- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF500-24P-K9-G5 Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960X48LPDL-RF Switch
- What are SFP slots?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C4948E-F-E Switch
- The difference between GBIC and SFP
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750G-48TS-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-X9636PQ= Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF200E-24P-UK Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-42.14's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- What is a PCI Express slot for?

Advantages of fiber telecommunication
●Large telecommunication capacity
●Long relay distance
●No electromagnetic interference
●Abundant resources
●Light fiber with small volume
Electromagnetic wave spectrum
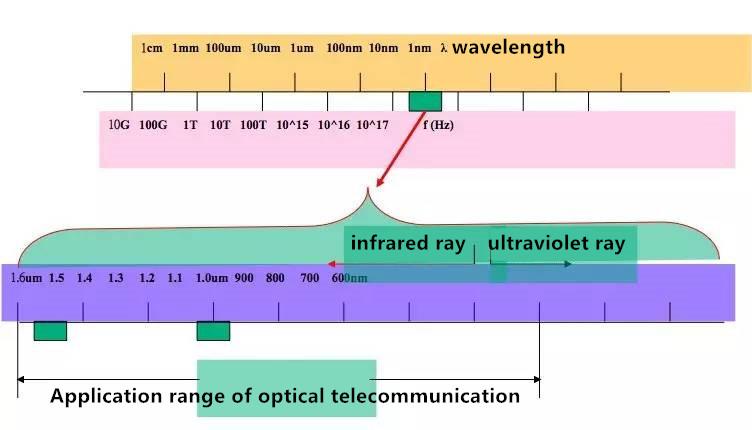
Telecommunication band partitions and their corresponding transmission media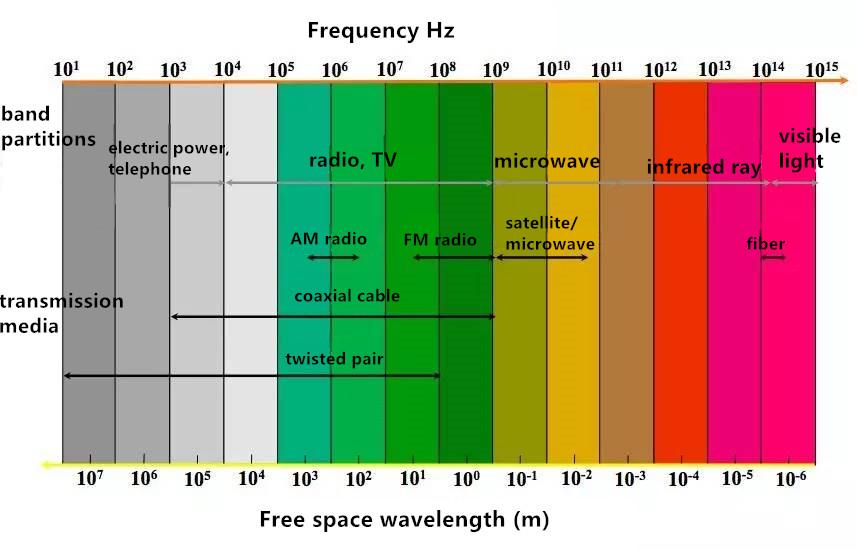
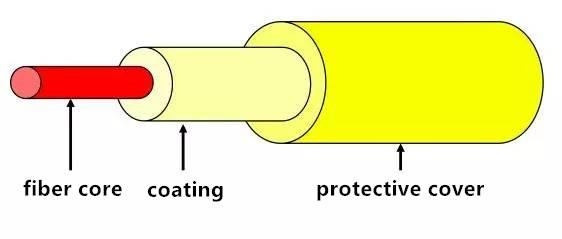
Fiber Structures
Bare fiber is generally divided into three layers:
First layer: innermost glass core with high refractive index (core diameter with general 9-10μm (single-mode), 50 or 62.5μm (multi-mode)
Second layer: middle silicon glass coating with low refractive index (diameter with general 125μm)
Third layer: outermost resin coating to intensify
1) core: high refractive index for light transmission;
2) coating:low refractive index, forming the total reflection condition combined with core;
3) jacket:great intensity, suffering the stronger shock to protect fiber.
3mm fiber cable orange MM multi-mode
yellow SM single-mode
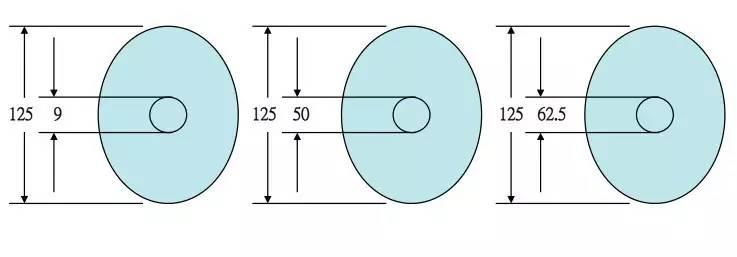
Fiber sizes
Outer diameter: generally 125 um (one hair’s average diameter with 100um)
Inner diameter: 9um for single mode, 50/62.5um for multimode.
Numerical aperture
The incident light to the fiber end face cannot be totally transmitted by fiber. Only the incident light within a range of a certain angle is called numerical aperture of fiber. If fiber’s numerical aperture is larger, it will be beneficial to its butt joint. Different manufacturers will produce fibers with different numerical apertures.
Fiber varieties
According to the transmission modes of light in the fiber, fiber variety is divided int
1. Multi-Mode (abbreviation: MM)
2. Single-Mode (abbreviation: SM)
Multi-mode fiber: center glass core is relatively wide (50 or 62.5μm)can transmit multi-mode light. However, its large mode dispersion not only limits the transmission frequency of digital signals but also becomes more serious with the increase of distance. For example, the fiber with 600MB/KM has a just 300MB bandwidth in 2KM. Therefore, the transmission distance of multi-mode fiber is short, generally with a few kilometers.
Single-mode fiber: center glass core is relatively narrow (core diameter with general 9-10μm), only transmitting the single-mode light. Actually, it comes from the step-index fiber. But its core diameter is very small, and theoretically only allows the incident and straight light with the sole transmission way into the fiber and allows this light’s rectilinear propagation. Fiber pulse is hardly widened. Therefore, its small mode dispersion is suitable to long-distance telecommunication. But its chromatic dispersion plays a critical role so that the single-mode fiber requires highly on light source’s spectral width and stability, which means narrow spectral width and better stability.
Common fiber specifications
Fiber sizes:
1)diameter of single mode core:9/125μm,10/125μm
2)outer diameter of coating(2D):125μm
3) outer diameter of disposable coating:250μm
4)pigtail:300μm
5)multimode:50/125μm in European standard,62.5/125μm in American standard
6)industry,healthcare and low-speed internet:100/140μm, 200/230μm
7)plastic:98/1000μm for car control