- Related articles
- All Cisco CWDM-GBIC-1510's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960XR-48FPD-I Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG355-10P-K9-UK Switch
- The Things You Need to Know about 10BASE-FX Ethernet Standards
- What is Ethernet Port?
- Overview Cisco GLC-LH-SM Of SFP Transceiver Module
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-2000-16PTC-G-E Switch
- Things You Need to Know About 4-port PCIE Network Card
- What is Packet over Sonet?
- Cisco GLC T SFP Transceiver

As we all know, 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceivers usually use a parallel multimode fiber (MMF) link to achieve 40G. It offers 4 independent transmit and receive channels, each capable of 10G operation for an aggregate data rate of 40G over 100 meters of OM3 MMF or 150 meters of OM4 MMF. However, for 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceivers, there are two kinds of links. One is coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) and the other is parallel single-mode fiber (PSM). What’s the difference between them? In this article, I will show their working principles to you respectively.
40GBASE-LR4 CWDM QSFP+ Transceiver
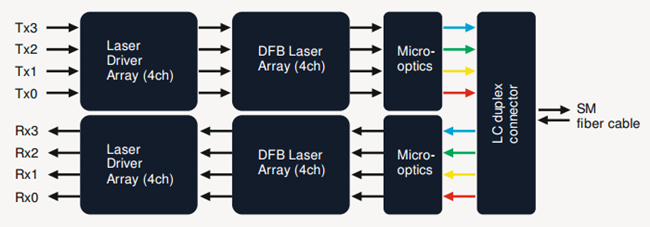
QSFP-40G-LR4The 40GBASE-LR4 CWDM QSFP+ transceiver, such as QSFP-40GE-LR4, is compliant to 40GBASE-LR4 of the IEEE P802.3ba standard. It contains a duplex LC connector for the optical interface. The maximum transmission distance of this transceiver is 10km. To minimize the optical dispersion in the long-haul system, single-mode fiber (SMF) has to be used. This transceiver converts 4 inputs channels of 10G electrical data to 4 CWDM optical signals by a driven 4-wavelength distributed feedback (DFB) laser array, and then multiplexes them into a single channel for 40G optical transmission, propagating out of the transmitter module from the SMF. Reversely, the receiver module accepts the 40G CWDM optical signals input, and demultiplexes it into 4 individual 10G channels with different wavelengths. The central wavelengths of the 4 CWDM channels are 1271, 1291, 1311 and 1331 nm as members of the CWDM wavelength grid defined in ITU-T G694.2. Each wavelength channel is collected by a discrete photo diode and output as electric data after being amplified by a transimpedance amplifier (TIA).

40GBASE-LR4 PSM QSFP+ Transceiver
What’s the Difference?
| Name | CWDM | PSM |
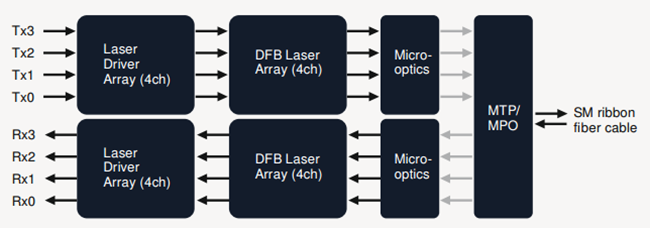
| Optical TX | 4 uncooled 1300nm CWDM directly-modulated laserswavelength spacing 20 nm | 4 integrated silicon photonic modulators and one CW laseruncooled 1300nm DFB laser |
| 4-wavelength CWDM multiplexer and demultiplexer | Needed | No need |
| Connector | Duplex LC connector | MTP/MPO fiber ribbon connector |
| Cable | Via 2 optical single-mode fibers | Via 8 optical single-mode fibers |
Conclusion
40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ Key Features
- 40GBASE-LR4 40G Ethernet QSFP+
- Up-to 10 km over SMF @ 40Gbps
- 1330nm CWDM QSFP+ Transceiver
- 0º - 70º Operating Case Temperature
- SFF-8724 Digital optical monitoring
- Hot-swappable for QSFP+ MPO ports
- Metal enclosure, for lower EMI
- FTL4C1QM1C is RoHS compliant
- 40GBASE-LR4 40G Ethernet
- OTN OTU3 C4S1-2D1





















































