- Related articles
- Not confused! How to choose PCI-E and SATA SSD
- All Cisco SFP-OC12-SR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matri
- What Is Network Card PCI Express x4?
- Difference between single-mode and multi-mode SFP
- How to Replace Network Card in Laptop?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560V224PSS-RF Switch
- Cost Effective Compatible Cisco Transceivers
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C4948E-F-E Switch
- All Cisco DS-CWDM-1470's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- The Things You Need to Know about 100GBASE-SR10 Ethernet Standards

This new set of optics does not have unnecessary features for these applications, leading to a more attractive price.
S-class optics are available only in the most common reaches needed in enterprise and data center applications. The following Table shows 10G and 40G S-class PIDs.
S-Class Optics
| Data Rate | Protocol | Media | Reach | Temp. Range | S-Class PID |
| 10G | Ethernet | MMF (duplex) | 300m | Commercial | SFP-10G-SR-S |
| 10G | Ethernet | SMF (duplex) | 10km | Commercial | SFP-10G-LR-S |
| 10G | Ethernet | SMF (duplex) | 40km | Commercial | SFP-10G-ER-S |
| 10G | Ethernet | SMF (duplex) | 80km | Commercial | SFP-10G-ZR-S |
| 40G | Ethernet | MMF (ribbon) | 100m | Commercial | QSFP-40G-SR4-S |
| 40G | Ethernet | SMF (duplex) | 10km | Commercial | QSFP-40G-LR4-S |
SFP-10G-LR-S= Features and Benefits
SFP-10G-LR= Features and Benefits
- Industry’s smallest 10G form factor for greatest density per chassis
- Hot-swappable input/output device that plugs into an Ethernet SFP+ port of a Cisco switch (no need to power down if installing or replacing)
- Supports “pay-as-you-populate” model for investment protection and ease of technology migration
- Digital optical monitoring capability for strong diagnostic capabilities
- Optical interoperability with 10GBASE XENPAK, 10GBASE X2, and 10GBASE XFP interfaces on the same link (the same feature as the SFP-10G-LR-S=’s)
- Cisco quality identification (ID) feature enables a Cisco platform to identify whether the module is certified and tested by Cisco (the same feature as the SFP-10G-LR-S=’s)
SFP-10G-LR-S= and X2-10GB-LR= are compatible as they have same specifications
| Cisco SFP+ | Wavelength (nm) | Cable Type | Core Size (Microns) | Modal Bandwidth (MHz*km) | Cable Distance |
| Cisco SFP-10G-LR-S | 1310 | SMF | G.652 | - | 10km |
| Cisco X2-10GB-LR | 1310 | SMF | G.652 | - | 10km |
Q2: SFP-10G-LR-S vs. SFP-10G-LR. What is (are) the difference(s) between the two optics?In particular what are the “unnecessary features” of the SFP-10G-LR-S? Can they be used in UA to Core deployment?
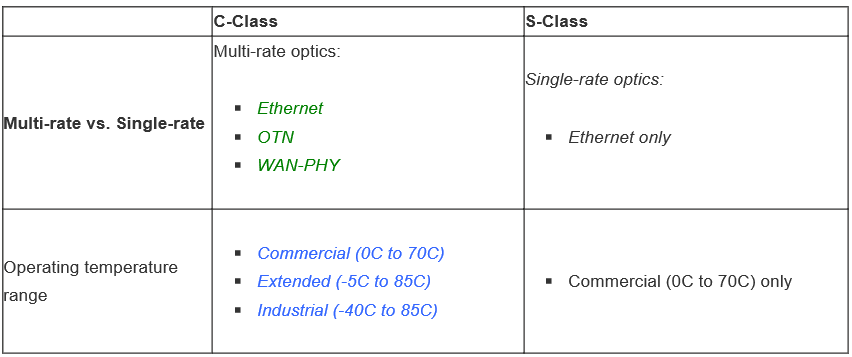
The table below shows the key feature differences for the 10 Gbps S-class vs. C-class.
For UA to core campus applications, S-class is quite suitable.
What’s your experience of using this Cisco S-class Optics and Non-S-Class Optics? Any sharing here will be appreciated.
Cisco S-class optics are with the following features:
1.Cisco S-class optics aren’t TIA certified. However, the non-S-class optics are all compliant to TIA.
2.Cisco S-class optics only have COM (Commercial temperature range: 0~70℃). However, the temperature range of Cisco non-S-class optics can be EXT (Extended temperature range: -5~85℃), IND (Industrial temperature range: -40~85℃) and Storage temperature range (-40~85℃).
