- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960XR-24PD-I Switch
- What is Mini PCI Express Network Card?
- The difference between QSFP+ and GBIC
- EoS and EoL Cisco 2960-S Series and 2960-SF Series Switches
- Things you need to know about integrated network card
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SLM2024T-UK Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-X2-44.53's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- Applicable to 10GBASE-LRL Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- All Cisco SFP-10G-ZR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix
- All Cisco DWDM-SFP10G-61.41's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility

We know that it’s the fibers inside the fiber optic cables that transmit light signals which carry information or data. So it’s necessary to understand how light travels in optical fiber. Actually, the materials and structure of fibers are the key reason for transmitting light, below will give answers from structure and materials of fibers.
Materials of optical fiber
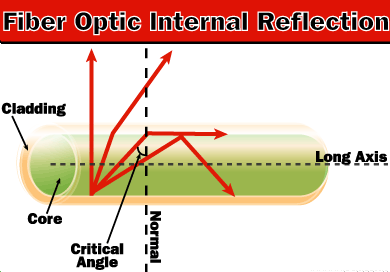
An optical fiber is a long thin strand of glass, and most of fibers are normally coated a layer of cladding layer on the surface. This cladding layer serves as optical medium to refract light, and enhance the flexibility of fibers. On the other side, the main material of fiber is quartz. During the manufacturing of fiber, some chemicals are mixed into quartz in terms of different demands, which cause the fiber through processing equipped with complex structure. As a result, there are various kinds of fibers to be used to transmit multiple light-waves at a time or only single light beam.
While except for the cladding layer that make contribution to transmitting light in fiber, the core of fiber combines with cladding layer to cause continuous refraction happened in fiber. Fiber core and the cladding layer are different in density, and the density of fiber core is greater than cladding layer. Therefore, when a light beam is sent into fiber in a certain and proper angle, it will be transmitted to the other end by continuous total internal reflection.
Structure of optical fiber
Light beam can stimulate a certain mode of electromagnetic wave when traveling in fiber, the mode of electromagnetic wave is related with the thickness of fibers. If the fiber is too thin, it’s hard to form a certain mode of transmission. If the fiber is too thick, it would increase the modes of transmission so that the dispersion gets worse. Thus, the dimension of fiber core is suggested to be several times to dozens times bigger than transmission wavelength.
How is data transformed in fiber?
Having understood the principle of light transmission in fiber, then how are the texts, images or audios or other data transmitted through fiber?
Actually texts, images or audios can be transformed into forms of electrical signals by electronic technology, and through digital technology, these data will be finally translated into numeric groups made of “1” and “0”, which respectively stands for circuit on and off. So that all light signals can be represented by “light” and “non-light” in optical electronic technology. Basically, a series of light signals with different degrees of bright are sent into optical transceiver, and they are received by the device at the other end. These light signals can be transformed into the original digital signals by special optical device. Eventually, these digital signals could be returned to texts, images audios or other data in TV, radio or computers.
Conclusion
To sum up, data or information travels in the form of light signal in the optic fiber. The structure and materials of fiber optic cables are exclusively designed for transmitting light. In addition, there are optical devices necessarily involved to accomplish the transformation of information or data. This article gives clear and detailed ideas about the whole process of data transmission in optical fibers.