- Related articles
- Difference between XENPAK and QSFP+
- All Cisco GBIC-BX-D's information (Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48PD-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG355-10P-K9-UK Switch
- All Cisco DS-CWDM4G1470's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-48LPS-L Switch
- All Cisco MA-SFP-10GB-LRM's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility m
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-58.17's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- Do You Really know About Fiber Optic Cable?
- What is a SFP module?

Introduction
The fiber amplifier is an essential component of transmission applications such as metropolitan area networks. Its biggest feature is that it can directly amplify the optical signal without going through the process of optical-electrical-optical conversion. It is often used in wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) system. This tutorial will detail several commonly used fiber amplifiers, and compare their advantages and disadvantages.
Basic knowledge of fiber optic amplifier
Before we start to introduce several different fiber amplifiers, we need to have a general understanding of it. It is well known that when the transmission distance is too long (greater than 100 km), the optical signal will be a lot of loss, in the past people usually use optical repeaters to amplify the optical signal, it works by the photodetector weak light signal conversion And then the electrical signal is reproduced or amplified and then converted into optical signal transmission, this device in the practical application of a certain limit, has been gradually replaced by fiber amplifier, fiber amplifier works as shown below, it Can be directly on the optical signal amplification, without going through the light - electricity - light conversion process.
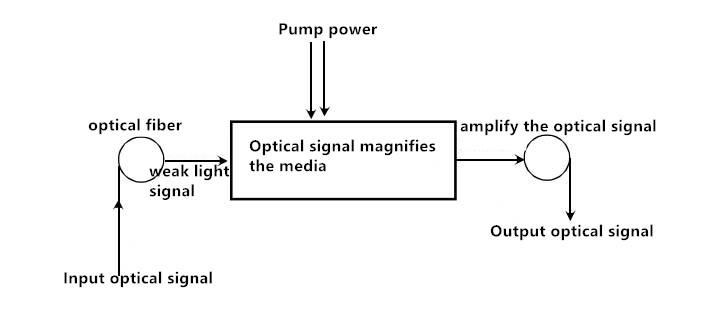
Common fiber amplifiers
Commonly used fiber amplifiers are erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA), Raman amplifier and semiconductor fiber amplifier (SOA), this part will be described in detail.
Erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA)
The erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is mainly composed of erbium-doped fiber, pump light source, optical coupler, optical isolator and the optical filter. Among them, erbium-doped fiber is an important component of optical signal amplification, mainly used to achieve the 1550 nm (EDFA) in the 1530 nm to 1565 nm wavelength range of the best results. Its advantages and disadvantages are as follows:
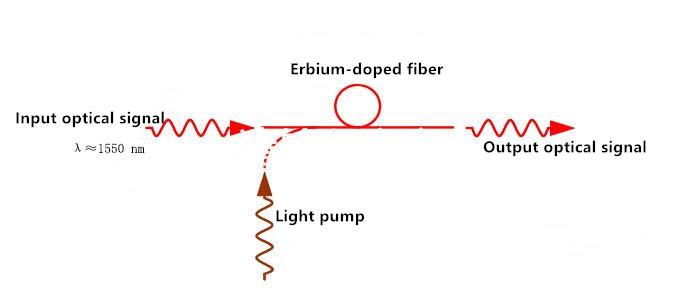
Advantages:
Maximum pump power utilization (greater than 50%). Direct and simultaneous amplification of optical signals in the 1550 nm band over 50 dB Long distance transmission with low noise.
Disadvantages:
Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFA) are larger and cannot work with other semiconductor devices.
Raman amplifier
The Raman amplifier is the only device that can amplify the optical signal in the 1292 nm to 1660 nm band. Its working principle is based on the stimulated Raman scattering effect in quartz fiber, as shown in the following figure. The weak light signal is amplified by the Raman scattering effect when the weak light signal in the man gain bandwidth is transmitted in the fiber at the same time as the strong pump lightwave. The advantages and disadvantages of this fiber amplifier are as follows:
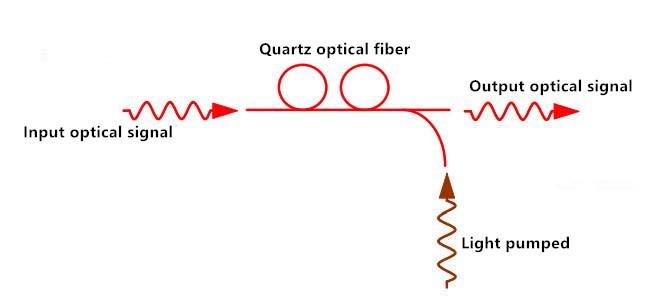
Advantages:
A wide range of applicable bands can be used in installed single-mode fiber-optic cabling applications can add erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) low power consumption, low crosstalk.
Disadvantages:
Pump power high gain control system complex noise.
Semiconductor Fiber Amplifier (SOA)
Semiconductor optical fiber amplifier (SOA) semiconductor materials as a gain medium, the optical signal input and output are the anti-reflective coating, to prevent the reflection of the amplifier end, remove the resonator effect. Its advantages and disadvantages are as follows:
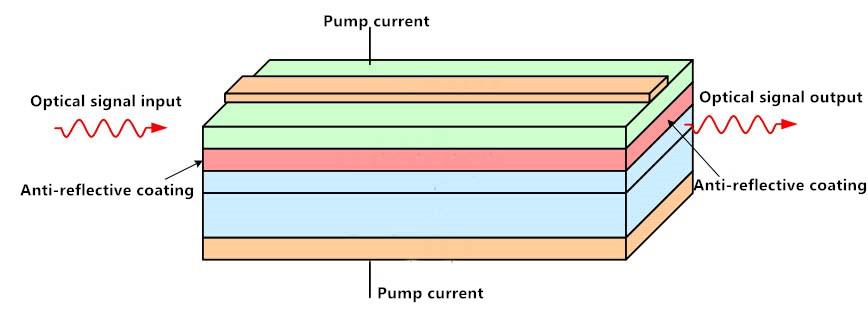
Advantages:
Small output power Small gain bandwidth is small but can be used in a variety of different wavelengths than erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is cheap and can be used with semiconductor devices to achieve cross-gain modulation, cross-phase modulation, wavelength conversion and four Mixing four non-linear operations.
Disadvantages:
Performance is less than erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) high noise, small gain.





































































