- Related articles
- The Uses of PCI Express x1
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG350XG-24F-K9-UK Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750G-12S-S Switch
- What Does LC Stand for in Fiber?
- Difference between transponder and muxponder
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-48LPS-L Switch
- All Cisco GLC-ZX-SM-RGD ’s Information (Overview, Features, Data Sheet PDF, Price, Specif
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG300-28MP-K9-EU Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-47.72's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-2000-8TC-B Switch

Introduction
Today, fibers are installed almost in every home. That is a clear indication that the fiber technology has been adopted by every person. However, the fiber optic cables have a defined design that enables them to effectively perform their roles. Fiber Optic Cables have strands inside that are used to carry the light waves. Consequently, they are covered with the cable jacket that gives the cables shape. The signals are transmitted by a pulse of light along the cable. The Fiber Optic Cables are widely and commonly used for the fiber optic telecommunication networks.
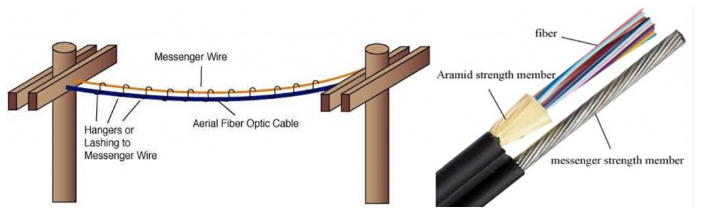
Discussion
The optical fiber cables come in many different designs to fit for different environment and application areas. Choosing the right designed fiber cables is essential for your networking jobs.
1. Loose Tube and Tight Buffer Cables
Loose tube and tight buffer are two typical designs of the fiber optic cables. Loose tube fiber cables are used for the outside plant applications, in the Loose Tuber fiber cables, the fibers are placed loosely within a large plastic tube. Usually, there are 6-12 fibers placed in the single loose tube. These tubes are filled with a gel or water absorbent powder to protect them from moisture and physical stresses. Loose tube fiber cables are commonly used for underground installations, lashed or self-supporting aerial installations, and other outside plant applications.
Tight Buffer cable designs are used for inside plant application. The fibers inside coated with a buffer coating, with an outside diameter of 900um. Tight buffer cable has two typical constructions with come in breakout design and distribution design.
2. Ribbon and Aerial Cables
Except for the loose tube and tight buffer cables, there are also ribbon design and aerial design fiber cables. A ribbon cable is a cable with many conducting wires or fibers running parallel to each other on the same flat plane, ribbon cables offer the highest fiber density relative to cable size, maximize use of pathway and spaces, and facilitate ease of termination., which make the ribbon fiber cables the beat choice for deployment in campus, building, and data-center backbone applications where fiber counts more than 24 are required. The ribbon cable can be used in Local area network (LAN) campus and building backbones as well as data center backbones.
Conclusion
Different fiber optic cables have a different structure. However, they have a common design that differentiates them from other forms of cables. If not for the defined design of Fiber Optic Cables, many people couldn’t differentiate fiber optic cable and other electrical cables.





































































