- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG355-10P-K9-UK Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG550XG-24F-K9-UK Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N3K-C3172TQ-10GT= Switch
- What Is Network Card PCI Express x1?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG500-28MPP-K9-G5 Switch
- What is Linux PAM module?
- What is fiber optics used for?
- The Difference between SFP+ and X2
- All Cisco MFEFX1's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48TS-E Switch

PCI
The name PCI has been derived from Peripheral Component Interconnect which describes a set of industry standard computer bus architectures which are used to connect components on the computer main board to each other, and also provides an expansion bus to install add-in cards.
PCI interface is divided into 32bit and 64bit, 32bit is the ordinary PCI interface which used of in the desktop, 64bit is longer than 32bit, which only used in server, 32bit and 64bit have two kinds of voltage: 5V and 3.3V. 5V is PCI2.1 standard, clock frequency of 33MHz, 3.3V is PCI2.2 standard, and it can work in the clock frequency of 66MHz. But now, in general, cards and slots are made can be compatible with both of voltages, and also have the design of error proofing, they can work as long as plug it, but in which kind of clock frequency is necessary to analyze, 32bit PCI interface is widely used, even the latest motherboard will stay a few slots for it, but 64bit PCI interface seems to be basically eliminated on the server.
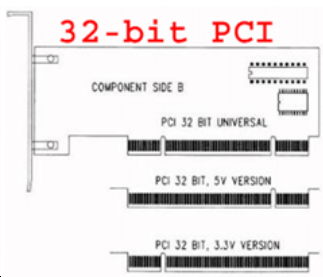


PCI-X

PCI-E


PCI, PCI-X, PCI-E specifications
|
Standards |
Bus |
Clock |
Transmission rate |
|
PCI 32bit |
32bit |
33MHz |
133Mb/s |
|
PCI 64bit |
64bit |
33MHz |
266Mb/s |
|
PCI-X |
64bit |
66MHz |
533Mb/s |
|
PCI-E X1 |
8bit |
2.5GHz |
512Mb/s(Duplex) |
|
PCI-E X4 |
8bit |
2.5GHz |
2Gb/s(Duplex) |
|
PCI-E X8 |
8bit |
2.5GHz |
4Gb/s(Duplex) |
|
PCI-E X16 |
8bit |
2.5GHz |
8Gb/s(Duplex) |
Summary





































































