- Related articles
- All Cisco DWDM-SFP10G-61.41's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-24TD-L Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960XR-48LPS-I Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560G-24PSS-RF Switch
- Several Best-Selling Cisco GBIC Transceivers
- All Cisco DWDM-X2-60.61's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- All Cisco GLC-EX-SMD's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix
- The Things You Need to Know about 100BASE-CX Ethernet Standards
- The Things You Need to Know about 10GBASE-R Ethernet Standards
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48TD-S Switch

Fiber to the home (FTTH) to the home access network based on passive optical network technology (PON, passive optical network) is a point to multipoint network structure, that is, the use of optical splitter center signal to multiple end users. Optical splitter has two different distributions in the FTTH network: centralized distribution and cascade distribution, respectively, corresponding to primary and secondary spectral two sub-spectral modes. These two spectroscopic methods have their own advantages and disadvantages, this tutorial will be a detailed description of it.
The primary optical splitting
The primary splitting means that the optical splitter between the optical line terminal (OLT) and the optical network unit (ONU) is parallel, and the basic form is "OLT → optical splitter → ONU "The optical splitter used here is typically 1:64. In a primary beam application, the optical splitter can be centrally installed at the central office, but in order to save fiber costs, the optical splitter is typically installed between the OLT and the ONU. The central office and optical splitter are connected by trunk cable (also called feeder cable), and the user terminal and optical splitter are connected via wiring cable. Among them, the backbone of the general selection of general outdoor fiber optic cable, the number of cores from 12 to 144 core range; wiring cable should be based on specific application environment selection, the general selection of general outdoor cable, for some occasions, may need to choose flame retardant cable.
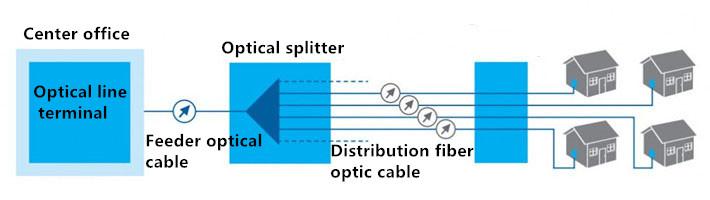
The secondary optical splitting
Secondary splitting refers to the optical splitter between the OLT and the ONU is cascaded, the basic form of "OLT → optical splitter 1 → optical splitter 2 → ONU", optical splitter 1 spectral Is typically 1: 4 or 1: 8, and the splitter ratio of the optical splitter 2 is usually 1: 8 or 1:16. In the second-class spectroscopic applications, the first-stage optical splitter is often installed in the optical transfer box or split fiber box, the second class optical splitter often installed in the terminal from the end of the station, the district.
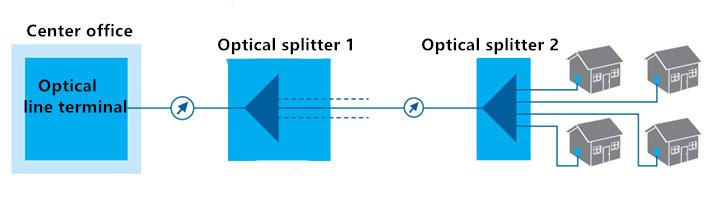
Primary optical splitting VS Secondary optical splitting
As mentioned above, the optical splitter in the primary beam splitting application is concentrated in one place, so it can maximize the use of the OLT port, suitable for use in the end user concentration, the larger number of applications; The splitter is cascaded and suitable for use in end-user decentralized, smaller applications. In addition, the two spectral methods have the following advantages and disadvantages:
|
Primary
optical splitting |
|
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
OLT port utilization is high |
need to use more wiring cable |
|
More able to adapt to the needs
of the future development |
of the use of more network
accessories |
|
Easy monitoring and maintenance |
may require additional network infrastructure |
|
Secondary
optical splitting |
|
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Low user access costs |
require the use of more active
devices and optical splitter |
|
The lower requirements of the
split fiber box |
network structure is not flexible |
|
Service area of the
splitting ratio can be flexible |
adjustment is not easy to monitor
and maintain |
Conclusion
FTTH based on PON technology is the trend of future access network development, and the choice of primary or secondary spectroscopy for the network investment and operating costs have a significant impact, we should choose according to the actual situation which can save costs and meet future needs spectral way.





































































