- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960X-24PSL-RF Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-54.13's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-F48TS-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960X-48TD-L Switch
- All Cisco DS-SFP-FC8G-LW’s Information (Overview, Features, Data Sheet PDF, Price, Specifi
- What is PAM?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF200E-48-UK Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco ESW-540-8P-K9 Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco ME-3600X-24TS-M= Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48TD-S Switch

Definition:
Optoelectronics is the study and application of electronic devices that source, detect and control light, usually considered a sub-field of photonics. In this context, light often includes invisible forms of radiation such as gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet and infrared, in addition to visible light. Optoelectronic devices are electrical-to-optical or optical-to-electrical transducers, or instruments that use such devices in their operation. Electro-optics is often erroneously used as a synonym, but is a wider branch of physics that concerns all interactions between light and electric fields, whether or not they form part of an electronic device.
What Is Optocoupler in Electronics?
In electronics, an opto-isolator, also called an optocoupler, photocoupler, or optical isolator, is a component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits by using light. Opto-isolators prevent high voltages from affecting the system receiving the signal. Commercially available opto-isolators withstand input-to-output voltages up to 10 kV and voltage transients with speeds up to 10 kV/μs.
A common type of opto-isolator consists of an LED and a phototransistor in the same opaque package. Other types of source-sensor combinations include LED-photodiode, LED-LASCR, and lamp-photoresistor pairs. Usually opto-isolators transfer digital (on-off) signals, but some techniques allow them to be used with analog signals.
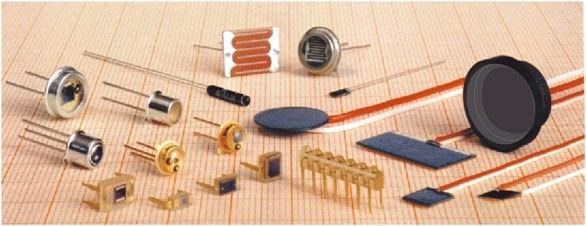
What Is Optoelectronics Components?
Optoelectronic components (or as often referred to photo-electronic components), are electronic components which produce light or react to it. Some components among them are LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes), photo transistors, photo diodes, photo resistors (or LDR – Light Dependant Resistors), different visual indicators, light emitters and detectors, optocouplers, etc. Many of those components can be recognized easily recognized because of the “window” on the component’s case which is used to pass the light. Sometimes, instead of a window, there is a small lens, which directs light to some predestined location inside of the component.
A large number of optoelectronic devices consist of a p-type and n-type region, just like a regular p-n diode. The key difference is that there is an additional interaction between the electrons and holes in the semiconductor and light. This interaction is not restricted to optoelectronic devices. Regular diodes are also known to be light sensitive and in some cases also emit light. The key difference is that optoelectronic devices such as photodiodes, solar cells, LEDs and laser diodes are specifically designed to optimize the light absorption and emission, resulting in high conversion efficiency.
Photonics refers to the study and application of the physical science of light.
Optoelectronics is quickly becoming a fast emerging technology field that consists of applying electronic devices to sourcing, detection, and control of light. These devices can be a part of many applications like military services, automatic access control systems, telecommunications, medical equipment, and more.
Since this field is so broad, the range of devices that fall under optoelectronics is vast, including image pick up devices, LEDs and elements, information displays, optical storages, remote sensing systems, and optical communication systems.
Examples of optoelectronic devices consist of:
-
Telecommunication laser
-
Optical fibre
-
Blue laser
-
LED traffic lights
-
Photodiodes
-
Solar cells
The most common optoelectronic devices that feature direct conversion between electrons and photons are LEDs, photo and laser diodes, and solar cells.
As a specialist in the development of optoelectronicdevices for demanding areas of application, TT Electronics is dedicated to staying on top of the rapidly evolving electronics industry.
Optoelectronics is based on the quantum mechanicaleffects of lighton electronic materials, especially semiconductors, sometimes in the presence of electric fields.[2]
-
Photoelectricor photovoltaiceffect, used in:
-
photodiodes(including solar cells)
-
phototransistors
-
photomultipliers
-
optoisolators
-
integrated optical circuit(IOC) elements
-
-
Photoconductivity, used in:
-
photoresistors
-
photoconductive camera tubes
-
charge-coupled imaging devices
-
-
Stimulated emission, used in:
-
injection laser diodes
-
quantum cascade lasers
-
-
Lossev effect, or radiative recombination, used in:
-
light-emitting diodesor LED
-
OLEDs
-
-
Photoemissivity, used in
-
photoemissive camera tube
-
Important applications[3]of optoelectronics include:
-
Optocoupler
-
Optical fibercommunications
Optoelectronic devices are used in a wide variety of application areas, such as optical fiber communications, lasertechnology, and all kinds of optical metrology.
Optoelectronics is largely based on semiconductormaterials. These exhibit suitable bandgap energies for absorbing e.g. near-infrared and visible light, and their electric conductivity (albeit not perfect) is also essential for such applications. In both aspects, dielectricswould be hard to use, while metals serve mostly as conductors, apart from the exploitation of the external photoelectric effectin some photodetectors.
Indirect band gapmaterials such as silicon and germanium are often sufficient for exploiting absorption processes, for example in photodetectors, but are generally less suited for emitting light. This is a substantial challenge for silicon photonics, where however various kinds of solutions has been found. Still, emitting devices such as laser diodesare largely based on direct band gap materials, particularly of III–V type – for example, gallium arsenide and indium phosphide.
Conclusion:
Optoelectronics is a branch of electronics that overlaps with physics. The field concerns the theory, design, manufacture, and operation of hardware that converts electrical signals to visible or infrared radiation (infrared) energy, or vice-versa.
Please click to check more related concepts:
| Types |
|
Laser Diode |
| Optoelectronic devices |