- Related articles
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48FS-L Switch
- Applicable to 10GBASE-LRL Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-X9464TX= Switch
- The Things You Need to Know about 100GBASE-CR4 Ethernet Standards
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-2000-8TC-G-E Switch
- All Cisco CWDM-SFP-1570's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- All Cisco MFELX1's information (Overview, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SF302-08PP-K9-EU Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750X-12S-S Switch
- What Is Multiport Network Card

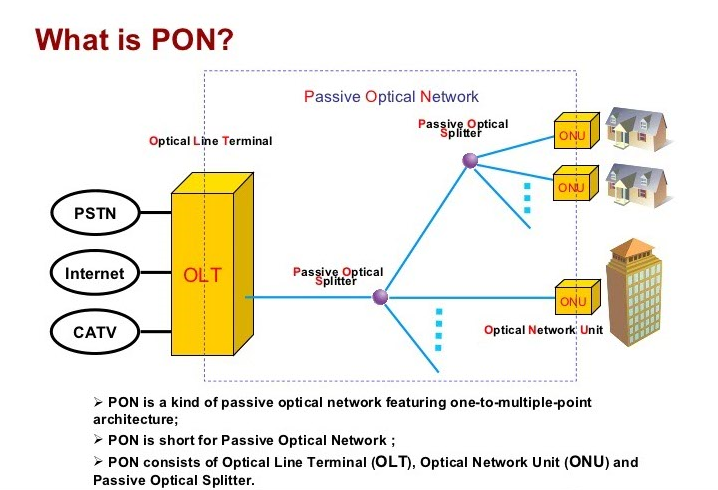
PON is Passive Optical Network.
This is a telecommunications technology that implements a point-to-multi-point architecture, in which unpowered Fiber Optic Splitters are used to enable a single optical fiber to serve multiple end-points such as customers, without having to provision individual fibers between the hub and customer.
A PON consists of an optical line terminal (OLT) at the service provider's central office (hub) and a number of optical network units (ONUs) or Optical Network Terminals (ONTs), near end users. A PON reduces the amount of fiber and central office equipment required compared with point-to-point architectures. A passive optical network is a form of fiber-optic access network.
In most cases, PON downstream signals are broadcast to all premises sharing multiple fibers. Encryption can prevent eavesdropping. PON upstream signals are combined using a multiple access protocol, usually time division multiple access (TDMA).
In 2004, the Ethernet PON (EPON or GEPON) standard 802.3ah-2004 was ratified as part of the Ethernet in the first mile project of the IEEE 802.3. EPON uses standard 802.3 Ethernet frames with symmetric 1 gigabit per second upstream and downstream rates. EPON is applicable for data-centric networks, as well as full-service voice, data and video networks. 10 Gbit/s EPON or 10G-EPON was ratified as an amendment IEEE 802.3av to IEEE 802.3. 10G-EPON supports 10/1 Gbit/s. The downstream wavelength plan support simultaneous operation of 10 Gbit/s on one wavelength and 1 Gbit/s on a separate wavelength for operation of IEEE 802.3av and IEEE 802.3ah on the same PON concurrently.
There are currently over 40 million installed EPON ports making it the most widely deployed PON technology globally. EPON is also the foundation for cable operators’ business services as part of the DOCSIS Provisioning of EPON (DPoE) specifications.
A PON takes advantage of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), using one wavelength for downstream traffic and another for upstream traffic on a single mode fiber (ITU-T G.652). BPON, EPON, GEPON, and GPON have the same basic wavelength plan and use the 1,490 nanometer (nm) wavelength for downstream traffic and 1,310 nm wavelength for upstream traffic. 1,550 nm is reserved for optional overlay services, typically RF (analog) video.
A PON consists of a central office node, called an optical line terminal (OLT), one or more user nodes, called optical network units (ONUs) or optical network terminals (ONTs), and the fibers and splitters between them, called the optical distribution network (ODN). “ONT” is an ITU-T term to describe a single-tenant ONU. In multiple-tenant units, the ONU may be bridged to a customer premises device within the individual dwelling unit using technologies such as Ethernet over twisted pair, G.hn (a high-speed ITU-T standard that can operate over any existing home wiring - power lines, phone lines and coaxial cables) or DSL. An ONU is a device that terminates the PON and presents customer service interfaces to the user. Some ONUs implement a separate subscriber unit to provide services such as telephony, Ethernet data, or video.
Difference between EPON and GPON
EPON and GPON are popular versions of passive optical networks (PONs).These short-haul networks of fiber-optical cable are used for Internet access,voice over Internet protocol (VoIP),and digital TV delivery in metropolitan areas.Other uses include backhaul connections for cellular basestations,Wi-Fi hotspots, and even distributed antenna systems (DAS). The primary differences between them lie in the protocols used for downstream and upstream communications.
If you need a components for your PON network Cozlink is the place for you. They offer innovative decisions for your needs at the best price. So do not hesitate to take a look at all of their products and to contact us.
Please click to check more related concepts:
| Types | Protocol | Application |