- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560V2-48PS-SM Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-X2-35.82's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- What is multi-mode and single-mode fiber?
- What is DWDM technology?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-3000-4TC Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-55.75's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- All Cisco 15454-GBIC-SX's information (Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- All Cisco DS-SFP-FC4G-MR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- All Cisco DS-CWDM4G1550's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-24TS-L Switch

What is an optical switch?
An optical switch is a device for opening or closing an optical circuit in a communication application that selectively switches the signal in an optical fiber or integrated optical circuit (IOC) from one circuit to another. In the network system, the optical switch plays an important role in protecting the path. It can turn on or off the optical path (in a position for a long period of time, the key features must be able to operate reliably), complete system monitoring and diagnosis. Typically, an optical switch has one or more input ports and two or more output ports.
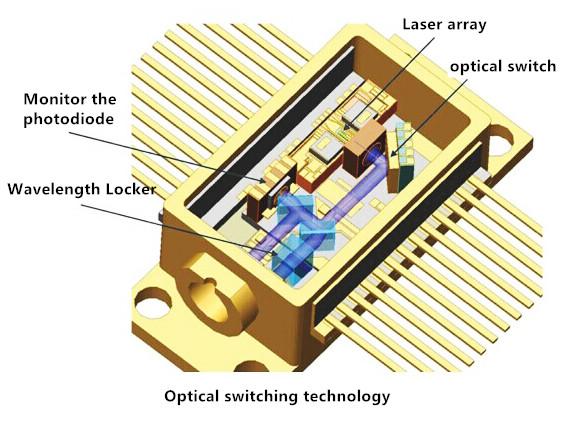
Optical switching technology
As an important basis for all-optical communication network technology, the development and application of optical switching technology will greatly affect the future development trend of the optical communication network. Therefore, to understand the working principle of optical switching technology is very necessary for future research. As we all know, optical signals have three multiplexing modes: space division multiplexing, time division multiplexing and wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). Therefore, the realization of the three kinds of multiplexing mode of the corresponding optical exchange is air separation, time-sharing, and wavelength division switching.
1. Air separation
Space separation is achieved by using space division multiplexing. In an air separation switch, the path from one device to another is spatially separated from the other path, and a specific connection between the two users is established with an intersection. It can form an empty spectral exchange unit, and other types of switches can also be together to form a time exchange unit or wave star. Empty spectral switches are usually based on fiber and space-based air separation, which is a segmentation of swap space.
2. Time exchange
Time division is done by using time division multiplexing. The working principle of time-division switching technology is also applicable to analog and digital signals. It takes a shorter period of time to share the intersection. In terms of other required connections, this technology paves the way for the redistribution of intersections and their associated circuits. As a result, more cross points can be saved in time-division switching. Therefore, through the dynamic control mechanism, it will be assigned to a number of switching elements in a few microseconds time.
3. Wavelength division exchange
Wavelength division exchange is accomplished by WDM technology. In WDM systems, the spectrums are exchanged at the intermediate transmission nodes and can achieve the communication between the source and target without the attendance of any other devices, which greatly helps to save the resources of the system and improve resource utilization. In the spectral switching system, the demultiplexer divides the first optical wave signal into several shunts to exchange the wavelength channel. In each channel, the wavelength of the last signal is exchanged by the multiplexed signal of the optical output port. Due to the advantages of fiber broadband, the low-loss band multiplexing multiple optical signals greatly improves the utilization of fiber channel and the capacity of the communication system.
In addition, there are some hybrid communication technologies for large-scale communication networks, such as the time-space (TS) switching technology. The TS switching system enables the broadcast operator to seamlessly exchange channels in the same or different TS streams. In fact, as technology continues to evolve, more and more new switching technologies are being used in the field of optical communications and telecommunications.
The application of optical switches
Optical switch plays a very important role in the optical network, not only key equipment exchange core in WDM network, but also a key component of the optical network. The main applications of optical opening include network switching; laboratory research and development; fiber optic sensors; channel blockage; system monitoring; channel blocking module and system integration; metropolitan area network; network protection and recovery; instrumentation, detection, and measurement.





































































