- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-CBS3125G-S Switch
- All Cisco DS-SFP-GE-T's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matri
- The Things You Need to Know about 1000BASE-X Ethernet Standards
- All Cisco GLC-BX40-U-I's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- The Things You Need to Know about 10GBASE-T Ethernet Standards
- All Cisco AJ906A's information (Specs, Datasheet PDF)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960C-8TC-L Switch
- What is GPON and EPON
- What Is External Ethernet Card?
- What Is GYXTC8S Optical Fiber Cable?

Network is everywhere in modern society. And it can be classified in many ways in terms of different information carried. But also it is generally categorized as two types: passive network and active network.
Passive network, refers to no electric drive apparatus or components used in network for transmitting signals. Relatively, active network means electric drive apparatus or components joining in network to transmit signals. In addition to the difference in their concepts, they also differ in other ways. This article will give a clear introduction of them by following concepts.
Passive Copper Network
There are various types of passive copper network, household cable TV network is one of the common passive copper networks. In the cable TV network, service provider conveys the TV signals to users’ houses via coaxial cables. If there are multiple TV sets in a user’s house, it’s necessary to use PLC splitter to distribute the signal in coaxial cable into multiple ones, thus to ensure each TV set have signal. The used PLC splitter is a passive optical component, which normally has one input port and 2/3/4 output ports as following shown.
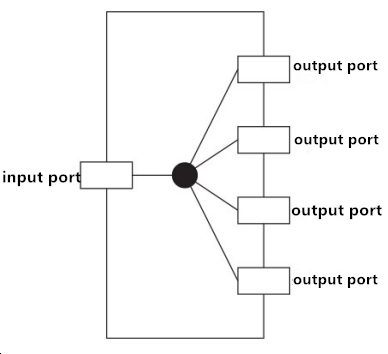
In above networks, TV signals are mostly weakened due to shunting. What’s more, if there is much more shunting, it is more likely to cause each TV set out of normal work, in this case, active cable TV network is effective.
Active Copper Network
Likewise, there are also multiple categories of active copper network. What is different with passive copper network, is some active equipment added in active copper network like amplifier which is used to amplify the damped TV signal so as to ensure signals can transmit over a long distance. Active equipment makes the structure of active copper network more complicated, and makes network more rely on themselves. In other words, the whole active copper network would break down as long as there is any active equipment out of work.
Passive Optical Network
Passive optical network is quite similar with the passive copper network, the difference is fiber optic cable used in passive optical network instead of coaxial cable. In any kind of passive optical networks, coupler plays an important part which takes charge of distributing or coupling optical signals. Below is a common kind of structure of seven ports coupler.
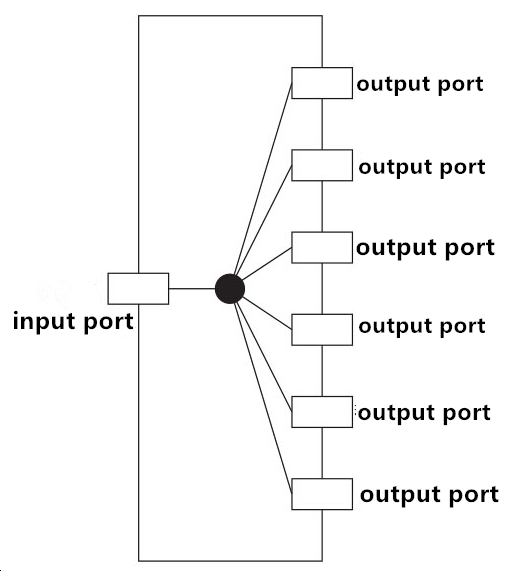
Most of the couplers now are capable of two-way operation, which means not only distributing and also coupling optical signals. Moreover, any port can work as input port and also output port. While in the passive optical network, there is an exclusive equipment called optical splitter used to distribute light signals. Same with the passive cable TV, there exists a certain of loss in the course of optical signals transmitting from input port to output port. Therefore, optical signal is normally distributed into no more than 32 shunts in the passive optical network.
Active Optical Network
Active optical network is very similar with active cable TV, the different point lies in the switch instead of amplifier connected with fiber optic cable. Switch is an active equipment used to forward data to each end user. This network is able to avoid loss of optical signals, but it has much more complicated structure, what’s more, it needs power supply. That is, once switch is out of power or breaks down, there will be no data signals transmitted to users.
Conclusion
This article gives detailed introduction to passive copper network, active copper network, passive optical network and active optical network. These different networks have their own advantages and disadvantages, knowing well about them will be greatly helpful for network deployment as well as selection based on actual demands and application.





















































