- Related articles
- Difference between GLC-T and SFP-GE-T
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG300-52MP-K9-EU Switch
- All Cisco ONS-SI-GE-SX's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SLM2048PT-EU Switch
- All Cisco DS-X2-FC10G-LR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- What Is Dual Port Network Card?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG550XG-24F-K9-EU Switch
- All Cisco WS-G5484's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960X-48FPD-L Switch
- All Cisco QSFP-40G-CSR4's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat

Vertical (trunk) cabling and horizontal cabling are two important cabling methods that can be used in modern structured cabling systems. These two types of cabling are not only different in structure but also different types of cables. This tutorial will give a detailed description on wiring method.
Basic knowledge of structured cabling system
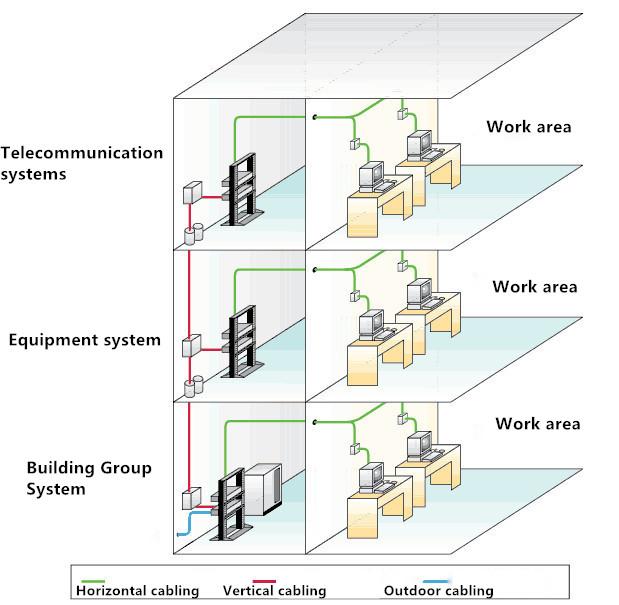
In order to better understand the vertical (trunk) cabling and horizontal cabling, we need to have a basic understanding of the structured cabling system. Structured cabling system is mainly composed of six subsystems; these six subsystems are usually distributed in a building throughout the six co-operation of various data transmission, as follows:
Building systems: including the communication equipment and devices required for cables to extend from one building to other buildings in buildings;
Equipment room system: also known as the engine room system, usually installed a large number of communications equipment, host and server;
Telecommunication systems: also known as wiring interconnection systems, provide a place for horizontal cabling and terminal equipment in building floors;
Vertical (trunk) cabling system: is the trunk line in the building wiring system, for the wiring between the equipment and buildings between the introductions of facilities between the cable connections;
Horizontal cabling system: used to extend the vertical wiring of the trunk line to the user work area;
User work area: refers to the office, computer and other equipment where the area.
Vertical (trunk) cabling
As mentioned above, vertical (trunk) cabling is mainly used to connect intercom systems, inter-equipment systems, and building systems, through the floor between the shaft, ventilation pipes and other buildings across the floor. The cables used in vertical (trunk) cabling are: unshielded (UTP) cables, shielded cables (STPs), cables, coaxial cables, and so on.
 cabling.jpg)
Now with the rise of Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet, the cable becomes a common cable type in vertical (trunk) cabling systems. Compared with the traditional five, six, seven twisted pair, fiber optic cable with high bandwidth, transmission distance, no electromagnetic interference, etc., by the vertical (trunk) cabling system widely favored.
Horizontal cabling
One end of the cabling system is connected to the user work area and the other end is connected to the telecommunications room. As shown below, the horizontal cabling is generally star topology, including communication socket, horizontal cable, patch panel and so on.
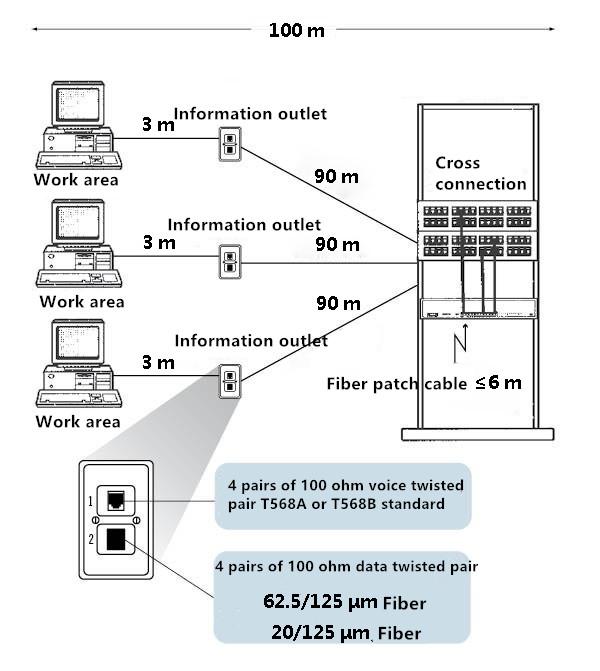
Horizontal cabling system is usually used in 4 pairs of 100 ohm twisted pair (five or super five twisted pair), this type of cable can support both voice transmission, but also to support high-speed data transmission. However, according to the EIA / TIA standard, the length of the twisted pair between the work area and the telecommunications cannot exceed 90 m, and the length of the jumper between telecommunications cannot exceed 6 m. The network cable connecting the user's computer and communication socket cannot exceed 3 m.
Vertical (trunk) cabling VS horizontal cabling
Although the vertical (trunk) cabling system and the horizontal cabling system will use the same cable type in some cases, the fire performance will vary depending on the environment in which the cable is located. The cables in the vertical (trunk) cabling system typically pass through the floor and must have a higher fire rating, usually using the OFNR cable. If the cable is in a high-voltage environment, the OFNP cable must be used. In addition, the vertical cable must also have sufficient strength to support its own weight. Horizontal cabling system cable will be simpler.