- Related articles
- Selection of Fiber Optic Cable
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48FS-E Switch
- All Cisco ONS-SC-GE-SX's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- Applicable to 10GBASE-SRL Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- The Things You Need to Know about 1000BASE-FX Ethernet Standards
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-2000-8TC-G-E Switch
- What is 10GBASE-SR transceiver?
- All Cisco ONS-SE-GE-BXD's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- All Cisco SFP-10G-SR-S’s Information (Overview, Features, Datasheet PDF, Price, Specificat
- All Cisco DS-X2-FC10G-LR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma

Introduction
In this article we will talk about the 10BASE-FX Ethernet standard and what is the difference between 10BASE-FX and 10BASE-T. All this just to give you more understanding about 10BASE-FX technology.
| Compatible Brands | MFG PART# | Wavelength | Type | Distance | Media |
| Cisco | GLC-FE-100FX | 1310nm | SFP | 2km | MMF |
| Juniper | QFX-SFP-1GE-LX | 1310nm | SFP | 10km | SMF |
| Juniper | QFX-SFP-1GE-T | RJ45 | 100m | ||
| Juniper | QFX-SFP-1GE-SX | 850nm | SFP | 550m | MMF |
| Alcatel-Lucent | SFP-DUAL-SM10 | 1310nm | SFP | 10km | SMF |
| Alcatel-Lucent | SFP-DUAL-MM | 1310nm | SFP | 2km | MMF |
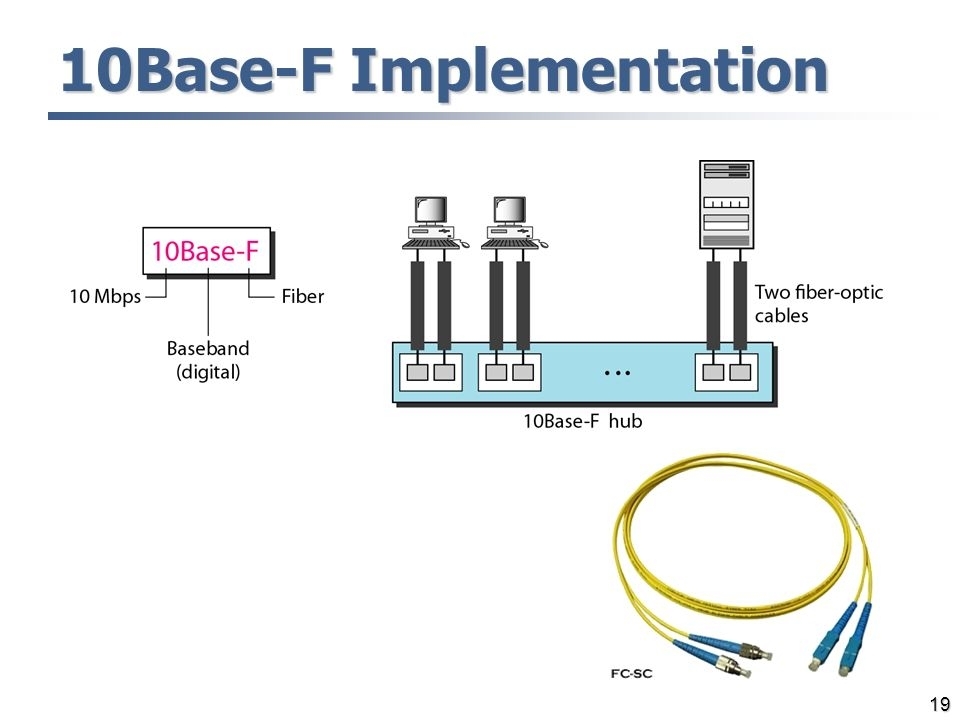
What is the 10BASE-FX technology?
A type of standard for implementing Ethernet networks 10BASE-FX is different from other 10-Mbps Ethernet technologies because it uses fiber-optic cabling instead of copper unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cabling. 10BASE-FX is based on the 802.3 specifications of Project 802 developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE). 10BASE-FX is similar to 10BaseT in that each station is wired into a fiber-optic hub in a star topology to form the network. The maximum length of any segment of 10BASE-FX fiber-optic cabling is 2 kilometers. The recommended cabling type for 10BaseF networks is 62.5-micron diameter fiber-optic cabling. This cable can be terminated with either ST connectors or SMA connectors, depending on the vendor and the hub configuration. Two-strand multimode fiber-optic cabling is used, with one strand allotted for transmitting data and the other for receiving data.
What are the Difference Between 10BASE-FX and 10BASE-T?





















































