- Related articles
- Difference between GLC-T and SFP-GE-T
- Cisco SFP vs. GBIC vs. XFP vs. SFP Plus
- Applicable to 40GBASE-LX4 Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- What is DWDM in networking?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-2000-8TC-G-L Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SLM2048PT-UK-RF Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750G-48TS-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960-24PC-S Switch
- Cisco GLC T SFP Transceiver
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560C-8PC-S Switch

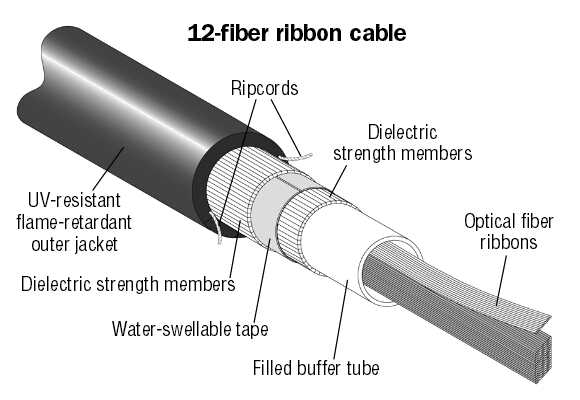
With the rapid development of LAN and optical fiber access network, the era of the high-density fiber-optic network is coming, large-core optical cables including ribbon fiber optic cable have been gradually used in the construction of communication network.
Application of ribbon optical fiber uses multi-channel welding technology, which can save laying costs and bring better economic benefits, for example, in the FTTC access network project, single-channel fiber welding costs accounts for 9%, while the use of ribbon optical fiber multi-channel welding will be able to save 60% of the welding cost.
There are many differences between the ribbon optical fiber multi-channel welding and the single-channel welding. In order to ensure the low welding loss, the Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (OTDR) is mostly used for two-way monitoring in the single-channel welding. However, in the multi-channel welding, there is a lot of fiber cores, blindly splicing is adopted instead of the optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR).
The advantages of multi-channel welding contributed to the development of passive positioning welding technology which is able to determine the loss of welding by the geometrical dimension of fiber. Therefore, the geometrical dimension of the fiber directly affects the actual welding capacity, in which the fiber warpage, fiber core concentricity, and cladding diameter are the main influencers.
1. Fiber warpage
Fiber warpage refers to the bending degree of the fiber along a specific length. Excessive fiber warpage can cause excessive deviations in the multi- channel splicing machine, resulting in high welding losses.
Optical fiber warpage can measure the lateral distance X and the fiber offset δf by side-view microscopy.
2. The core-cladding concentricity
The core is not in the center of the cladding and will cause core positioning errors in a variety of welding machines and connectors, improving this parameter will be extremely significant to improve the quality of fiber fusion and to reduce the welding loss.
3. Cladding diameter
The inconsistency of the cladding will cause core misalignment in the passive positioning of the weld and the connector.
Fiber splice loss includes two types, one is the inherent loss caused by the optical fiber characteristics, but by the welding process caused by external wear and tear, that is, to strictly maintain the good performance of welding equipment and according to the provisions of the normal operation of the program in order to ensure the dissolution quality of fiber.
Procedure and related precautions of ribbon fiber splicing
1. Pull out the ribbon fiber from the cable and process it
A. Remove its loose tube which the ribbon fiber is about 1M;
B. Use a neutral solvent to remove the cable cream;
C. Make the ribbon fiber placed in the ribbon fixture, keep it clean, good grip.
Optical band fixture needs to be chosen appropriate, its width and thickness should be based on the number of ribbon fiber core and ribbon fiber processing methods. The thickness of the ribbon-like optical fiber is about 400 microns, and the thickness of the ribbon-like ribbon fiber is about 300 microns. The length of the ribbon-like optical fiber in the optical tape fixture is generally 30mm, ensuring that after cutting, there is 10mm bare fiber.
2. Ribbon optical fiber stripping procedures
The base material and the optical fiber coating of the ribbon optical fiber are removed by the thermal peeling method:
A. In the ribbon fixture in the ribbon fiber into the hot stripper (also known as heating peeling clamp) within 5-8s, the length of time according to the ribbon fiber and the optical fiber coating may be;
B. The fiber is stripped, the fiber surface can be found in a small amount of the remaining coating material, the application of cotton-free paper towels and more than 99% purity of alcohol for cleaning.
3. Ribbon fiber cutting
Fiber cutting quality is an important factor in ensuring a low loss of welding. To maintain the good performance of the cutting knife, the v-groove and the fiber surface of the cutting blade must be kept very clean. After cutting the fiber end face angle <1 °, cutting length 10mm.
4. Ribbon fiber welding process
A. Ribbon fiber placed in the v-slot, pre-melting arc burned fiber surface impurities, check the fiber end;
B. Welding;
C. Check and test the weld strength of the splicer before proceeding, find the best continuity condition, and show the weld loss estimate (the estimate is based on the distance between the fiber end face, the fiber end angle and the outer diameter of the fiber cladding).
5. The protection after welding mechanical
A. The sleeve will be placed in the welding point of the casing into the welding machine attached to the heater tank, the casing of the support rod should be placed in the bottom;
B. Will be reinforced through the welding point after the protection of fiber installed in the connector box.
Conclusion
In short, in order to achieve low loss in multi-channel welding, we need to use excellent optical properties of the fiber, and in strict accordance with the provisions of procedures to ensure that the fiber surface and face treatment is good. At the same time, we must pay attention to fiber, the environment and the cleanliness of the instrument, to maintain good equipment performance.