- Related articles
- What is DWDM in networking?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-F24TS-S Switch
- Best-selling models of Intel Ethernet server adapters
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48TS-S Switch
- What is PCI Express?
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-35.04's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG300-52MP-K9-EU Switch
- The difference between SFP+ and SFP
- All Cisco XENPAK-10GB-SR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- All Cisco SFP-OC12-LR1's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr

When operating the WDM system, make sure to pay extra attention to the following parameters:
1. wavelength
A wavelength is a distance traveled by a wave in a vibration period. The wavelength λm of the monochromatic light propagating in the optical fiber is represented by the following formula:
λm = λ / n = v / f where" λ "means the wavelength in the vacuum, " n "refers to the refractive index," v " means the phase velocity, and" c "is calculated by c / n, The propagation speed in vacuum, is 2.99792458 X 108 m/s, "f" refers to the optical frequency.
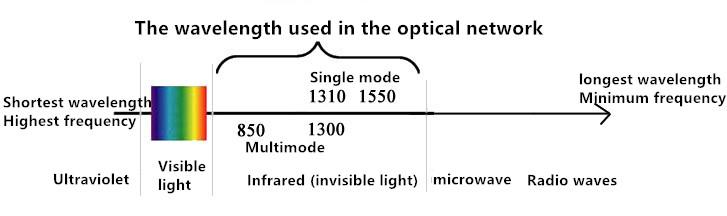
Note: In the practical application of WDM, the wavelength of the communication laser, the wavelength of the optical filter, the wavelength of the transmission channel of the light propagating in the fiber are represented by "λ", and the wavelength in nanometer is usually in the vacuum.
2. Channel
In the WDM system, each input channel has a unique wavelength, so each channel can go through the fiber "parallelly".
3. Passband
Passband refers to the frequency or wavelength range that can pass through the filter, which is one of the parameters of the WDM filter. In fact, the passband is a wavelength range centered on the center wavelength, for example, the typical passband of the CWDM filter is within the range of ± 6.5 nm of the center wavelength. Thus, a light having a wavelength of 1551 nm can be transmitted in the range of 1544.5 nm to 1557.5 nm without additional channel loss.

4. Insert loss
The insertion loss is the attenuation caused by the insertion of the WDM filter into the optical transmission system, which is usually the maximum insertion loss in the passband of the filter. The insertion loss of a WDM product is the maximum insertion loss generated by the channel port. In WDM networks, insertion loss is part of the total loss of the communication link. The insertion loss values of the different thin film filters are also different, and the thin film filter needs to be screened before being used in WDM products.
5. Polarization loss
The loss of the WDM filter varies with the light polarization of the light. The polarization loss is different from the maximum insertion loss produced by the entire polarization process. The polarization loss of a WDM product is the maximum polarization loss of each channel.
6. Polarization mode dispersion
Polarization mode dispersion is a linear phenomenon in the fiber, it will lead to the optical receiver can not correctly read the signal, resulting in high bit error rate. This is another kind of polarization effect, will cause damage to the long-distance optical fiber transmission system.
7. Return loss
Return loss is the signal return/reflection due to fiber breakage in the transmission link or WDM system. In order to prevent the problem of light source laser, reduce the transmission loss, the value of the return loss is better. The return loss of the WDM product is the measurable minimum return loss generated in all ports.
8. Fluctuation in the band
In-band fluctuation is the maximum peak-to-peak variation in the filtered passband of a channel.
9. Channel isolation
Channel isolation is the degree of interference of a channel signal to another channel in dB. It is the difference between the maximum insertion loss in the passband of the filter and the minimum loss in the other filter channels. Channel isolation is measured by inserting the sweep power supply into the default port of the filter and then measuring the loss in the passband and other passbands of the filter. In other filters, the filter with the passband of the filter closest to the signal isolation is called the adjacent channel isolation, and the filter does not approach the passband of the filter, the signal isolation Called non-adjacent channel isolation.
10. Operating temperature
Operating temperature (℃) refers to the performance of the equipment can reach the operating temperature range.
11. Storage temperature
Storage temperature (° C) means that it does not affect its future use of the storage temperature range.
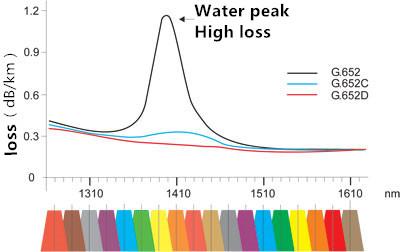
12. Water Peak
The water peak refers to the loss peak caused by OH- ions. Now, the water peak and its water peak up and down the attenuation can be more than 2dB / km.
On the basis of WDM, a new network technology has been derived: Wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network (WDM-PON, Wavelength Division Multiplexing-Passive Optical Network).
13. WDM-PON
WDM-PON is an innovative concept in access and backhaul networks that use WDM on a physical point-to-multipoint (P2MP) fiber infrastructure without any active devices. WDM-PON can provide high bandwidth to multiple endpoints over long distances.

14. Optical Transport Network (OTN)
OTN is used to support optical networks that use WDM (rather than SONET / SDH), which can transmit, reuse, transform, manage, monitor and destroy optical channels carrying signals.





































































