- Related articles
- Cisco S-Class Optics vs. Non-S-Class Optics
- The Difference between Internal Network Card and External Network Card
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG550XG-8F8T-K9-UK Switch
- Cost-effective & Scalable Solution To Cisco CWDM SFPs
- All Cisco SFP-10G-LR’s Information ( Overview, Features, Datasheet PDF, Price, Specificati
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48FD-S Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-47.72's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF350-48MP-K9-EU Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-X9464PX= Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco UCS-FI-6296UP-CH2 Switch

Computer I / O technology is a key technology in the development of high performance computing. Its technical characteristics determine the computer I / O processing power, and then determine the overall performance of the computer and application environment. Fundamentally, I / O technology will restrict the application and development of computer technology both now and in the future, especially in the field of high-end computing. In recent years, with the high-end computing market is increasingly active, the competition of high-performance I / O technology is becoming increasingly fierce.
When the contradiction has becoming increasingly serious between the computer processing power and bus data transfer speed. The new bus technology should be born. Over the past decade, PCI (Peripheral component Interconnect) bus is successful. Its parallel bus execution mechanism is still very advanced now, but its bandwidth has long been showing weakness, PCI bus is divided into six specifications (shown in Table 1), data transfer rate provided by it from 133MBps to 2131MBps. For high-performance products such as 10 Gigabit Ethernet or fiber-optic communications, the data transfer rates of traditional PCI has been unable to meet the requirements.
6 specifications of PCI bus
|
Bus type |
Bus form |
Clock frequency |
Peak bandwidth |
Numbers of slots |
|
PCI32Bits |
parallel |
33MHz |
133MB/s |
4-5 |
|
PCI32Bits |
parallel |
66MHz |
266MB/s |
1-2 |
|
PCI-X 32Bits |
parallel |
66MHz |
266MB/s |
4 |
|
PCI-X 32Bits |
parallel |
133MHz |
533MB/s |
1-2 |
|
PCI-X 32Bits |
parallel |
266MHz |
1066MB/s |
1 |
|
PCI-X 32Bits |
parallel |
533MHz |
2131MB/s |
1 |
|
For a 64-bit bus implementation, all of the above bandwidths are doubled. |
||||
PCI-Express Multi-Link Transfer Rate Table
|
PCI Express Link width |
X1 |
X2 |
X4 |
X8 |
X12 |
X16 |
X32 |
|
Transfer bandwidth (Gb/s) |
5.0 |
10.0 |
20.0 |
40.0 |
60.0 |
80.0 |
160.0 |
|
Effective bandwidth (Gb/s) |
4.0 |
8.0 |
16.0 |
32.0 |
48.0 |
64.0 |
128.0 |
|
8b/10b encoding makes the actual effective data bandwidth loss of 20%, each link contains a pair of send / receive module, each module transmission bandwidth is 2.5Gb/s. |
|||||||
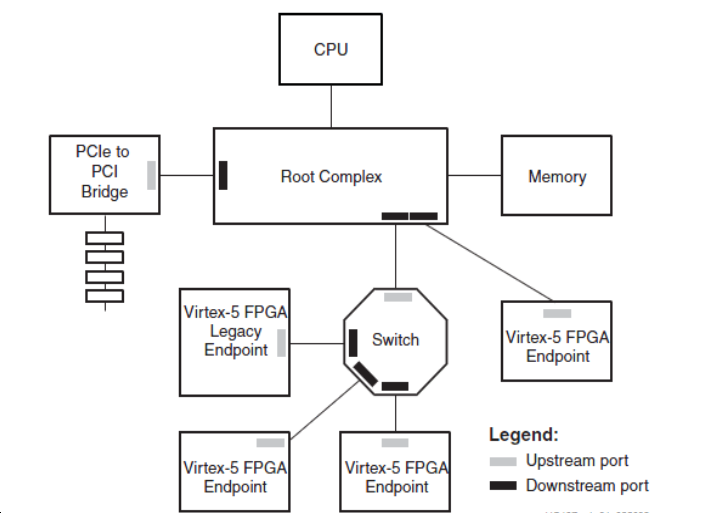
The topology of PCI-Express