- Related articles
- All Cisco SFP-10GE-SR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matri
- What Is GYDXTW Fiber Optic Cable?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960XR-24TD-I Switch
- All Cisco XENPAK-10GB-SR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- All Cisco SFP-10G-ER's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix
- All Cisco GLC-FE-100LX-RGD’s Information (Overview, Features, Datasheet PDF, Price, Specif
- Used in 10GBASE-ER Standard optical transceiver models
- EoS and EoL News for the Cisco 10GBASE DWDM XENPAK Modules
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48FS-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-24PD-E Switch

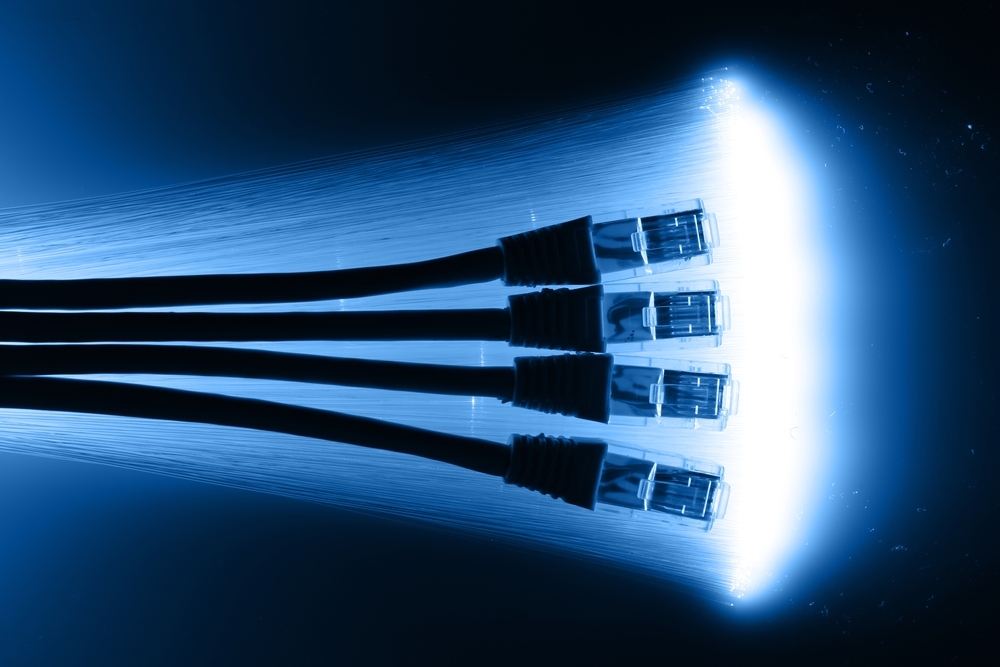
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and metropolitan area networks (MANs). In order to achieve barrier-free communication in industry, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) proposed the first criterion to standardize LANs in 1980. Later on, owing to the fast development of Ethernet, lots of standards have been put forward to adapt to different changes. Nowadays, the Ethernet standards can be mainly classified to eight parts and they are early Ethernet standards, 10 Mbps Ethernet standards, Fast Ethernet standards, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) standards, 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 GbE) standard, 25 Gigabit Ethernet standards, 40 Gigabit Ethernet standards and 100 Gigabit Ethernet (100 GbE) standards. These Ethernet standards for optical fiber networking will be briefly introduced in the following table.

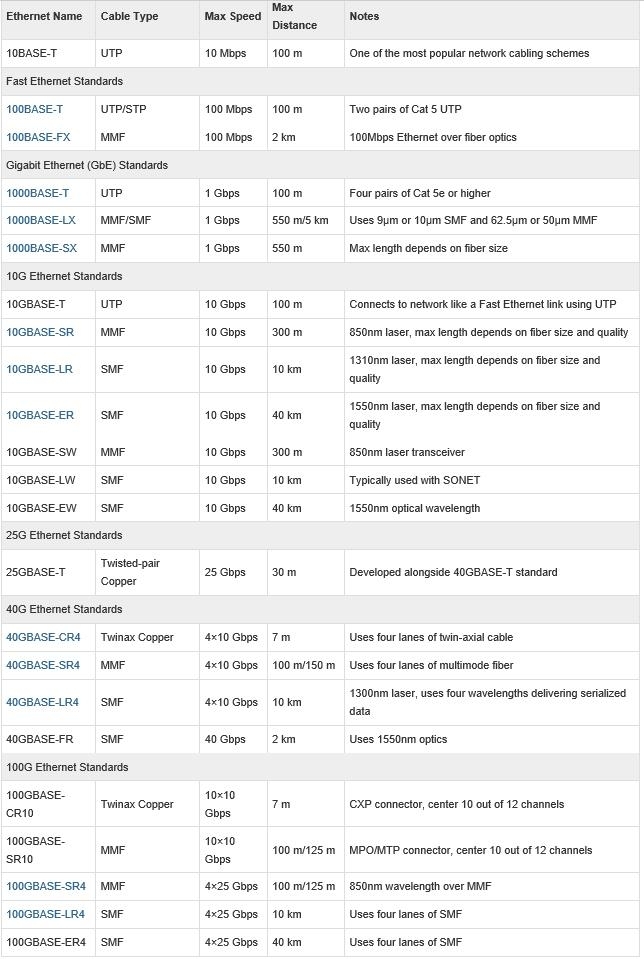
Conclusion
From the introduction of these frequently-used Ethernet standards in optical fiber networking, it is clear to see that these criteria define every subtle aspect so as to create an environment that is accessible to a more convenient communication among users. Without the fiber optic transceivers, it is hard to put the theory into practical use. However, the original transceivers are very expensive. Luckily, cozlink.com provides all the compatible transceivers such as 100BASE SFP, 1000BASE SFP, 10G SFP+, 25G SFP28, 40G QSFP+ , 100G CFP and 100G QSFP28 for manufacturers like Cisco, Finisar and so on. Please visit cozlink.com for more information.
Ethernet Standards
Ethernet standards define several elements that enable transmission of data over LANs. Ethernet refers to both the original DIX Ethernet and IEEE’s 802.3 specifications. Data link layer protocols were discussed in the Ethernet Basics lesson. This lesson focuses on the physical layer protocols, comparing various Ethernet signaling devices and physical media.
The IEEE 802.3 Ethernet CSMA/CD architecture is based on the original DIX format established in the early 1980s by Digital, Intel, and Xerox. Ethernet employs physical/logical bus and physical star/logical bus topology. Current Ethernet networks use a combination of copper and fiber optic cabling. The IEEE 802.3 cabling standards recommend the specifications for cable types, lengths, signaling devices, and so on. Ethernet standards change as the demands and needs of networking change. With each change, new protocols are established.
The naming schemes for each of the Ethernet standards assist with the identification of transmission type and cable used. For example, 10BASE5 is a 10 Mbs baseband transmission with a 500 meter distance limitation and 100BASE-T is a 100 Mbs baseband transmission using category 5 UTP cabling.





















