3.In terms of protocols, Cisco S-class optics use Ethernet only, they cannot use OTN (Optical Transport Network) or WAN-PHY (Wide Area Network Physics).
4.So far, Cisco S-class optics just have 10G and 40G applications, which is specified for 10G and 40G enterprise and data center.
The Difference Between Cisco S-Class and Non-S-Class Optics
According to Cisco, S-class optics are intended for enterprise and data center 10G and 40G applications This new set of optics does not display several unnecessary features for these applications, bringing about a more attractive price. That explains why S-class optic is cheaper than Non-S-class. Meanwhile, Cisco announced that S-class optics are available only in the most common reaches needed in enterprise and data center applications. “unnecessary features” and “the most common reaches” really made buyers who want to have a try puzzled.
Considering the appealing price, many users who are enamored of Cisco optics prefer to choose S-class optics. At the same time, consumers may ask some questions. What are the unnecessary features? When should we use S-class optics? ... Unfortunately, there is no special document yet for them. Even the datasheet is unable to give answers. But don’t feel at a loss. Here are some helpful experiences for you.
S-class is Ethernet only, not OTN (Optical Transport Network) nor WAN-PHY (Wide Area Network Physics). What’s more, S-class is not compliant with TAA. On the other hand, S-class and Non-S-class optics show differences in temperature ranges. Thus, if you are an enterprise or data center environment that doesn’t need to go on any special distant signal transmission, doesn’t allow for temperature tolerances, or other special features, S-Class optics should be suitable for you. In fact, there may be more unknown differences. But there is no doubt that the differences are not the main concerns of Cisco when they introduced the S-class. The lower price serves as the main selling point, and there is no problem in compatibility. As the third-party compatible optics market develops rapidly, S-class optics are as trendy as Cisco expected. For instance, you may prefer to buy a SFP-10G-SR compatible optic transceiver in Fiberstore instead of in Cisco when Fiberstore offers a much lower price at 18 dollars than 500 dollars at Cisco. Undoubtedly, you can enjoy the same functions and performance the Cisco SFP-10G-SR optics have.
Is Cisco S-class optics compatible with non s-class optics?
According to Cisco, S-class optics are designed for enterprise and data center 10G and 40G applications (don’t scale down to 1GbE). It announces that both S-class and non S-class optics feature optical interoperability with 10GBASE XENPAK, 10GBASE X2, and 10GBASE XFP interfaces on the same link. From this, we can judge that Cisco S-class optics is compatible with non s-class optics as they have the same specifications. But you need to keep in mind that S-class and non-S-class optics are with different temperature ranges. Thus, if you are an enterprise or datacenter environment that doesn’t need any special long distance, temperature tolerances, or other special features, S-Class optics are cheaper and should be just fine for you. But there is no doubt that the differences are not the main concerns of Cisco when they introduced the S-class. The low price is the main selling point, and the compatibility is no problem.
What do Cisco S-Class Optics and Non S-Class Optics represent respectively?
What is Cisco S-Class Optics ?
Cisco S-Class Optics refer to a specific range of optical transceivers designed by Cisco for enterprise and data center networking applications. These optics are a cost-effective solution tailored to specific application needs, particularly where advanced optical features are not required. They are intended for use in enterprise networks, data centers, and other environments where high-speed data transmission over fiber optic cables is needed, but without the full range of features or the extended reach provided by more advanced and expensive optical modules.
Key characteristics of Cisco S-Class Optics include:
-
Targeted Applications: S-Class optics are optimized for common use cases in enterprise and data center environments. They are typically used for short to medium distances where advanced features such as long-haul transmission are not necessary.
-
Cost-Effective: These modules are more budget-friendly compared to their full-feature counterparts. They are designed for environments where cost savings are a priority without sacrificing quality or reliability.
-
Data Rate and Reach: S-Class optics support various data rates such as 1G, 10G, 40G, and even 100G, suitable for different levels of network throughput. They also offer varying reaches (distance capabilities), typically optimized for shorter ranges common in enterprise and data center applications.
-
Limited Features: While providing the essential functions required for enterprise-level performance, S-Class optics may not include advanced features found in more expensive transceivers, such as extended temperature ranges or support for longer distances.
-
Compatibility: Cisco S-Class optics are designed to be compatible with Cisco networking equipment. However, like all Cisco optics, it’s important to ensure compatibility with specific devices and systems before purchase.
-
Reliability: Despite being more cost-effective, these optics are still designed to meet Cisco’s quality and reliability standards, ensuring stable and reliable network performance.
