- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960XR-24PD-I Switch
- Applicable to 40GBASE-UNIV Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- What Is GYDTS Fiber Optic Cable?
- What is Optical Ethernet?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960+48TC-L Switch
- What are SFP slots?
- The History of Network Interface Card
- All Cisco ONS-SI-622-L2's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- All Cisco DWDM-SFP10G-60.61's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-24PDL-RF Switch

Definition:
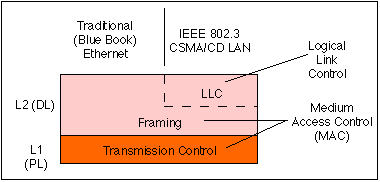
IEEE 802.3 is a working group and a collection of IEEE standards produced by the working group defining the physical layer and data link layer's media access control (MAC) of wired Ethernet. This is generally a local area network technology with some wide area network applications. Physical connections are made between nodes and/or infrastructure devices (hubs, switches, routers) by various types of copper or fiber cable. 802.3 is a technology that supports the IEEE 802.1 network architecture. 802.3 also define LAN access method using CSMA/CD.
Application:
IEEE 802.3 specifies the physical and networking characteristics of an Ethernet network, like how physical connections between nodes (routers/switches/hubs) are made through various wired media like copper coaxial or fiber cable. The technology was developed to work with the IEEE 802.1 standard for network architecture and its first released standard was Ethernet II in 1982, which featured 10 Mbit/s over thick coax cable and featured frames with a "Type" field. In 1983 the first standard with the name IEEE 802.3 for 10BASE5 (thick Ethernet or thicknet) was developed. It had the same speed as the previous Ethernet II standard, but the "Type" field was replaced by a "Length" field. 802.3a followed in 1985 and was designated as 10BASE2, which was essentially the same as 10BASE5 but ran on thinner coax cables, therefore it was also known as thinnet or cheapnet. There are a multitude of additions and revisions to the 802.3 standard and each is designated with letters concatenated after the number "3". Other notable standards are 802.3i for 10Base-T for using twister pair wire and 802.3j 10BASE-F for using fiber-optic cables.
What is IEEE 802.3 used for?
802.3 is a standard specification for Ethernet, a method of physical communication in a local area network (LAN), which is maintained by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). In general, 802.3 specify the physical media and the working characteristics of Ethernet. The original Ethernet supports a data rate of 10 megabits per second (Mbps) and specifies these possible physical media:
Conclusion:
This designation is an IEEE shorthand identifier. The "10" in the media type designation refers to the transmission speed of 10 Mbps. The "BASE" refers to baseband signaling, which means that only Ethernet signals are carried on the medium (or, with 10BASE-36, on a single channel). The "T" represents twisted-pair; the "F" represents fiber optic cable; and the "2", "5", and "36" refer to the coaxial cable segment length (the 185 meter length has been rounded up to "2" for 200).
Please click to check more related concepts:
| Ethernet standard | Application |
| 100Base-FX | Gigabit Ethernet |
| 1000Base-X | SONET |
| 1000BASE-T | |
| 10GBASE-SR | |
| 10GBASE-T |