- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG500-52P-K9-G5 Switch
- Applicable to 40GBASE-LRL4 Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-24TS-S-RF Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco ME-3600X-24FS-M= Switch
- Cisco SMARTnet Total Care Service
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG250-26-K9-UK Switch
- What is PAM Authentication?
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-32.68's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- What is a PCI Express slot for?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco ME-3400-24FS-A Switch

Definition:
A gigabit interface converter (GBIC) is a standard for transceivers, commonly used with Gigabit Ethernet and fiber channel in the 2000s.[citation needed] By offering a standard, hot swappable electrical interface, one gigabit port can support a wide range of physical media, from copper to long-wave single-mode optical fiber, at lengths of hundreds of kilometers. A variation of the GBIC called the small form-factor pluggable transceiver (SFP), also known as mini GBIC, has the same functionality but in a smaller form factor. Announced in 2001, it largely made the GBIC obsolete.
Appeal:
The appeal of the GBIC standard (and hot-swappable transceivers in general) in networking equipment, as opposed to fixed physical interface configurations, is its flexibility. Where multiple different optical technologies are in use, an administrator can purchase GBICs as needed, not in advance, and they can be the specific type needed for each link. This lowers the cost of the base system and gives the administrator far more flexibility. On the other hand, if a switch will mostly have one port type (especially if that port type is copper) purchasing a switch with that port type built in will be cheaper and take up less space per port.
Standards:
The GBIC standard is non-proprietary and is defined by the Small Form Factor committee in document number 8053i. The first publication of the proposal was in November 1995. A few corrections and additions were made through September 2000. Robert Snively of Brocade Communications was technical editor. Original contributors were AMP Incorporated, Compaq Computers, Sun Microsystems, and Vixel Corporation
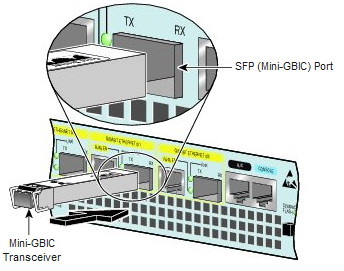
What is Mini GBIC port?
A Gigabit Ethernet Combo port is an Ethernet port and a Mini GBIC port (also called SFP´s) that shares the same switch fabric and port number. A Combo port is a way to provide different types of connectivity without taking up unused switch fabric. These Combo ports can also be labeled as tied, meaning two different physical ports that can only be used one at a time. A Gigabit Ethernet Combo port consists of one 1000Base-T Gigabit over Copper port (provided), and one Mini GBIC port (empty port that requires Mini GBIC module).
What is a Mini GBIC used for?
GBIC modules allow technicians to easily configure and upgrade electro-optical communications networks. The typical GBIC transceiver is a plug-in module that is hot-swappable (it can be removed and replaced without turning off the system). The devices are economical, because they eliminate the necessity for replacing entire boards at the system level. Upgrading can be done with any number of units at a time, from an individual module to all the modules in a system.
Conclusion:
A gigabit interface converter (GBIC) is a transceiver that converts electric currents (digital highs and lows) to optical signals, and optical signals to digital electric currents. The GBIC is typically employed in fiber optic and Ethernet systems as an interface for high-speed networking. The data transfer rate is one gigabit per second (1 Gbps) or more.
Please click to check more related concepts:
| Transceivers Package | Ethernet standard | Application | Transceivers Wavelength | Fiber mode |
| SFP | 1000Base-X | Bidi | Multi-mode | |
| SFP+ | 100Base-FX | DWDM | ||
| XFP | 1000BASE-T | WDM | ||
| QSFP+ | ||||
| X2 | ||||
| CFP | ||||
| CSFP |