-
Standard Form Factors: They are available in standard form factors like SFP, SFP+, QSFP, etc., making them interchangeable with other Cisco optics or compatible third-party transceivers.
Cisco S-Class optics are particularly well-suited for cost-sensitive applications within controlled environments that do not require the full feature set of higher-end transceivers. They provide an effective solution for businesses looking to balance performance needs with budget constraints.
What is Non-S-Class Optics?
Non-S-Class Optics in the context of Cisco's product offerings refer to the standard or regular line of optical transceivers that Cisco manufactures. These are the more feature-rich, versatile, and often more expensive counterparts to the S-Class optics. While S-Class optics are designed for cost-effectiveness and specific use cases (typically within enterprise and data center environments), Non-S-Class optics offer a broader range of features and capabilities suitable for a wider array of applications, including those requiring extended reach, enhanced performance, and advanced functionalities.
Key characteristics of Non-S-Class Optics include:
-
Advanced Features: Unlike S-Class optics, the Non-S-Class optics often include advanced features like monitoring capabilities, longer transmission distances, and support for a wider range of wavelengths.
-
Broader Application Range: They are suitable for a wider range of applications, including long-haul transmissions, metropolitan area networks (MANs), and environments requiring rugged specifications like extended temperature ranges.
-
Higher Cost: Due to the additional features and capabilities, these optics are generally more expensive than S-Class optics.
-
Various Data Rates and Distances: They support a wide range of data rates, from 1G up to 100G and beyond, and can cater to various transmission distances, from short-range to long-haul applications.
-
Compatibility: While designed for Cisco equipment, these optics are often compatible with a wide range of devices and network environments, making them versatile for different networking needs.
-
Reliability and Quality: Cisco's Non-S-Class optics are known for high performance, quality, and reliability, meeting stringent industry standards and requirements.
-
Standard and Specialized Form Factors: They are available in common form factors like SFP, SFP+, QSFP, CFP, and others, including specialized form factors for specific applications.
In summary, Non-S-Class Optics are ideal for businesses and network operators who need high-performance, long-distance, and versatile optical solutions for a variety of networking environments, including those that are more demanding in terms of technical specifications and environmental conditions. They represent the full spectrum of Cisco’s optical transceiver offerings, excluding the more narrowly focused and cost-effective S-Class range.
Precautions for purchasing Cisco S-Class Optics and Non-S-Class Optics:
When purchasing Cisco S-Class Optics and Non-S-Class Optics, it's important to consider several factors to ensure you are selecting the right modules for your network needs. Here are some key precautions and considerations:
-
Understand Your Requirements:
-
S-Class Opticsare typically designed for cost-sensitive, enterprise, and data center applications where advanced features are not required.
-
Non-S-Class Opticsoffer a wider range of features and are suitable for more demanding applications, including longer distance transmissions and specialized environments.
-
-
Compatibility Check:
-
Ensure the optics are compatible with your existing Cisco equipment, such as switches and routers.
-
Check the module interface and the fiber type (single-mode or multi-mode) required for your network.
-
-
Performance Requirements:
-
S-Class Optics are generally sufficient for basic networking requirements.
-
Non-S-Class Optics provide enhanced performance and features, which may be necessary for specific applications.
-
-
Budget Considerations:
-
S-Class Optics are more budget-friendly and are a good choice for cost-constrained projects.
-
Non-S-Class Optics are more expensive but offer additional functionalities and better performance.
-
-
Distance and Data Rate Needs:
-
Select optics based on the required data transmission rate and the distance over which the signal needs to be carried.
-
-
Quality and Reliability:
-
Opt for reliable suppliers to ensure the quality and durability of the optics.
-
Consider the warranty and support options available for the products.
-
-
Environmental Factors:
-
If your network operates in challenging environmental conditions, ensure the optics you choose are rated for such use.
-
-
Future-Proofing:
-
Consider the potential future expansion of your network and choose optics that can accommodate future growth and technological advancements.
-
-
Certifications and Standards Compliance:
-
Ensure that the optics comply with relevant industry standards and certifications, such as IEEE, MSA, RoHS, etc.
-
-
Installation and Maintenance:
-
Consider the ease of installation and the maintenance requirements of the optics.
-
Determine if you need technical support for installation and troubleshooting.
-
Always align your choice with your specific network requirements, operational conditions, and budget constraints. It's essential to balance cost with the need for performance and future scalability.





















































