of NCQ was used to optimize the transmission capability, but the interface does not allow the SSD to really maximize the parallelism it deserves. In addition, for mobile users, the use of NVMe storage device can continue to play a great help on the battery. NVMe adds automatic power state switching and dynamic power management. The device can quickly switch to the power state 1 from the energy state 0 after idle 50ms, and it will enter the state of lower energy consumption 2 after idle 500ms. Although the state of switching power consumption will produce a short delay, but the power consumption in these two states can be controlled at a very low level in the idle, so compared to the mainstream SATA interface SSD, it also has a larger advantage in energy management.
The comparison of speed
Let us check the speed of two SSD (Left for SATA SSF, right for PCI - E SSD)
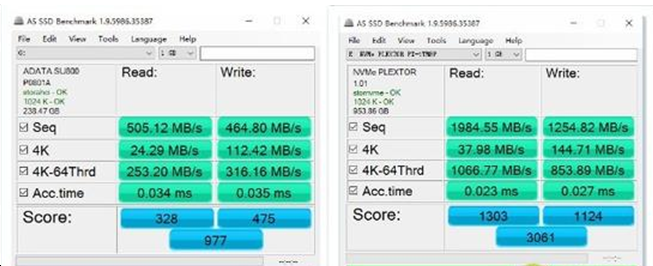
The gap of these two types of AS SSD running speed is obvious, whether read or write, or 4K test, PCI-E SSD are better than SATA SSD. The score of PCI-E SSD is higher 3 times than SATA SSD.
How to install for ordinary user
So for, many people may feel a little confused, for help you to have a more profound understanding, we will use a table to explain different interfaces and the comparison of speed.
|
Protocols
of SSD with different interface
|
|
Interface
|
Protocol
|
|
SATA
|
AHCI
highest speed is 6Gbps
|
|
SATA-Express
|
AHCI
highest speed is 12Gbps, not commonly used
|
|
M.2
|
AHCI
highest speed is 6Gbps or NVMe, highest speed is 32Gbps
|
|
U.2
|
NVMe,
highest speed is 32Gbps
|
|
PCI-E
|
NVMe,
highest speed is 32Gbps
|
Tips for purchasing
Although the PCI - E SSD has many benefits, but it doesn’t means that is suitable for everyone. Due to flash memory particles and master quality problems, compared to the traditional SATA SSD, the cost of PCI-E is much high. In addition, because PCI-E will take up the bus channel, entry and a small number of CPU channel in the mid-range platform, so that are not suitable for adding PCI-E SSD, only for these top platform can make full use of its performance like Z170, or X79, X99. For users who use dual graphics card, the use of PCI - E SSD can cause some impact on the graphics performance but not serious. In general, choose PCI-E SSD if without being limited by the budgets, or enough to choose an ordinary one if not require too much.









































































