- Related articles
- The Difference between Internal Network Card and External Network Card
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco UCS-FI-6296UP-CH2 Switch
- Applicable to 1000BASE-EZX Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- The difference between XENPAK and X2
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-54.94's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- The Uses of PCI Express x1
- All Cisco ONS-SI-622-L2's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- How to Identify Fiber Optic Cable?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG550XG-24F-K9-UK Switch
- All Cisco ONS-SI-155-I1's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat

Definition
Muxponder: In optical fiber communications, a muxponder is the element that sends and receives the optical signal from a fiber in much the same way as a transponder except that the muxponder has the additional functionality of multiplexing multiple sub-rate client interfaces onto the line interface.
It has one input port and one output port. It is used for 10 Gigabit ethernet. It can be used to convert client signal in the form of grey optics to line signal in the form of color optics.
It has one output port and multiple input ports. Optical Signals of different wavelength and rates are combined into one channel output. MUXPONDER used for 10 Gigabit ethernet is shown in the figure.
Applications
Following are the applications of Optical Transponder:
Wavelength Conversion: It converts the output of the optical switch to wavelength useful to be transported over DWDM or CWDM networks.
Dark fiber contribution: Dark fiber is the unused fiber optic cable which is yet to be connected to a fiber optic network.
Following are the applications of 10G Optical Muxponder:
• It aggregates about 10 client signals into a single line signal at 10Gbps.
• Takes care of individual transport of sync and data signals through SDH, fiber and ethernet etc.
• It incorporates FEC functionalities to enable transmission over long haul optical networks.
How Does Fiber Optic Transponder Work?
The most obvious feature of a transponder is that it automatically receives, amplifies, and then retransmits a signal on a different wavelength without altering the data/signal content. Wavelength conversion in commercial networks today is only carried out by optical to electronic to optical (O-E-O) transponders. O-E-O Transponder works as a regenerator which converts an optical input signal into electrical form, generates a logical copy of an input signal with a new amplitude and shape of its electrical pulses and uses this signal to drive a transmitter to generate an optical signal at the new wavelength.
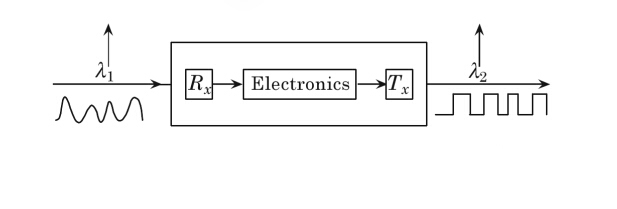
Function of transponder in DWDM
DWDM wavelengths from the transponder are multiplexed with signals from the direct interface to form a composite optical signal which is launched into the fiber. A post-amplifier boosts the strength of the optical signal as it leaves the multiplexer.
100G DWDM Muxponder Solutions
The 100G DWDM Multiprotocol Multirate Muxponder for high capacity optical transport solution is highly integrated platform for providing a unified 100G optical transport layer- supporting various client services including protocols: 40G LAN, 10G LAN/WAN, STM64/OC-192, OTU2/2e and 8G/10G FC.
The 100G Muxponder is designed to provide 100G transport solution in modular and cost effective way for rolling out services. It uses standards based, pluggable optical modules on all the optical interfaces on both client and line side. It is targeted for meeting the market demands for low power consumption, rack space savings and reduction in the overall solution CAPEX and OPEX by increasing the capacity of optical fiber as for enterprise as for carrier networks.
Transponders and muxponders for all needs
- 1U transceiver-based solutions that reduce networking complexity
- CWDM / DWDM / OTN
- All topologies and protocols supported up to 100Gbps
- Compact 1U platform and reduced footprint
- Simple to install and configure
- System capacity and new services easily added
- Approved by major system vendors
- Encryption
Conclusion
In today’s optical networks, WDM technology (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is commonly used. With WDM solution, each service whether a GbE, 10G LAN, SONET/SDH,Fibre Channel or HD/SD-SDI, is assigned an independent dedicated wavelength which then are multiplexed into one single fiber rather than using multiple fibers. WDM technology allows the single fiber optic cable to be used for transport of multiple services while assigning to each dedicated spectral wavelength, thus increasing fiber capacity. However, to even further maximize the fiber capacity, muxponder technology is often preferred.























































