- Related articles
- How to Configure the Dual Ethernet Adapter?
- The difference between TDM and WDM
- All Cisco SFP-10G-LR-X's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3850-24XS-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48PS-E Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-C9396PX= Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48FQ-E Switch
- What 802.3 Standard Originally Defined Poe Functionality?
- What is PCI Wireless Ethernet Adapter?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N3K-C3172TQ-32T Switch

Introduction
Fibre Optic Cable is made of different components that are known as properties. Different Fibre Optic Cables have different properties depending on its purpose and therefore is very important to discuss the properties of various fiber optic cable based on the application and structure. However, there are common properties of the Fibre Optic Cable as highlighted below.
Overview of Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cables consist of multiple strands of optic fibers, hairlike strands of pure glass designed to transmit light. When hundreds or thousands of these strands are put together, they are able to transmit waves of light up to 60 miles. Electrical signals, such as television, voice or data signals, are converted to high-quality optical signals using an optical transmitter and sent at the speed of light, producing a fast, high-quality method of data transmission.
Structure of Fiber Optic Cable
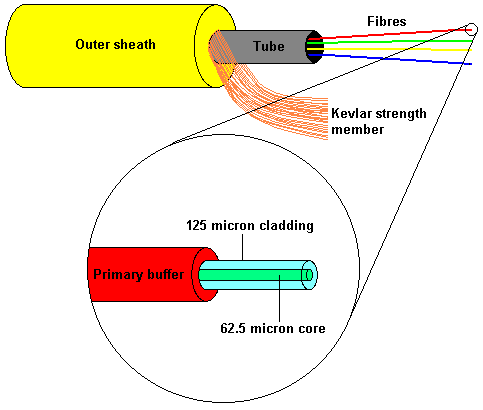
Optical fibers consist of a pure glass core surrounded by multiple layers. The first layer is a reflective cladding, which acts like a long, flexible mirror, reflecting light along the length of the glass core. This principle is known as total internal reflection. Next, an outer protective layer known as a “buffer” coating is applied to shield the fiber from damage and moisture. Bundles of these optical fibers are then enclosed by a strengthening layer of aramid yarn, and finally a plastic "jacket" to create a complete fiber optic cable.
Applications of Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cables are now used as the predominant form of transmission in communications, cable television and the Internet. The continuous development of Internet technology has only been possible through the use of fiber optics. The latest development is a direct Internet connection, called “fiber to the home” (FTTH), which gives superior speed and connection quality. FTTH services are still only very limited because the cost compared to standard Internet connections is very high.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cables provide superior quality transmissions compared to satellite and copper systems. Long distance telecommunications using satellite technology are prone to weak connections and echoing, which are greatly improved when optic fiber is used. Copper cables used for electrical transmission are much larger and heavier, have a much lower bandwidth capacity, are affected by electromagnetic interference and are prone to higher rates of loss over long distances. These problems are virtually eliminated with the use of fiber optic technology.
Conclusion
The properties enable the fiber optic cable to perform perfectly in its role. For instance, fiber optic cable which is used to transmit high voltage have similar properties, those made to be used in cold areas have similar properties while those made to be used in watery areas have similar properties. Depending on the properties of fiber optic cable, it performs up to standards.





































































