- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48PQ-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco UCS-FI-6248UP-CH2 Switch
- What Is GYXTC8S Optical Fiber Cable?
- What Is GYTA Fiber Optic Cable?
- The difference between SDI and HD SDI
- Types of network card speed
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N5020P-4N2232PF-B Switch
- All Cisco ONS-SI-100-LX10's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility m
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF102-24-UK Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG102-24-UK Switch

It is well known that the quality of transmission medium is quite important for the whole project in the cabling system. It not only involves the lifespan of cabling project, more importantly, the quality and performance of cabling system have to be secure. Fiber optic cable is commonly used to be the transmission medium for the long distance transmission, because of its benefits strong anti-electromagnetic interference, less signal attenuation, large capacity, light-weight, small size and long transmission and so on.
Even though fiber optic cables are widely used, most people still do not have a deep knowledge about how to select them. This time we will give a detailed explanation about how to select a good fiber optic cable from the structure, materials and technique.
Technique one: materials
The materials of fiber optic cables are the key that relates to its longevity. And the manufacturing techniques are the critical process of determining the quality of fiber optic cable. Additional loss ≤0.01dB/km is the standard that measures the level of fiber optic cable manufacturing techniques for manufacturers. The essential materials of fiber optic cables include fiber core, optical fiber ointment, protective cover materials and PBT, all of these materials have different quality requirements. The fiber core requires a higher charge capacity, higher signal to noise ratio, lower bit error rate, longer amplifier spacing, higher information carrying capacity; optical fiber ointment is filled in the fiber bundle, its role is to prevent erosion from the moisture in the air, and another role is to act as the pad for fibers to buffer the vibration or impact.
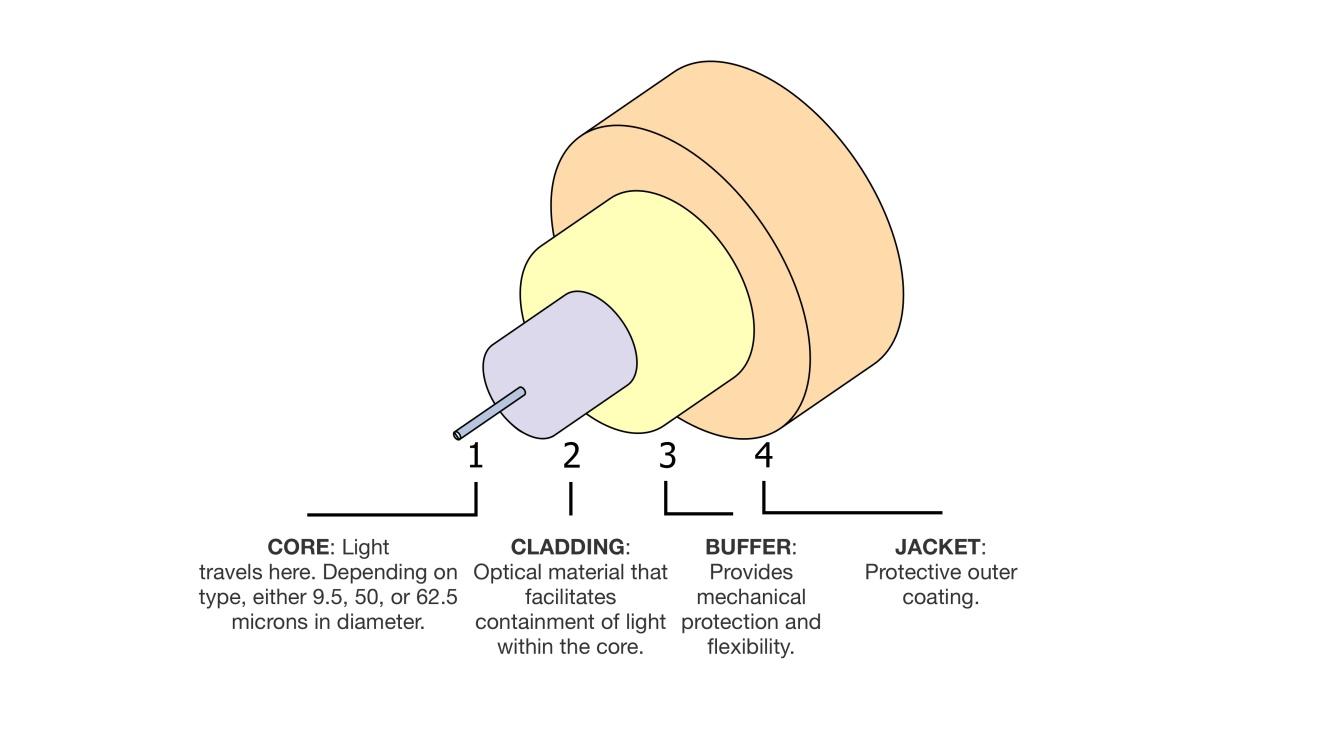
Technique two: fiber count
There are several types of fiber optic cables that can work for different demands for fiber count: central beam tube type, layer twist type, skeleton type and belt type and others. Different structures are designed for different uses. Generally, central beam tube type fiber optic cable is suitable for less than12-fiber demand; this type has a simple technique and is low-cost, it is also a good choice for overhead laying or trunk line network with strong pipe protection. Layer twist type fiber optic cable can contain 144-fiber, which is reinforced by center strand or single steel wire, and uses SZ to synthesize the cable. The greatest advantage of layer twist type is waterproof, anti-strong pull. It can be used for direct burial. Besides, it’s easy to bifurcate, namely, parts of the fiber optic cable to be used separately; there is no need to break the entire cable, just need to fork the needed fiber, which is beneficial for data communication network and adding optical nodes along the cable television network. The number of cores of the ribbon fiber optic cable can be up to a thousand. 4 to 12-core fiber arrays alignment, which forms a ribbon fiber unit, then multiple ribbon fiber units are arrayed into a cable that is the ribbon fiber optic cable. For network-level fiber optic cable, the loose-tube type and layer type are generally used.
Technique 3: applications
If selecting fiber optic cables according to the applications, there are also several types for options: overhead fiber optic cable, buried fiber optic cable, duct fiber optic cable, submarine fiber optic cable and non-metal fiber optic cable and others. Overhead fiber optic cables require high intention and small temperature difference; buried fiber optic cable requires resistance to pressure, moisture and chemical attack; duct fiber optic cable and submarine fiber optic cable both require resistance to water pressure and tension, water-proof; non-metal fiber optic cables have a good insulation and resistance to tension, it can be laid along with high-voltage wire. Therefore, when selecting fiber optic cables, applications have to be taken into consideration and it’s better to communicate completely with the manufacturers so as to ensure the performance of fiber optic cables is stable and reliable.
Conclusion
To sum up, selecting fiber optic cables is more complicated than selecting coaxial cables; you can’t judge them only by the fiber count and the price, because the truth of good products and manufacturers lies in the raw materials they used, the producing techniques, technical requirements and structural designs which are the considerations you should really have for a cost-effective selection.





































































