- Related articles
- What Is the Components of Network Interface Card?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-C9396PX= Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-31.90's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- All Cisco DWDM-SFP10G-60.61's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- The difference between SDI and HD SDI
- All Cisco SFP-10G-BX40U-I's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility m
- All Cisco 15454-SFP-OC48-IR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- The Difference between GBIC and X2
- All Cisco X2-10GB-ZR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-43.73's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma

Introduction
In this article we will discuss about the 40GBASE-CR4 Ethernet standard and what are the difference between 40GBASE-CR4 and 40GBASE-KR4. So you can have a basic understanding for 40GBASE-CR4 technology to understand the basic solutions to 40GBASE-CR4.
What is the 40GBASE-CR4 technology?
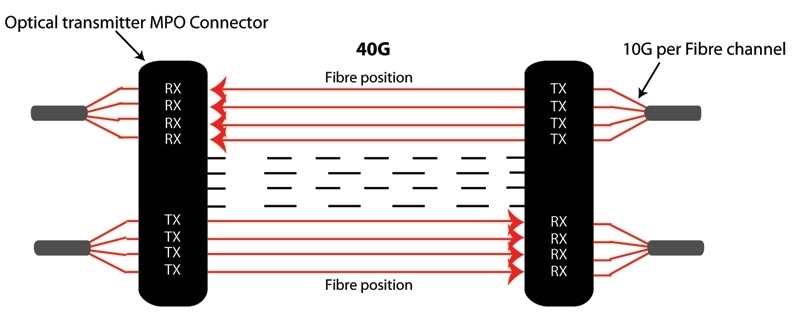
40GBASE-CR4 ("copper") is a port type for twin-ax copper cable. Its 64b/66b PCS is defined in IEEE 802.3 Clause 82 and its PMD in Clause 85. It uses four lanes of twin-axial cable delivering serialized data at a rate of 10.3125 Gbit/s per lane. CR4 involves two clauses: CL73 for auto-negotiation and CL72 for link training. CL73 allows communication between the two PHYs to exchange technical capability pages, and both PHYs come to a common speed and media type. Once CL73 has been completed, CL72 starts. CL72 allows each of the four lanes' transmitters to adjust pre-emphasis via feedback from the link partner.
What are the Difference Between 40GBASE-CR4 and 40GBASE-KR4?
Copper based 40GBASE-CR4 QSFP+ module (TwinAx copper cable, 1 to 7m) and the optical modules such as the short reach 40GBASE-SR4 (MMF 150m) and the long reach 40GBASE-LR4 (SMF 10km).
40GBASE-KR4 is a port type for backplanes. Normally backplanes are board traces, such as Megtron6 or FR4 materials. Its Physical Coding Sublayer 64b/66b PCS is defined in IEEE 802.3 Clause 82 and its Physical Medium Dependent PMD in Clause 84. It uses four lanes of backplane delivering serialized data at a rate of 10.3125 Gbit/s per lane.





































































