- Related articles
- The difference between DWDM and OTN
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-52.52's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- Used in 10GBASE-USR Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- Buy Cisco GLC-SX-MM SFP For Fiber Optic Networks
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG250-26P-K9-EU Switch
- What is the difference between LX and SX in transceiver?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF250-48-K9-UK Switch
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-40.56's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- What Is ADSS Optical Fiber Cable?
- Cisco SFP vs. GBIC vs. XFP vs. SFP Plus

Definition:
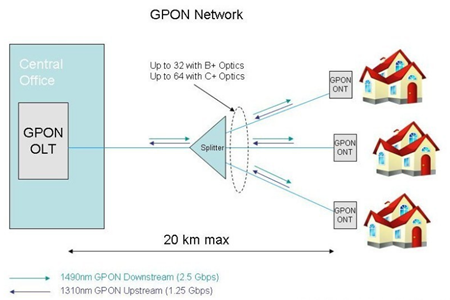
GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Networks. GPON is defined by ITU-T recommendation series G.984.1 through G.984.6. GPON can transport not only Ethernet, but also ATM and TDM (PSTN, ISDN, E1 and E3) traffic. GPON network consists of mainly two active transmission equipments, namely- Optical Line Termination (OLT) and Optical Network Unit (ONU) or Optical Network Termination (ONT). GPON supports triple-play services, high-bandwidth, long reach (upto 20km), etc.
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) is the rival activity to GPON which uses Ethernet packets instead of ATM cells. GEPON uses 1 gigabit per second upstream and downstream rates.
What Is Difference Between GPON and EPON
GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) is based on the TU-TG.984.x standard for the new generations of broadband passive optical access. Compared with the other PON standards, GPON provides the unprecedented high bandwidth downlink rate of up to 2.5 Gbit/s, the asymmetric features better adapt to the broadband data services market. It provides the QoS full business protection, at the same time carries ATM cells and (or) GEM frame, the good service level, the ability to support QoS assurance and service access. Carrying GEM frame, TDM traffic can be mapped to the GEM frame, 8kHz using a standard frame able to support TDM services. As a carrier-grade technology standards, GPON also provides access network level protection mechanism and full OAM functions. GPON is widely deployed in FTTH networks. It can develop into two directions which is 10 GPON and WDM-PON.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) developed another newer PON standard. Based on the Ethernet standard 802.3, EPON 802.3ah specifies a similar passive network with a range of up to 20 km. It uses WDM with the same optical frequencies as GPON and TDMA. The raw line data rate is 1.25 Gbits/s in both the downstream and upstream directions. You will sometimes hear the network referred to as Gigabit Ethernet PON or GEPON.
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) is the rival activity to GPON which uses Ethernet packets instead of ATM cells. GEPON uses 1 gigabit per second upstream and downstream rates. It is a fast Ethernet over PONs which are point to multipoint to the premises (FTTP) or FTTH architecture in which single optical fiber is used to serve multiple premises or users. EPON is an emerging broadband access technologies, through a single fiber-optic access systems, to access the data, voice and video service, and it has a good economy.
Conclusion:
EPON and GPON are popular versions of passive optical networks (PONs). These short-haul networks of fiber-optical cable are used for Internet access, voice over Internet protocol (VoIP), and digital TV delivery in metropolitan areas. Other uses include backhaul connections for cellular basestations, Wi-Fi hotspots, and even distributed antenna systems (DAS). The primary differences between them lie in the protocols used for downstream and upstream communications.
Please click to check more related concepts:
| Telecommunications technology | IEEE Standard | Transceiver wavelength |