- Related articles
- All Cisco WSP-Q40GLR4L's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960XR-24PS-I Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG350-28-K9-EU Switch
- All Cisco QSFP-40G-SR4-S’s Information ( Overview, Features, Datasheet PDF, Price, Specifi
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-31.12's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560E-12SD-S Switch
- What is LX and EX in Transceiver?
- Installation of Fiber Optic Cable
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-24TS-E Switch
- Market Trends for Optical Interconnection Hardware in 2023

A computer uses a network interface card (NIC) to become part of a network. The NIC contains the electronic circuitry required to communicate using a wired connection (e.g., Ethernet) or a wireless connection (e.g., WiFi). A network interface card is also known as a network interface controller, network adapter, or Local Area Network (LAN) adapter.
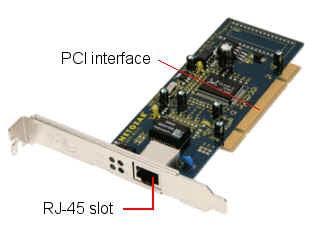
Components of Network Interface Card
The NIC is a slot-based card that connects directly to the motherboard of the computer. The major benefit to these cards is that they handle the buffer storage, encoding and decoding of data through the seven network layers. This allows the processor to concentrate on other tasks, rather than the data being received by it. Typically, there are more advanced feature sets available on network interface cards, as they have dedicated storage and the processing to support this without affecting the CPU. Conversely, an installed NIC will take one of your motherboard expansion slots, which can be troublesome if you are running several add-on components in a small form factor computer.
Motherboard-down controllers allow you to provide networking services without utilizing an expansion slot. They're typically less expensive than an add-in card, though.
The downside is that they do utilize processor power to encode and decode data through the network layers. When dealing with a high amount of traffic, especially encrypted data, this could become noticeable. It should be noted that most motherboard manufacturers do direct this traffic through the southbridge.
Types of Network Interface Card
Classified by bus interface
- ISA bus network card
- PCI bus network card
- PCI-X bus network card
- PCMCIA bus network card
- USB bus network interface card
ISA card and PCI card is the most common, but the PCI card tends to mainstream status. ISA network card bandwidth is generally 10Mbps, PCI bus network card bandwidth from 10Mbps to 1000Mbps.
Classified by network interface
- RJ-45 interface network card
- BNC interface network card
- AUI interface network card
- FDDI interface network card
- ATM interface network card
The common interfaces are Ethernet RJ-45 interface, thin coaxial cable BNC interface and thick coaxial AUI interface, FDDI interface, ATM interface and so on. And in order to apply to a wider range of applications, some cards providing two or more types of interface, some of them will also provide RJ-45, BNC interface or AUI interface simultaneously.
Classified by bandwidth
- 10Mbps network interface card
- 100Mbps network interface card
- 10Mbps/100Mbps network interface card
- 1000Mbps network interface card
With the development of network technology, network bandwidth is also increasing, but different bandwidth applied to different application, currently the main network card is 10Mbps network card, 100Mbps Ethernet card 10Mbps / 100Mbps adaptive network card, 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet card.
Classified by application fields
- Workstation's network interface card
- Server's network interface card
The network interface cards we mentioned above are basically workstation cards, in fact, usually they used in the general server. However, in large networks, the server usually uses a specialized network card. Relative to the workstation used by ordinary card, it has a better performance in bandwidth (usually 100Mbps, the mainstream server network card for the 64-bit Gigabit Ethernet), the number of interfaces, stability, error correction, etc. Some server NIC supports redundant backup, hot-plug and other server-specific functions.
Summary
The network card's controller is the piece of hardware that encodes and decodes the frames of data sent through the wire. In addition, while each layer of the network model is theoretically the same, each manufacturer has a different set of instructions that operate at varying efficiency levels. Therefore, buying a NIC powered by a ubiquitous controller vendor can improve your networking experience.





































































