- Related articles
- The Things You Need to Know about 10GBASE-SW Ethernet Standards
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-X9464TX= Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SLM2016T-UK Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960+48PST-L Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960+24LC-S Switch
- The Application of Cisco compatible SFP-10G-SR
- All Cisco GLC-FE-100ZX's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960XR-24PD-I Switch
- Cost Effective Compatible Cisco Transceivers
- Difference between transponder and muxponder

Common fiber nouns
1) Attenuation
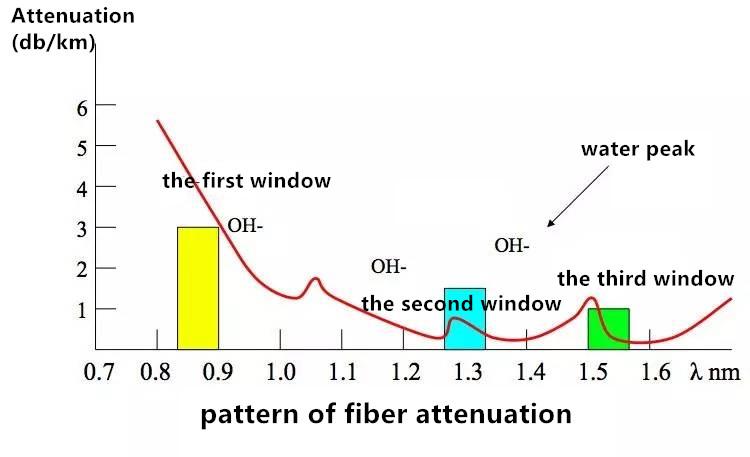
Attenuation: light’s energy loss transmitting in single-mode fiber 1310nm 0.4~0.6dB/km 1550nm 0.2~0.3dB/km plastic multi-mode fiber 300dB/km.
2) Dispersion
Dispersion: light pulse’s march for a distance along the fiber causes the wider bandwidth. It is the main factor that limits transmission rate.
Mode dispersion: it only occurs in multi-mode fiber as different mode lights transmit along different ways.
Material dispersion: lights with different wavelengths are different in gaits of march.
Waveguide dispersion: the reason is that light energy transmits in the fiber core and coating with relatively different gaits of march. In the single-mode fiber, changing fiber’s dispersion by changing its inner structure is very important.
Fiber types
G.652 zero dispersion point is around 1300nm
G.653 zero dispersion point is around 1550nm
G.654 negative dispersion fiber
G.655 dispersion shifted fiber
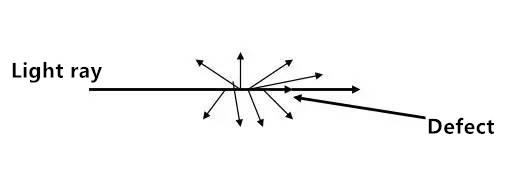
3) Scattering
As the imperfect light’s basic structure cause light energy loss, the light transmission has no good directivity anymore.
