- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960X-48LPD-L Switch
- Cisco SFP vs. GBIC vs. XFP vs. SFP Plus
- All Cisco ONS-SI-GE-SX's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- All Cisco ONS-SI-100-FX's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- What is Opto Electronics?
- What Is GJYXCH Fiber Optic Cable?
- Things You Need to Know About 4-port PCIE Network Card
- All Cisco WSP-Q40GLR4L's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- What type of connector does a network interface card use?
- The Things You Need to Know about 100GBASE-ER4 Ethernet Standards

In the PDS system, optical cable in the trunk (vertical) wiring usually contains 2-144 fibers or even more to transmit the data to multiple users. Tight-buffered trunk optical cable with characteristics of durability and easy termination is the common cable type for trunk (vertical) wiring, which is widely used in the data center, indoor applications like fiber to the home(FTTH)and outdoor applications. This tutorial will make a detailed introduction about tight trunk optical cable.

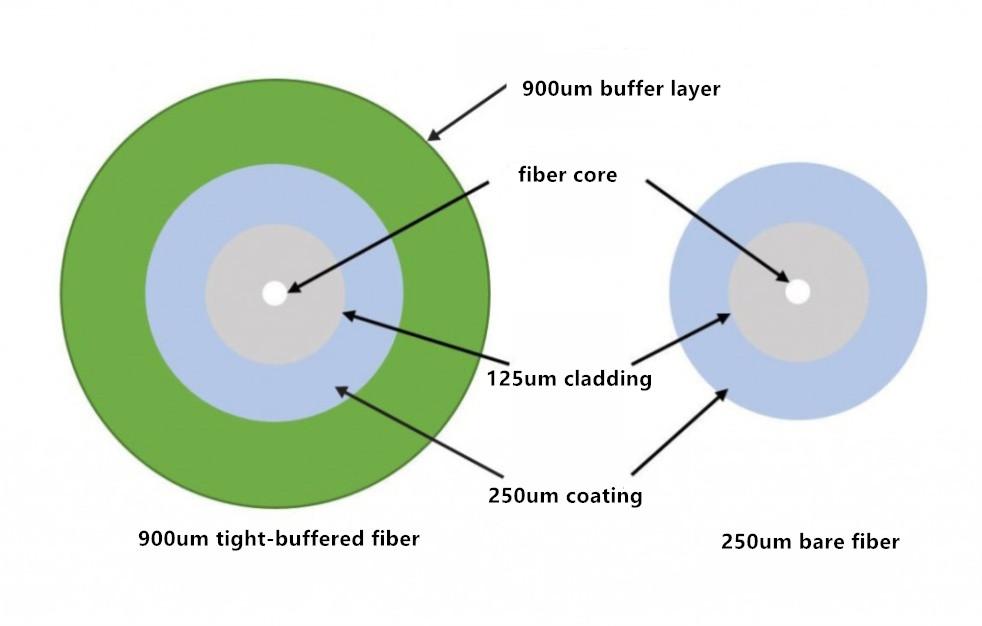
Advantages of 900um Tight-buffered Fiber
Most tight trunk optical cables use 900um tight buffered optical cable, mainly determined by the actual application. The picture is the comparison drawing between 250um bare fiber and 900um tight buffered fiber. It can be seen from the drawing that the two cables are similar. The difference is that 900um tight buffered fiber is one design of cushion, which provides ideal mechanical protection for the fiber and reduces its micro bending loss sensitivity. In addition, the cushion is easily peeled from the fiber, which is useful for fiber's welding and termination. The trunk fiber containing 900um tight buffered fiber has small bending semidiameter and strong flexibility, which is very suitable for the application of trunk cabling.
Selection for Proper Tight-buffered Trunk Optical Cable
According to different applications and the environment, tight-buffered trunk cable can be divided into a variety of different types. Their differences are mainly reflected in the fiber type, outer jacket type, and cable type. The following is a respective introduction to several common tight-buffered trunk optical cables.
