- Related articles
- Do You Really know About Fiber Optic Cable?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C4900M Switch
- All Cisco CVR-XENPAK-SFP10G's information (Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960+24TC-L Switch
- Analysis on the performance of common external wireless network card and purchasing skills
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-2000-8TC-G-N Switch
- All Cisco XENPAK-10GB-LW's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- All Cisco SFP-GE-L's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-46.92's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- What Is GYXTW Fiber Optic Cable?

Definition of Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber Optic Cable is a medium used to transmit data faster over a long distance. The fiber optic technology is widely used in the telecommunication industries. Consequently, it innovation have expanded the boundaries since you can communicate with someone anytime and anywhere without any limitation. In other words, Fiber Optic Cable has turned the world to be a small global village. The Fiber Optic Cables have been innovated as results of technological advancement experienced during the current age.
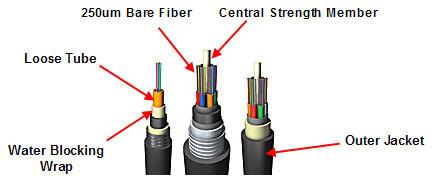
Discussion
Fiber Optics, also called optical fibers, is microscopic strands of very pure glass with about the same diameter of a human hair. Thousands of these optical fibers are arranged in bundles in optical cables and are used to transmit light signals over long distances. The bundles are protected by a jacket, which is the cable's outer covering. The single optical fiber consists of the core which is the thin glass center of the fiber where the light travels, the outer optical material that surrounds the core and reflects the light back into it is the cladding, and the plastic coating that protects the fiber from moisture and damage is the buffer coating.
Single-mode and multi-mode are the two types of optical fibers. The single-mode, used for long distances, has small cores and transmits infrared laser light. The multi-mode, normally used for short distances, has large cores and transmits infrared light.
History of Fiber Optics
Fiber optics go back as far as Roman times, but the first was an "optical telegraph," which allowed operators to relay a message from one tower to the next by a series of lights mounted on the towers. This was invented in the 1790s by the French Chappe brothers. The great achievement was made in optical science over the course of the next century.
Fiber Optics during the 1800s
Physicists Daniel Collodon and Jacques Babinet reported in the 1840s that light could be directed along jets of water for fountain displays. In 1854, John Tyndall, a British physicist, demonstrated that light could travel through water jets, thereby proving that a light signal could be bent.
In 1880, Alexander Graham Bell patented an optical telephone system which assisted in the advancement of optical technology. Also in 1880, William Wheeler invented a system of light pipes that illuminated homes from an electric arc lamp located in the basement. Bent glass rods were used to illuminate body cavities in 1888 by Dr. Roth and Professor Reuss of Vienna. Henry Saint-Rene designed a system of bent glass rods to guide light images in an early television scheme in 1895. A patent was applied for by an American, David Smith, in 1898 for a dental illuminator using a curved glass rod.
Conclusion
Basically, the Fiber Optic Cable is used for the effective communication. Its innovation has drastically changed the face of many telecommunication industries. Consequently, the lifestyle in rural areas has been also improved and now, there no more remote areas.





































































