- Related articles
- All Cisco XENPAK-10GB-LR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- All Cisco ONS-SC-GE-LX's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- What is SFP-10G-SR?
- What Is Network Card PCI Express x1?
- All Cisco DS-SFP-FC4G-MR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N7K-M148GS-11= Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N2K-C2232PF Switch
- All Cisco GLC-FE-100LX-RGD’s Information (Overview, Features, Datasheet PDF, Price, Specif
- The Things You Need to Know about 1000BASE-CX Ethernet Standards
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SLM2048T-UK Switch

Definition of Fiber Optic Cable
The fiber optic cables are typically made of thin strands of plastic or glass that are referred as the optical fibers. However, the number of the optical fibers inside the fiber optic cable differs from one cable to another. Some optic cables have two optical fibers while other have as many as hundreds of optical fibers. Those optical fibers are used to carry the information or data between two points using light-based technology.
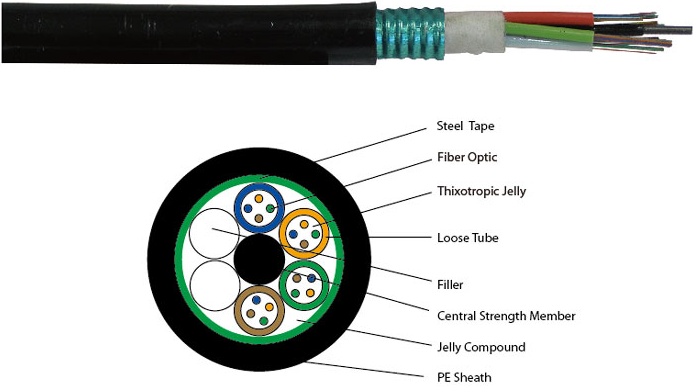
Overview of the fiber-optic cable
A fiber-optic cable is made up of incredibly thin strands of glass or plastic known as optical fibers; one cable can have as few as two strands or as many as several hundred. Each strand is less than a tenth as thick as a human hair and can carry something like 25,000 telephone calls, so an entire fiber-optic cable can easily carry several million calls.
Fiber-optic cables carry information between two places using entirely optical (light-based) technology. Suppose you wanted to send information from your computer to a friend's house down the street using fiber optics. You could hook your computer up to a laser, which would convert electrical information from the computer into a series of light pulses. Then you'd fire the laser down the fiber-optic cable. After traveling down the cable, the light beams would emerge at the other end. Your friend would need a photoelectric cell (light-detecting component) to turn the pulses of light back into electrical information his or her computer could understand. So the whole apparatus would be like a really neat, hi-tech version of the kind of telephone you can make out of two baked-bean cans and a length of string!
Fiber optic cable is unlike most types of cables; it draws on light instead of electricity to transmit signals. As you have already known, the light is the fastest way to transfer information, and fiber optic cable has additional advantages are immune to electrical interference. So, you can run it anywhere and at any time. Because light meets litter or no resistance, you can run the fiber optic cable in a long distance, literally countries apart, without increasing or clean signal.
Optical fiber velocity also has its own advantages. It has a cleaner signal than conventional copper wire and transmits signals over 10 Gb/s. Put it into perspective, fiber optic wiring is digital information as an electrical wiring is analog information. They are completely different.
At present, the fiber optic cable used to connect to the network, basically make the short run, the connection layer, construction and connection electric copper cable, fiber optic cable through the Ethernet converters. Despite the fiber optic cable can be very expensive, but because it is becoming more and more popular, it will be, the price of fiber optic cable (and related equipment including Ethernet converter and fiber optic transceiver) should be reduced. Knowing what’s inside this very functional invention is good to know. A fiber optic cable includes the core, cladding, strength member, buffer and jacket as its components.
Conclusion
The technicians prefer using fiber optic cables with thin optical fibers. This is because the thinner the optical fiber the more it has resistant and the more it performs well. The thin optical fibers are considered to be more effective in transmission of data as compared to the broad optical fibers. Also the number of the optical fibers is considered with the fiber-optic cable with many optical fibers being the best.





































































