- Related articles
- Used in 10GBASE-USR Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG550XG-24F-K9-UK Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-X2-59.79's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG300-10PP-K9EU-RF Switch
- All Cisco SFP-10G-BX40D-I's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility m
- The development background of PCI Express
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-24TD-L Switch
- Used in 40GBASE-ER4 Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- What is the speed of Gigabit Ethernet?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N3K-C3132Q-XL Switch

Introduction
There are big differences between Ethernet Cables & Fiber Optic Cable that any one needs to understand. Ethernet is referred as the fiber cable that comprises of many twisted copper wires that transmit data in form of electrical signals while Fiber optic cable is made of many thin strands of optical fiber that carries data in form of light signals. However, they all play strong role in internet connection for the survival of businesses.
Ethernet cables are comprised of multiple copper wires twisted together that transmit digital information using electrical signals. The technology was first developed by the company Xerox in the early 1970s and was made commercially available in 1980. Since then, the cable has been through several iterations before arriving at the most current and popular version;
The Cat 6 is able to produce very high internet speeds, with some gigabit Ethernet cables allowing speeds of as much as 1000Mbps. Having said that, Ethernet cables are still unable to offer as much bandwidth as fibre optic options. A Cat 6a cable can relay 600 MHz over a distance of 100m. This is still a high level and is suitable for most people’s network needs. Due to the transmission of data via electronic signals, ethernet cables are susceptible to both interference from nearby electrical devices and interception from hackers. Using shielded cables will help mitigate interference and the use of ethernet switches will improve security. The main limitation of ethernet cables are the distances that they can be laid over. The maximum is just a few hundred feet before they have to be hooked up to a LAN server or outside connection.

Fibre Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are made up of many thin strands of glass that transmit data using light signals. The first fiber optic cable was laid in 1977 in California, but the idea for the technology has been dated as far back as the 1800s. Since then, it has become very popular and synonymous with high-speed internet. There are two kinds of fiber optics, single-mode fiber optic cable and multi-mode fiber optic cable. Single-mode cables use laser lights to transmit data and multi-mode cables use light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Multi-mode cables are significantly thicker than single-mode and are ordinarily used for shorter distances.
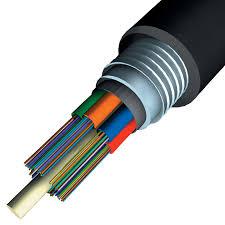
Both single mode and multimode fiber optic cables are generally lighter than Ethernet cables. This is due to the copper wires being much thicker and heavier than the glass strands, which are almost as thin as a single human hair. This means that a greater numbers of wires can be bundled into a single cable, allowing for more efficient cabling. The bandwidth is usually higher than that of Ethernet. Over a distance of 100m, it’s able to relay 1000MHz. Another aspect of fiber optic cabling which is essential in some business areas is that it’s able to function safely in high-voltage locations and in areas where flammable gasses are present. The fire risk of Ethernet cables is very low, but is an important factor to be aware of when selecting data solutions in certain environments.
Conclusion
Despite their differences, both the Ethernet Cables & Fiber Optic Cables are used to transmit data. However, they are used in different areas. Consequently, they differ in terms of cost, structure and properties.





































































