- Related articles
- What is PCI Express 1.0 2.0 and 3.0?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48TQ-E Switch
- All Cisco XFP10GLR192SR-RGD's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- What is 100BASE FX?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco CGS-2520-24TC Switch
- What Is GJDFBV Fiber Optic Cable?
- All Cisco 15454-GBIC-SX's information (Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Name Brands vs Third-Party Transceivers: Which Do You Prefer?
- The Things You Need to Know about 10GBASE-X Ethernet Standards
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560E-48TD-S Switch

Definition:
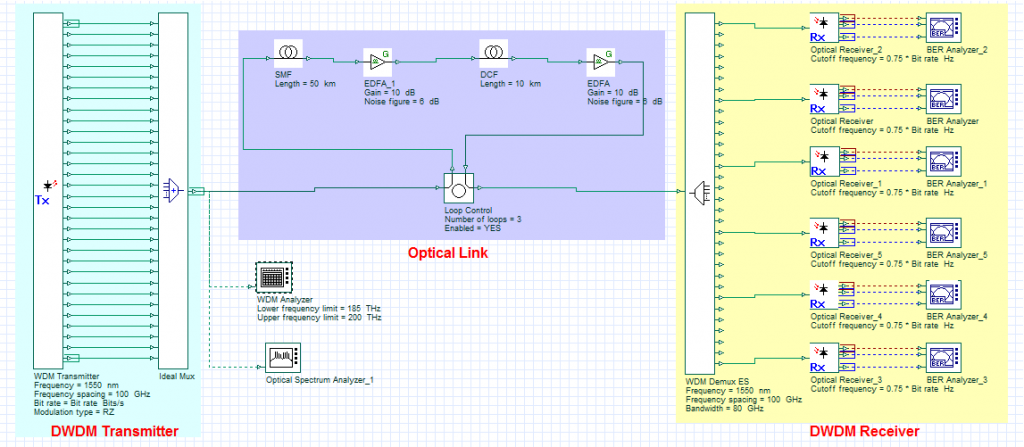
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) is an optical multiplexing technology used to increase bandwidth over existing fiber networks. DWDM works by combining and transmitting multiple signals simultaneously at different wavelengths on the same fiber. The technology creates multiple virtual fibers, thus multiplying the capacity of the physical medium.
What is WDM in Telecom
Wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) is a method of combining multiple signals on laser beams at various infared (IR) wavelengths for transmission along fiber optic media. Each laser is modulated by an independent set of signals. Wavelength-sensitive filters, the IR analog of visible-light color filters, are used at the receiving end. WDM is similar to frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). But instead of taking place at radio frequencies (RF), WDM is done in the IR portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Each IR channel carries several RF signals combined by means of FDM or time-division multiplexing (TDM).
Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is a technology that puts data from different sources together on an optical fiber, with each signal carried at the same time on its own separate light wavelength. Using DWDM, up to 80 (and theoretically more) separate wavelengths or channels of data can be multiplexed into a lightstream transmitted on a single optical fiber. Each channel carries a time division multiplexed (TDM) signal. In a system with each channel carrying 2.5 Gbps (billion bits per second), up to 200 billion bits can be delivered a second by the optical fiber. DWDM is also sometimes called wave division multiplexing (WDM).
The first WDM systems were two-channel ones that used 1310 nanometer (nm) and 1550 nm wavelengths. Shortly afterward came multi-channel systems that used the 1550 nm region, where the fiber attenuation is lowest. Depending on their wavelength patterns, WDM systems are typically divided into coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) and dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM).
Infinera’s founding vision is to enable an infinite pool of intelligent bandwidth that the next communications infrastructure is built upon, and the company is well-recognized in the technology segments of optical WDM transport and packet optical transport network (OTN) switching. Infinera pioneered a new approach for networks with photonic integration, which provides massive WDM capacity in a small power and space footprint to handle growing bandwidth needs.
Conclusion:
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing, an optical technology used to increase bandwidth over existing fiber optic backbones.DWDM works by combining and transmitting multiple signals simultaneously at different wavelengths on the same fiber. In effect, one fiber is transformed into multiple virtual fibers. So, if you were to multiplex eight OC-48 signals into one fiber, you would increase the carrying capacity of that fiber from 2.5 Gb/s to 20 Gb/s. Currently, because of DWDM, single fibers have been able to transmit data at speeds up to 400Gb/s.
Please click to check more related concepts:
| Transceivers Wavelength |
| Bidi |
| WDM |