- Related articles
- What is 10Gb Network Card?
- All Cisco XENPAK-10GB-SR's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- All Cisco GLC-FE-T-I's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix
- Types of network card speed
- Optical Transceivers for WS-C4948E Switch
- All Cisco GLC-ZX-SM's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-24PD-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48FWQ-S Switch
- The Things You Need to Know about 1000BASE-SR Ethernet Standards
- All Cisco QSFP-40G-CSR4's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat

Introduction
Generally, the Fiber Optic Cable is made of various components that are critical in defining its structure. However, there are basic components which are common in every Fiber Optic Cable. Despite the structure of the Fiber Optic Cable, the basic components are similar. Therefore, you should have knowledge of the basic components as an engineer or technician.
Discussion
Optical components include lasers, splitters, multiplexers, switches, photodetectors and other receiver types, silicon optical benches, and other building blocks of fiber optic communications modules, line cards, and systems. You find new product announcements and tutorial information on this page.
Basic structure of an optical fiber
The basic structure of an optical fiber consists of three parts; the core, the cladding, and the coating or buffer. The basic structure of an optical fiber is shown in figure 2-9. The core is a cylindrical rod of dielectric material. Dielectric material conducts no electricity. Light propagates mainly along the core of the fiber. The core is generally made of glass. The core is described as having a radius of (a) and an index of refraction n1. The core is surrounded by a layer of material called the cladding. Even though light will propagate along the fiber core without the layer of cladding material, the cladding does perform some necessary functions.
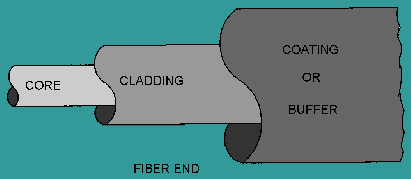
The cladding layer is made of a dielectric material with an index of refraction n2. The index of refraction of the cladding material is less than that of the core material. The cladding is generally made of glass or plastic. The cladding performs the following functions;
Reduces loss of light from the core into the surrounding air
Reduces scattering loss at the surface of the core
Protects the fiber from absorbing surface contaminants
Adds mechanical strength
For extra protection, the cladding is enclosed in an additional layer called the coating or buffer. The coating or buffer is a layer of material used to protect an optical fiber from physical damage. The material used for a buffer is a type of plastic. The buffer is elastic in nature and prevents abrasions. The buffer also prevents the optical fiber from scattering losses caused by microbeads. Microbends occur when an optical fiber is placed on a rough and distorted surface.
Conclusion
The basic components of Fiber Optic Cable include the central core, the covering sheath and other more. For the sake of identification, you should master those common components of Fiber Optic Cable otherwise, you will get confused when purchasing.





















































