- Related articles
- All Cisco GLC-LH-SM's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560G-48PS-E Switch
- All Cisco ONS-SI-155-SR-MM's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF112-24-UK Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48TQ-L Switch
- The difference between DWDM and WDM
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750G-12S-SD Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SLM2048PT-EU Switch
- All Cisco SFP-10G-BXD-I’s Information (Overview, Features, Data Sheet PDF, Price, Specifi
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N5K-C5020P-B-S Switch

Growing data center consolidation, higher-performance servers, and increasing application density on virtualized servers are driving network capacity demands to levels previously unimagined. The data center network is shifting to 10 Gbps at the access layer and 40 Gbps at the aggregation layer. However, to support 40-Gbps connectivity, data center architects need to upgrade the cabling infrastructure. This can be too expensive or disruptive to allow data centers to quickly adopt and migrate to the 40-Gbps technology. Now the problem can be solved with 40G Bi-Directional QSFP, which allows for zero-cost fiber migration by reusing the current 10-Gbps cabling for 40-Gbps device connectivity.
40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP vs. Legacy 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP: What’s the Difference?
As we know, existing 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP use independent transmitter and receiver sections, each with 4 parallel fiber strands. For a 40-Gbps connection, 8 fiber strands are required (shown in the picture below). Usually, a legacy 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP can support link lengths of 100 meters and 150 meters, respectively, on 12-fiber MPO/MTP OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers.
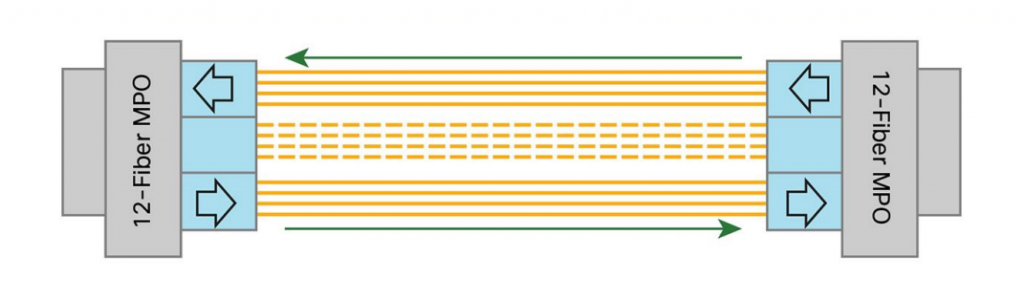
Unlike legacy 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP, 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP has two 20-Gbps channels, each transmitted and received simultaneously on two wavelengths over a single MMF strand, enabling an aggregated 40-Gbps link over a two-strand multimode fiber connection. The following picture shows the technology concept of the 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP transceiver. It can also support link lengths of 100 meters and 150 meters, but on duplex LC OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers, which enables it use the existing 10 gigabit duplex MMF infrastructure for migration to 40 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity.
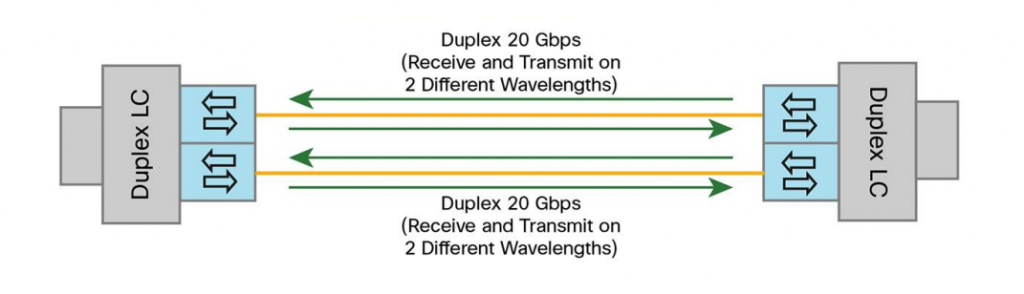
Upgrading from 10G to 40G: Why 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP Is More Cost-effective?
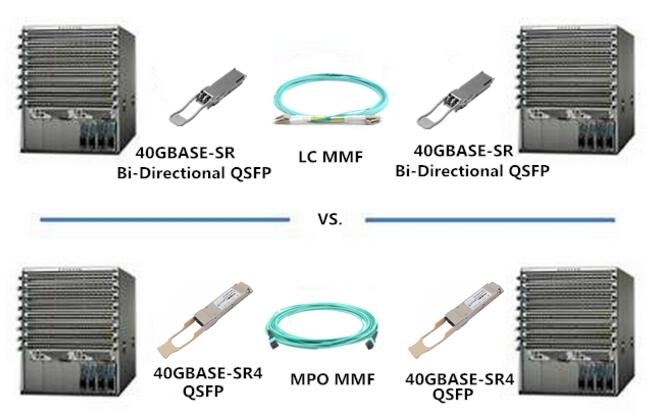
In an unstructured cabling system, devices are connected directly with fiber cables. This direct-attachment design can be used to connect devices within short distances in a data center network. Direct connection between two legacy 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP transceivers and two 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP transceivers is shown in the picture below. The legacy 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP use MPO MMF fiber, whereas 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP use LC MMF fiber. As we know, existing 10-Gbps direct connections also commonly use LC MMF fiber, 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP therefore allows cable reuse, resulting in zero-cost cabling migration from direct 10-Gbps connections to direct 40-Gbps connections.

Besides unstructured cabling system, a structured cabling system is commonly deployed in data center networks to provide more flexible and scalable cabling infrastructure. Structured cabling uses short patch cords to attach devices to a patch panel and then uses fiber trunk cables either to consolidate the cables in a central location for additional connectivity or to direct the cables to another patch panel, to which the remote devices are attached. Following picture shows 40-Gbps structured cabling solutions with both legacy 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP transceivers and 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP transceivers.
