- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco ME-3400-24TS-A Switch
- What Is GYDXTW Fiber Optic Cable?
- All Cisco GLC-ZX-SM's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- All Cisco GLC-2BX-D's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- The Difference between Ethernet PCI Adapter and Network Interface Card
- All Cisco SFP-10G-SR’s information (Overview, List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibil
- All Cisco CWDM-GBIC-1590's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- The Things You Need to Know about 1000BASE-SR Ethernet Standards
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-55.75's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF250-48HP-K9-UK Switch
Recommend tag

Explanation of WDM Technical Terminology (2)
2017-06-13
The topology used in WDM systems plays an important role in the utilization of WDM networks. Topology-related terms are:
Network topology structure
By using multi-channel on fiber, WDM products make fiber-optic networks more efficient. The network is invisible but can be identified by fiber routing or topology. Sometimes, networked, ring, point to point, point to multipoint and other network topology will use the specific WDM products, therefore, when selecting the WDM products, we must pay great attention to the type of network you use. A network is usually composed of several different sub-network topologies.
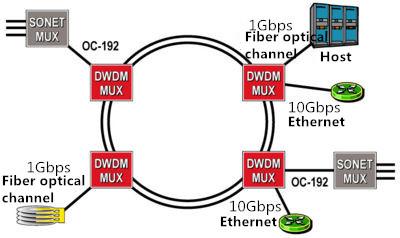
Ring topology structure
The infrastructure of the urban network is usually a ring topology. A ring topology network is a closed loop consisting of a series of fiber segments whose end points are located in each node in the loop, and each node is connected to only two adjacent nodes through the fiber segment. The ring network is usually a two-fiber bi-directional system.
Node
In a network topology, a node is the end point of a single branch or multiple branches of a network. A WDM network consists of a set of nodes that are connected by fiber (physical topology) so that a logical topology overwrites the entire network after establishing a link between the nodes. The use of WDM technology in fiber allows a node to become multiple service areas, thus expanding the user base and available bandwidth.
To build a WDM system, hardware devices are essential!
Multiplexer
A WDM multiplexer is a device that multiplexes or blends optical signals of different wavelengths onto an optical fiber.

Demultiplexer
In contrast to the multiplexer, the demultiplexer demultiplexes or separates optical signals of different wavelengths in the mixed optical signal and causes the separated optical signals to propagate on different fibers at respective wavelengths.
Note: There are CWDM / demultiplexed products and DWDM multiplex / demultiplex products on the market. These products are both multiplexer and demultiplexer. They are available in 19-inch rackmount, LGX cassette, and ABS cartridge pigtail output.
Optical add-drop multiplexer (OADM, Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer)
Optical add/drop multiplexer is a device used in WDM system. Its function is to selectively receive and transmit certain wavelength channels from the transmission optical path, without affecting the transmission of other wavelength channels.
So, for the ports on the WDM device, how much do you know?

Default port
The default port is the connection point of the composite channel in the WDM device. In a multiplexed product, the composite channel is routed from the default port. In the demultiplexed product, the composite channel is passed from the default port.
Expansion/Upgrade port
In CWDM products, usually there will be expansion port, or there will be upgrading the port, but the two will not appear in a WDM product. The expansion ports or upgrading ports on the CWDM multiplexer/demultiplexer are used to add, terminate, or pass new channels, which can be connected in series with two CWDM multiplexers/demultiplexers, In the case of the same way, the channel capacity is doubled.
In DWDM products, the role of the upgrade port is to increase, terminate or pass the unused C-band DWDM channel (ie, the channel between 1530nm and 1565nm). If the DWDM product is equipped with an upgrade port and a capacity port, the expansion port is typically used for additional channels other than the C-band, such as most CWDM channels.
1310nm port
The 1310nm port is a wide band of ports that is used to add other special CWDM wavelengths. For example, an 8-channel CWDM may require a 1310 nm port while using wavelengths from 1470 nm to 1610 nm. 1310nm ports are typically used in some traditional networks and are sometimes used as backhaul paths. Assuming that the existing traditional network is using the 1310nm port, and all the fiber has been all occupied, then if you want to increase the network capacity, you can use the 1310nm port at the same time, in the fiber to increase the other CWDM wavelength. The 1310nm port also supports LR optical module, LX optical module.
1550nm port
Similar to the 1310nm port, the 1550nm port can transmit the traditional 1550nm optical signal, but also support the ER optical module, ZR optical module, LX optical module, ZX optical module.
Monitoring port
The monitoring port is used to monitor or detect the power signal, which is a signal multiplexed by the CWDM multiplexer but not demultiplexed. The monitoring port is usually connected to a detection or monitoring device, such as a power meter or a network analyzer. If the signal changes or is not successfully transmitted, the network administrator can use the monitoring port to detect the fault without disconnecting the existing network.

TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Get solutions or consultation from the technical team.




































































