- Related articles
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-60.61's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- What Is ADSS Optical Fiber Cable?
- Applicable to 40GBASE-PLRL4 Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-48LPD-L Switch
- All Cisco MFEFX1's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-48TD-L Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-X9464TX= Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG350XG-24T-K9-UK Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-30.33's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-CBS3110X-S Switch

Definition of Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable is the type of external fiber optic cable that provides sufficient protection to the optical fibers inside. This type of fiber cable is widely used in areas where there is no enough security for the fibers from mechanical damages. For instance, if the areas have a risk of getting fire, Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable is highly recommended due to its ability to prevent fire. Consequently, Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable comprises some outstanding features that give it great protection like Breakout, Loose Tube, and fantastic strength members such as the metallic jacket. Additionally, Outdoor Fiber Optic Cables are commonly used in rural areas due to the high risk subjected there.
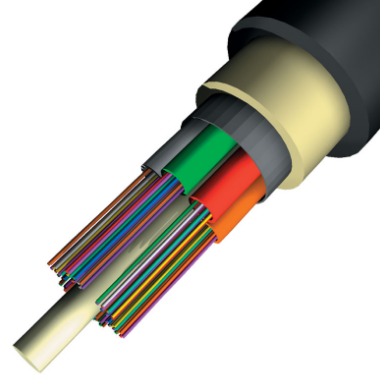
Application of Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
Cables for outdoor applications are engineered to withstand the more demanding conditions, seen outside from environmental extremes to mechanical forces. These are the cables you see strung along telephone poles (aerial), installed inside an underground duct or even buried directly below ground. Therefore, outdoor optic cables feature rugged constructions to resist ultra-violet light and temperature fluctuations and may include features to withstand the requirements of being installed outdoors.
Uses of different types of Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
1. Micro-duct Cables
Micro-ducts are miniaturized plastic conduits that sub-divide internal duct space into smaller compartments into which micro cables can be installed by blowing, jetting or pushing.
2. Direct Buried Cables
In the absence of duct infrastructure, cables can be buried directly into the ground in a trench or using a vibratory plow.
3. Aerial Cables
These cables are suspended from poles or pylons or mounted on buildings. Some are self-supporting, requiring no separate messenger wire between poles to support the cable’s weight.
4. Duct Cables
Ducts (or conduits) offer a highly protective environment for fiber-optic cables. They are typically buried, and then the cables are air-blown, jetted, pulled or pushed into the duct.
5. Drop Cables
Drop cables are cables that run from the distribution point or cable to the subscriber/user.
Conclusion
Today, the entertainment industry has been drastically changed by the Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable. The quality of videos, audios, data signals, telephony within the industry has been improved since the adoption of Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable. The installation process of this type of cable is very simple and therefore, you don’t need and person to guide you on how to do it, that has significantly reduced the total acquisition cost. Additionally, the Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable does not need any special storage and therefore, it has enabled the users to cut off the inventory cost that they usually incur.





































