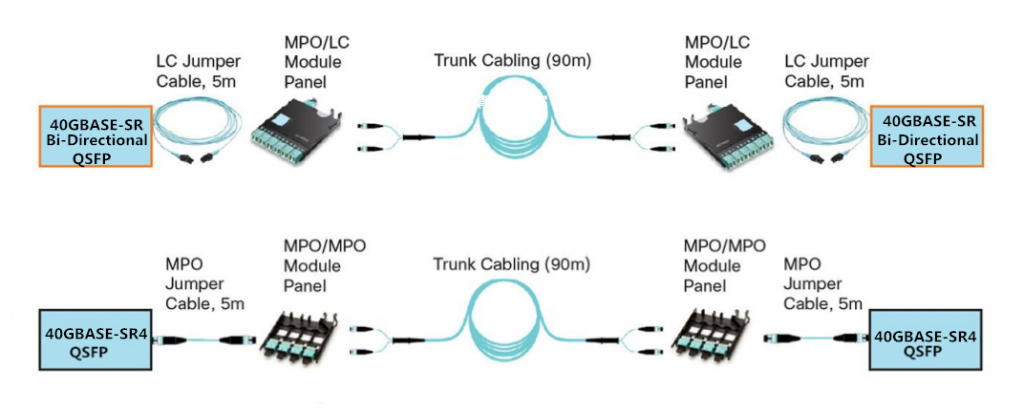
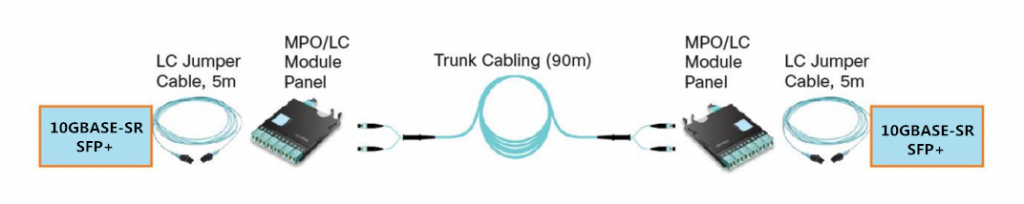
To further analyze which 40-Gbps structured cabling solutions is more cost-effective for 10G to 40G migration, we give a 10-Gbps structured cabling solutions in the following picture. From the picture above and below, we can see that the cabling infrastructure of 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP transceivers is the same as the 10-Gbps structured cabling solutions. Therefore, with 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP transceivers, the existing 10-Gbps fiber infrastructure can be reused. Customers can upgrade their network from 10 Gigabit Ethernet to 40 Gigabit Ethernet without incurring any fiber infrastructure upgrade cost.
Switches and Routers Supported for 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP
In market, there is a broad portfolio of high-performance and high-density 40-Gbps switches and routers available to support the 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP transceivers, especially the Cisco Nexus 6000 and 7000 Series and Nexus 5600 and 7700 platform switch models. Following table displays some available switches models.
| Switches & Routers Series | Models |
| Cisco Nexus 5000 Series | N5K-C5672UP, N5K-C56128P, N56-M24UP2Q |
| Cisco Nexus 6000 Series | N604-96Q-B-24Q, N6K-C6004-M12Q |
| Cisco Nexus 7000 Series | N7K-M206FQ-23L, N7K-F312FQ-25, N77-F324FQ-25 |
| Cisco Nexus 9000 Series | N9K-C93128TX, N9K-C9396PX, N9K-C93128PX, N9K-C9396TX, N9K-X9564PX N9K-C9336PQ, N9K-X9636PQ, N9K-X9736PQ, N9K-X9564TX |
40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP is now available and in stock for same-day shipping in cozlink.com. For more information, you can contact us via cozlink.com.
Cisco QSFP 40-Gbps Bidirectional Short-Reach Transceiver
- Main features and benefits of the Cisco QSFP 40-Gbps BiDi transceiver include:
- Low infrastructure cost for 40 Gigabit Ethernet network
- Seamless upgrade from 10 Gigabit Ethernet to 40 Gigabit Ethernet
- 100m reach over OM3 fiber, which meets most data center reach requirements
- Duplex LC connector for use with duplex MMF
- QSFP MSA specification-compliant form factor
- Hot-swappable I/O device that plugs into a Cisco QSFP-based switch, router, or optical platform port
- Support for “pay-as-you-populate” model
- Easy-to-use pull-release handle that is color coded for reach identification
Cisco QSFP 40G BiDi
The Cisco QSFP 40-Gbps bidirectional (BiDi) transceiver is a pluggable optical transceiver with a duplex LC connector interface for short-reach data communication and interconnect applications using multi-mode fiber (MMF). The Cisco QSFP 40-Gbps BiDi transceiver offers customers a compelling solution that enables reuse of their existing 10 gigabit duplex MMF infrastructure for migration to 40 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity. It supports link lengths of 100 and 150 meters on laser-optimized OM3 and OM4 multi-mode fibers, respectively. And complies with the QSFP MSA specification, enabling customers to use it on all QSFP 40-Gbps platforms to achieve high-density 40 Gigabit Ethernet networks. Each Cisco QSFP 40-Gbps BiDi transceiver consists of two 20-Gbps transmit and receive channels in the 832-918 nanometer wavelength range, enabling an aggregated 40-Gbps link over a two-strand multi-mode fiber connection.





































































