- Related articles
- All Cisco CWDM-GBIC-1550's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG500X-48P-K9-G5 Switch
- All Cisco SFP-OC48-SR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matri
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48PQ-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco ME2600-44FH-AA-K9 Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48TD-E Switch
- All Cisco QSFP-40GE-LR4’s Information (Overview, Features, Datasheet PDF, Price, Specifica
- All Cisco WS-G5484's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF300-24PP-K9-EU Switch
- The Things You Need to Know about 40GBASE-CR4 Ethernet Standards

Definition:
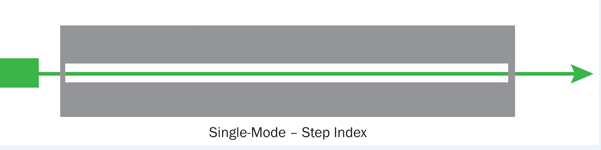
In fiber-optic communication, a single-mode optical fiber (SMF) is an optical fiber designed to carry light only directly down the fiber – the transverse mode. For single-mode optical fiber, no matter it operates at 100 Mbit/s or 1 Gbit/s date rates , the transmission distance can reach to at least 5 km. Typically, it is used for long-distance signal transmission.
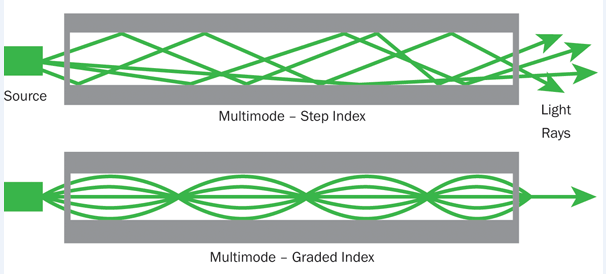
Multi-mode optical fiber (MMF) is a type of optical fiber mostly used for communication over short distances, such as within a building or on a campus. Typical transmission speed and distance limits are 100 Mbit/s for distances up to 2 km (100BASE-FX), 1 Gbit/s up to 1000m, and 10 Gbit/s up to 550 m. There are two kinds of multi-mode indexes: step index and graded index.
Application:
Single mode fiber is used for long distance communication and for carrying very high bandwidth signal. The major applications of single mode are CATV, Telcos, universities as well as colleges. Laser diode is used as optical transmission system equipment here. Multi mode fiber is used for short distance communication mainly for video/audio/data based Wireless LAN applications. LED based fiber optic equipment is used for this.
Single Mode Fiber and Multi mode Fiber:
Single-Mode
- Single-mode systems are usually, but not always more expensive because of the laser diodes and precise calibration required to inject light into the cable. The costs of single vs multi-mode cable itself are negligible, but single-mode devices often cost more.
- Light travels a longer distance inside single-mode cable than it does inside multi-mode. How much farther depends on many factors, but the rule of thumb we’ve heard from engineers is single-mode signal can survive up to 30 kilometers.
- The bandwidth (amount of information in the signal) of single-mode is higher than multi-mode. Um, much higher: as much as 100,000 GHz!
- Since the entrance pupil of single-mode is so small (~9 microns), single-mode connectors must be kept very, very clean. Even a microscopic particle blocking the pupil can partially or completely block signal.
- Single mode fiber has a lower power loss characteristic than multi mode fiber, which means light can travel longer distances through it than it can through multi mode fiber. Within a data center, it's typical to use multi mode which can get you 300-400 meters. If you have very long runs or are connecting over longer distance, single mode can get you 10km, 40km, 80km, and even farther.
Multi Mode
- Multi mode systems usually cost less. Although, again, the fiber cable itself is about the same price as single mode, the LED components used as transmitter optics in multi-mode devices are less expensive to purchase and calibrate, and so multi-mode systems as a whole are less expensive.
- Cable runs are much shorter than with single-mode, but still much greater than coaxial cable. 2 kilometers seems to be the maximum recommended distance floated by engineers.
- Multi mode bandwidth is smaller than single-mode—up to 1 GHz vs 100,000 GHz—but still enough transmit a large amount of A/V signal, data, or controls.
- The multi mode fiber has has much larger core diameter than single mode fiber. The core diameter of multi mode fiber is typically 50–100 micrometers, while that of single mode fiber is between 8 and 10.5 micrometers.
Conclusion:
That how to choose the kind of optical fiber is based on transmission distance to be covered as well as the overall budget allowed. If the distance is less than a couple of miles, multi-mode fiber will work well. If the distance to be covered is more than 3-5 miles, single-mode fiber is the choice. Cozlink has provide a wide range of single mode and multi mode fiber, if you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.