- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960-48TC-L Switch
- All Cisco ONS-SC+-10G-ER's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- Ways to Use PCMCIA Network Card Slot?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-24PD-L Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-48LPD-L Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560E-48TD-S Switch
- Cisco Catalyst 6500 WS-X6816-GBIC Expansion Module 16-Port Gigabit Ethernet
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960X-24TD-L Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-2000-8TC-G-L Switch
- All Cisco ONS-SE-2G-S1's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr

Definition
A networking standard that supports data transfer rates up to 100 Mbps (100 megabits per second). 100base t is based on the older Ethernet standard. Because it is 10 times faster than Ethernet, it is often referred to as Fast Ethernet. Officially, the 100BASE T standard is IEEE 802.3u.
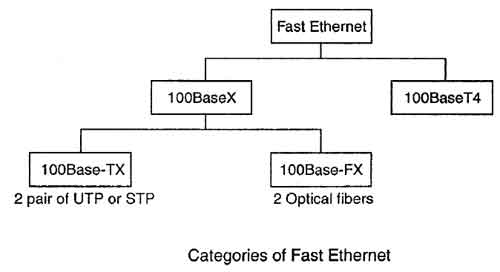
A type of standard for implementing Fast Ethernet networks. 100BASE TX is based on 802.3u, which is an extension of the 802.3 specifications of Project 802 developed by the IEEE. 100BASE T and a related standard, 100BASE TFS, are sometimes collectively referred to as 100BASE X.
Difference between 100BASE T and 100BASE TX
Actually 100base t is the generic name assigned to FastEthernet technology. Again 100base t is of three types.
1. 100BASE TX
2. 100BASE T4
3. 100BASE FX
100BASE TX use 4 wires, while 100BASE T4 uses 8 wires. 100BASE FX uses 2 strands of MMF.
100BASE TX requires that you use Cat5 STP cable.
100BASE T4 can be run on Cat3, 4 or 5 UTP cable.
100BASE T4
100BASE T4 was an early implementation of Fast Ethernet. It requires four twisted copper pairs, but those pairs were only required to be category 3 rather than the category 5 required by tx. One pair is reserved for transmit, one for receive, and the remaining two will switch direction as negotiated. A very unusual 8B6T code is used to convert 8 data bits into 6 base-3 digits (the signal shaping is possible as there are nearly three times as many 6-digit base-3 numbers as there are 8-digit base-2 numbers). The two resulting 3-digit base-3 symbols are sent in parallel over 3 pairs using 3-level plus-amplitude modulation (PAM-3). The fact that 3 pairs are used to transmit in each direction makes 100BASE T4inherently half-duplex. This standard can be implemented with CAT 3, 4, 5 UTP cables, or STP if needed against interference. Maximum distance is limited to 100 meters. 100BASE T4 was not widely adopted but the technology developed for it is used in 1000BASE T.
100BASE FX
100BASE FX is a version of Fast Ethernet over optical fiber. It uses a 1300 nm near-infrared (NIR) light wavelength transmitted via two strands of optical fiber, one for receive (RX) and the other for transmit (TX). Maximum length is 412 meters (1,350 ft) for half-duplex connections (to ensure collisions are detected), and 2 kilometers (6,600 ft) for full-duplex over multi-mode optical fiber. 100BASE FX uses the same 4B5B encoding and NRZI line code that 100BASE TX does. 100BASE FXshould use SC, ST, LC, MTRJ or MIC connector with SC being the preferred option.