- Related articles
- All Cisco ONS-SE-Z1's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-F48LPS-L Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-X2-58.98's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-24PWS-S Switch
- All Cisco CWDM-GBIC-1570's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SRW248G4-K9-UK Switch
- What Is the Importance of Network Interface Card?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750E-48PD-E Switch
- All Cisco GLC-LH-SM's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG350-10P-K9-UK Switch
Recommend tag

How do they differ? PCI vs PCI-E vs AGP
2017-01-19
PCI
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) is local bus that was introduced by Intel Corporation in 1991. Structurally, PCI is the primary bus which inserted between CPU and the system bus, to achieve the management of this layer by a bridge circuit and implement data transmission between the interfaces. Manager provides a signal buffer, so that it can support 10 kinds of peripherals, and maintains high performance in high clock frequency, it provides a connection interface for video cards, sound cards, network cards, MODEM and other equipment. Its operating frequency of 33MHz / 66MHz.
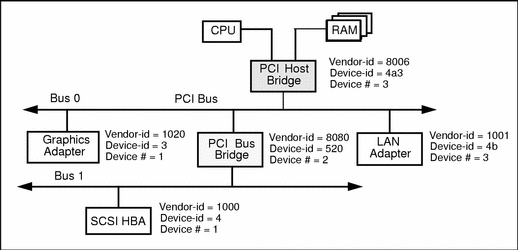
The first proposed PCI bus operating at 33MHz frequency, the transmission bandwidth of 133MB / s (33MHz X 32bit / 8), basically to meet the development needs of the processor at that time. With the higher performance requirements, proposed a 64bit PCI bus in1993, and raised the PCI bus frequency to 66MHz. Currently, 32-bit, 33MHz PCI bus is widely used, 64bit PCI slot is commonly applied to the server product.
PCI-E
As the PCI bus bandwidth is only 133MB / s, it seems more than enough for the needs of sound card, network card, video card and most of the input / output devices, but it cannot meet the growing needs of the graphics card. Now, the PCI interface is not commonly used, only appears on the older PC, and the vendors rarely introduced PCI interface products. Of course, many servers do not ask too high for graphics performance, so usually we consider the use of PCI graphics card on a motherboard that does not have a graphics card slot (such as AGP or PCI Express)
PCI - E bus bandwidth is complicated because it is a serial bus, PCI bus is parallel bus (33 MHZ @ 32 bit), bus bandwidth is 133 MB/s, all equipment that connect to the PCI bus shared 133 MB/s bandwidth. This bus state can meet the requirements of the sound card, 10/100 m CARDS and USB 1.1, but with the growing demands for transmission rate and the popularity of IEEE 1394, USB 2.0 devices, as well as 1000 m card that makes PCI bus of 133 MB/s bandwidth is unable to cope with the needs of high speed equipment, bus has become the performance bottleneck of the system.
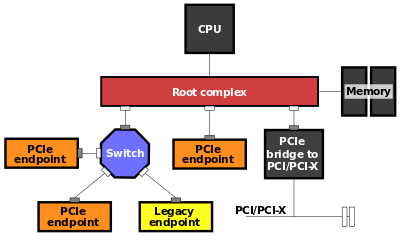
Different from PCI bus, PCI Express belongs to the serial bus, point to point transmission, each channel has its own exclusive bandwidth. In particular, the PCI Express bus also supports bidirectional transmission and data shunting. Data shunting mode of PCI Express bus divided into X1, X2, X4, X4, X8, X16 and X32 multi-channel connection, X1 unidirectional transmission bandwidth can reach 250MB / s, two-way transmission bandwidth can achieve 500MB / s. The 925X and 915 series chipsets support four PCI Express x1 lanes, while there is no any problems to cope with USB 2.0, IEEE 1394, and 1000M network devices, and system latency is a thing of the past.
AGP
AGP (Accelerate Graphical Port), with the development of display chips, PCI bus cannot meet needs of it. Intel lunched AGP interface in July 1996, it is a local bus that graphics card dedicated. Strictly speaking AGP cannot be called bus, because it uses point to point connection that differ from PCI bus, but we still call it AGP bus, AGP interface modified and expanded based on PCI 2.1 specifications, and its operating frequency is 66MHz.
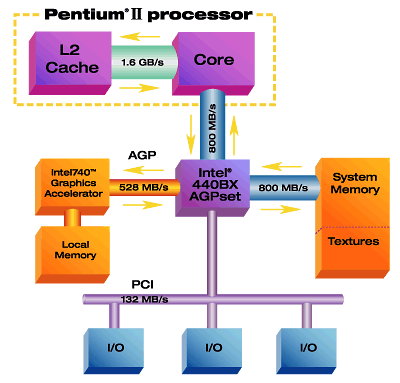
AGP bus directly connect with the motherboard's North Bridge chip, and allows display chips directly connect to the system memory though this interface, so that avoid the system bottleneck caused by PCI bus with narrow bandwidth, increase the speed of 3D graphics data transmission. And in the case of insufficient memory, it can also call the system main memory. So it has a very high transfer rate.
AGP standard has two operating frequency in use of 32Bit bus: 66MHz and 133MHz, the highest data transmission rate is up to 266Mbps and 533Mbps, theoretically PCI bus’s max transmission rate is only 133Mbps. Now, the data transmission of the highest specifications AGP 8X mode can reach 2.1GB/s.
The development of AGP interface experienced AGP1.0 (AGP1X, AGP2X), AGP2.0 (AGP Pro, AGP4X), AGP3.0(AGP8X) etc. stages, and the transmission rate was developed from AGP1X 266MB/s to AGP8X 2.1GB/s.

TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Get solutions or consultation from the technical team.




















































