- Related articles
- Applicable to 40GBASE-SR Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- All Cisco QSFP-40GE-LR4’s Information (Overview, Features, Datasheet PDF, Price, Specifica
- What is a transceiver module?
- What Is GYTC8S/GYTC8A Optical Fiber Cable?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750E-24TD-SD Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2975GS-96PS-LM Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560E-24TD-SD Switch
- All Cisco ONS-SI-GE-LX's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco ME-3600X-24FS-M= Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-X2-42.14's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat

Definition
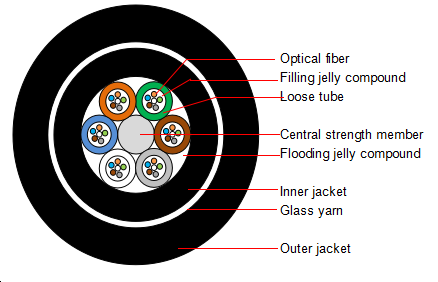
The structure of GYFTY73 fiber optic cable is very simple and easy to understand. It comprises several essential components that include; Outer jacket, Optional protection from physical damage, Strength members, Buffer, and Optical fiber stand. Consequently, each and every core found in the structure of GYFTY73 fiber optic cable contains three component which includes; Cladding, Core, and Coating.
Description
GYFTY73 (Loose tube stranding, Non-metal strength member, Flooding jelly compound, PE inner jacket, Glass yarn strength member, PE outer jacket) and its standards are; The YD/T 901-2009 Outdoor layer stranded optical cable for telecommunications
Features of GYFTY73 Fiber Optic Cable
The size of the core is varying between 8 and 63 microns. Pieces of the strand are so tiny they can easily penetrate the skin and in some cases travel through the human body with blood vessels. This is one more reason why installation should be done by professionals using specially intended gear.
Core and cladding are typically made of glass or plastic. Most important specification of the core is the index of refraction which is the value for light bending passing through the material and for the speed of that light could travel through the material. The cladding is having lower refractive index than the core. It allows light to stay inside the fiber and not escape into the cladding, since it will be reflected.
The coating is simply a protective layer that is protecting core and cladding from the fracture.
Whether the GYFTY73 fiber optic cable is single mode or multi-mode is defined by the thickness of the fiber optic stand. The thin core would support only single pathway for the light. Thicker core means more angles for the input signal, thus being able to transmit data in multiple paths and modes.
Single mode GYFTY73 fiber optic cable has some additional limitations due to nature of the cable. The concentrated laser is required, which is able to send signal precisely through such thin media. Every connection requires precision to connect small diameter fibers, and hold them in the position which affects the cost of installation. Single fibers are mostly used for backbone and other long-distance parts of the application.
On the other hand, multi-mode GYFTY73 fiber optic cable is having larger diameter core, which allows using cheaper lasers and LEDs as a source. Having larger cores simplifies the task of connecting fibers. All these points facilitate manufacturing process and reduce production costs. However, cheaper components have a negative effect on both transmission distance and bandwidth. That makes multi-mode solutions better suited for the short connections in the network.
Conclusion
GYFTY73 fiber optic cable is available in different diameters depending on the order. Therefore, you have an opportunity to make choice of your preferred size of diameter. Due to a simplicity of its structure, GYFTY73 fiber optic cable has been adopted widely by both residential and factories.
.