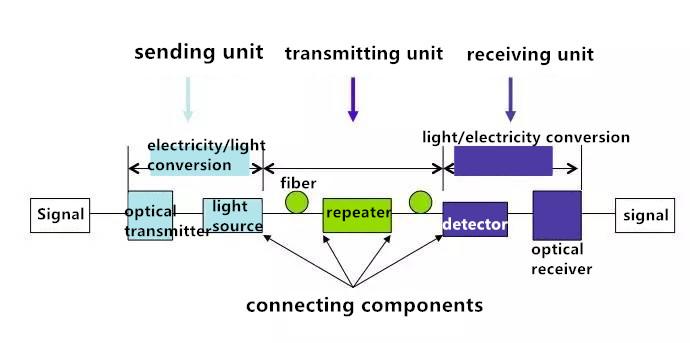
Basic knowledge of fiber system
The introduction to the basic framework and function of fiber system
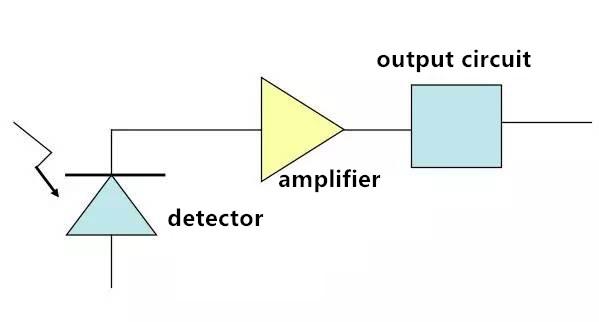
1. Sending unit: turning electronic signal into light signal;
2. Transmitting unit: media carrying light signal;
3. Receiving unit: receiving light signal and turning it into electronic signal;
4. Interface unit: connecting fiber with the light source, light detector, and other fibers.
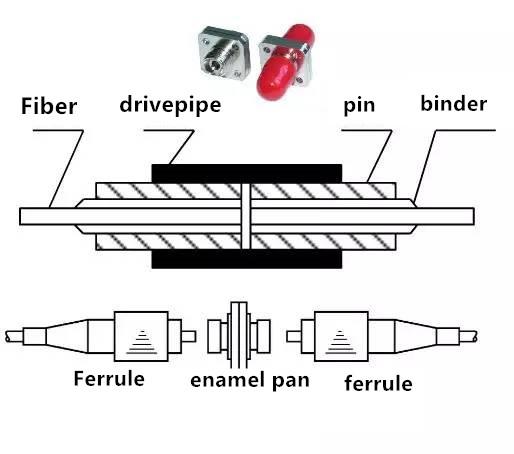
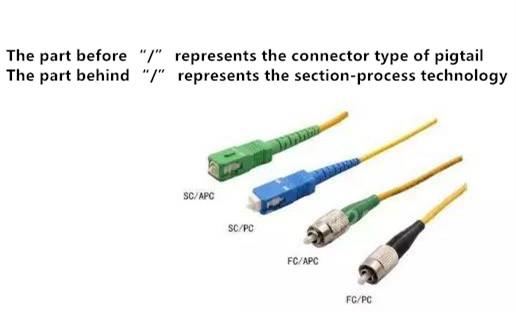
Common Connector Types
Coupler
1. Main function: redistributing light signal
2. Important application fields: fiber internet, especially the local area network
3. Application area: wavelength division multiplexer
Basic structure
1. A bidirectional passive device
2. Basic shapes: tree and star
——splitter corresponding to coupler
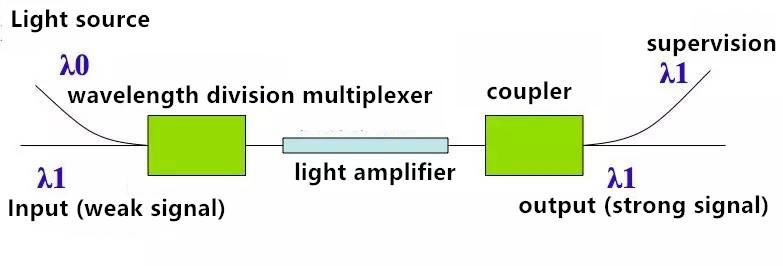
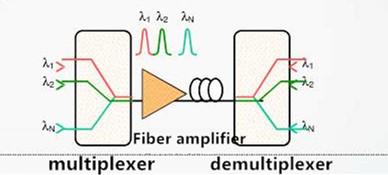
WDM
WDM—Wavelength Division Multiplexer transmits multi light signals in a fiber. These light signals’ frequencies and colors are different. WDM means the coupling of multi signals to the one fiber while wavelength division demultiplexer means the opposition.
WDM (legend)
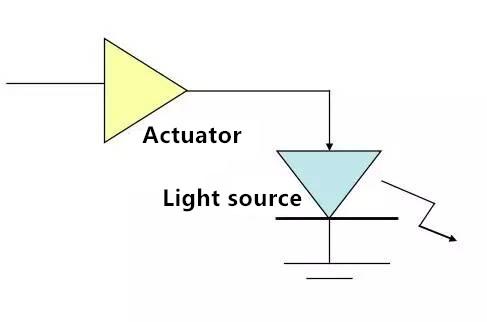
Sending unit
Receiving unit
Amplifier