- Related articles
- The difference between QSFP+ and CSFP
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG350XG-48T-K9-EU Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3850-32XS-E Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SLM2048PT-UK-RF Switch
- Applicable to 1000BASE-SX2 Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560G-48PS-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG250-10P-K9-UK Switch
- The difference between GBIC and SFP
- What is IEEE 802.3?
- All Cisco SFP-OC48-LR2's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr

There are so many different models or brands network cards on the market, so do you know which one is the fastest? Of course there is no fixed answer to this question, but all we need to know that how to choose the model which close to the fastest speed. Now we’ll list some factors that affect the transmission rate and give some Intel models for your reference.
The factors that affect the transmission rate:
There are three main factors that affect the network transmission rate: shared bandwidth, network latency and packet loss rate.
Shared bandwidth: When multiple networked devices are simultaneously connected to the same broadband bandwidth, the bandwidth allocated to a single device cannot reach the peak value. The more there are devices, the lower the transfer rate is.
Network latency: When the amount of information is too large to restrict, a variety of data in the network medium through the network protocol (such as TCP / IP) for transmission, excessive network traffic will cause the device to respond slowly, resulting in network latency, making the transmission rate slows down.
Packet loss rate: Typically, Gigabit Ethernet traffic is greater than 200Mbps, the packet loss rate is less than five ten thousandths; Fast Ethernet traffic is greater than 60Mbps, the packet loss rate is less than one ten thousandth. I would like to use two figures to illustrate the effect of packet loss and delay on network throughput.
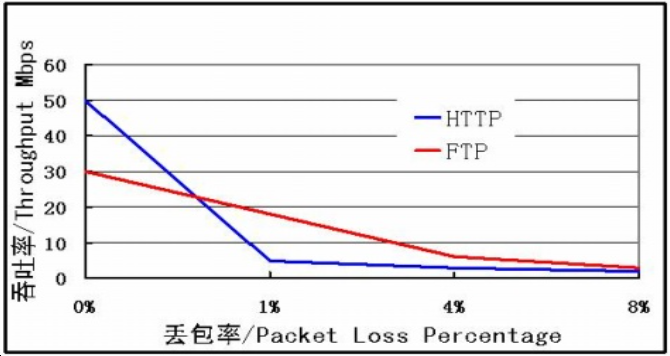
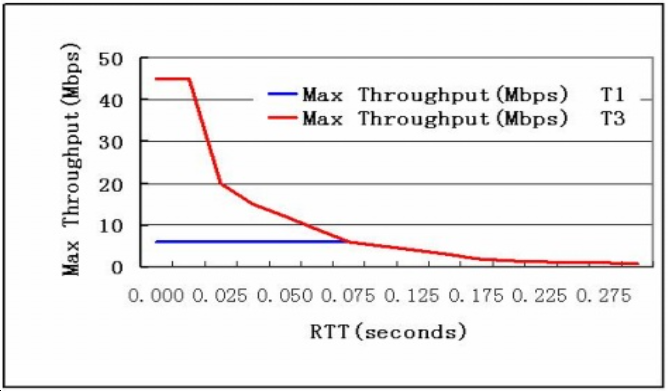
Some models of Intel fastest network cards
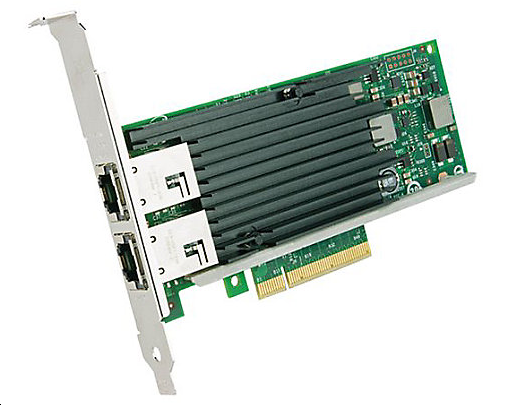

|
Applicable network type: |
10 Gigabit Ethernet |
|
Transmission rate: |
10000Mbps |
|
Bus type: |
PCI-E |
|
Network interface type: |
RJ-45 |
.png)
|
Applicable network type: |
10 Gigabit Ethernet |
|
Transmission rate: |
10000Mbps |
|
Bus type: |
PCI-E 8x |
|
Network interface type: |
SFP+ SR,LC×2 |

|
Applicable network type: |
10 Gigabit Ethernet |
|
Transmission rate: |
10000Mbps |
|
Bus type: |
PCI-E 8x |
|
Network interface type: |
SFP+ |

|
Applicable network type: |
10 Gigabit Ethernet |
|
Transmission rate: |
10000Mbps |
|
Bus type: |
PCI-E 8x |
|
Network interface type: |
LC |
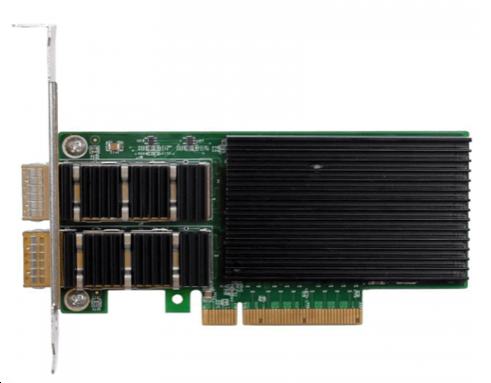
|
Applicable network type: |
40 Gigabit Ethernet |
|
Transmission rate: |
40G/s |
|
Bus type: |
x8 (x16) PCIe* 3.0 |
|
Network interface type: |
LC |





































