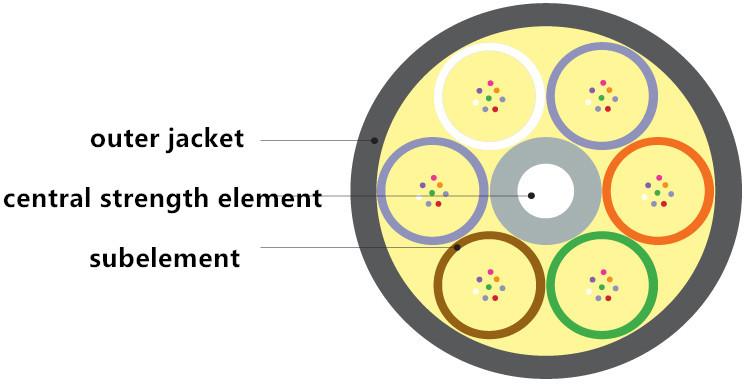
Indoor Tight-buffered Trunk Optical Cable
Indoor tight-buffered trunk optical cable is usually used in indoor trunk wiring and wiring in telecommunication machine room with the number of core from 2 to 144. familiar speaking, the domestic tight-buffered trunk optical cable with over 36 fiber cores usually has the design On the subelement, that is, multiple jackets in the optical cable (as shown in the above picture); the indoor tight-buffered trunk optical cable with 6/12/24 fiber cores has only one outer jacket, which is low in price, and Flexible in the distribution system. The following picture is the structure drawing of the machinery tight-buffered trunk optical cable with 24 fiber cores:
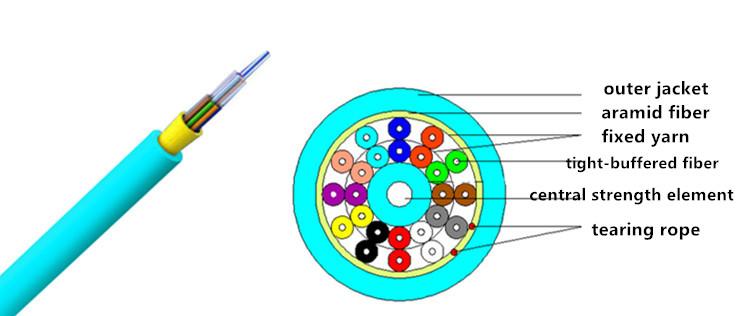
In the actual application, the indoor tight-buffered trunk optical cable with 6/12/24 cores are commonly used for welding and termination (as shown in the following picture), which are made into pigtail with multiple cores or fiber patches.
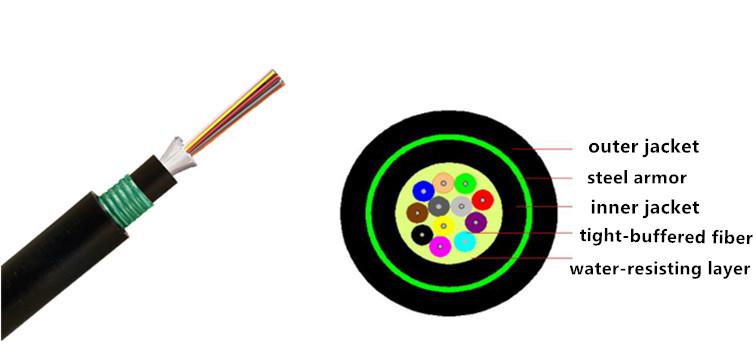
Indoor/Outdoor Armored Tight-buffered Trunk Optical Cable
In spite of the common indoor use of trunk optical cable, it can still be applied to indoor and outdoor applications through a design of metal armor internally. This cable is sturdy and durable, waterproof, and rodent proof applied to the wiring applications between buildings.
Here we introduce armored and tight-buffered trunk optical cable with the low number of cores (as below). Inside the outer jacket of this optical cable, there is a steel-armored design, which can be applied to not only indoor trunk wiring and historical wiring, but also outdoor bomb applications and aerial applications.