- Related articles
- All Cisco CWDM-SFP-1470's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- What type of cabling Ethernet 100BASE FX networks used
- The Difference between SATA, PCIe and NVMe
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG500-28MPP-K9-G5 Switch
- All Cisco CFP-40G-LR4's information (Overview, List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibi
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG500-52MP-K9-G5 Switch
- How to Identify Fiber Optic Cable?
- What is CSFP transceiver?
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48PQ-E Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N3K-C3064PQ-10GX Switch

Compared with copper network, fiber optical network has many obvious advantages that make it be the primary choice for almost all people and applications. In optical network based on optic fiber, fiber optic cable is an essential part as a transmission medium. It supports longer distance up to hundreds of kilometers than which traditional copper wire or coaxial cable does.
While although signal is able to be transmitted over a longer distance, it is inevitable that signal would get a loss over a long distance. Therefore, many people would rather select a relatively shorter distance to ensure the signal quality than accept a long distance with part of signal loss. In addition to signal loss, there are other factors that limit the exact distance that optical fiber can support. This has been becoming one of the most serious problems in fiber optical communication. The following content will list the major factors that may limit the optical transmission distance.
Type of optic fiber
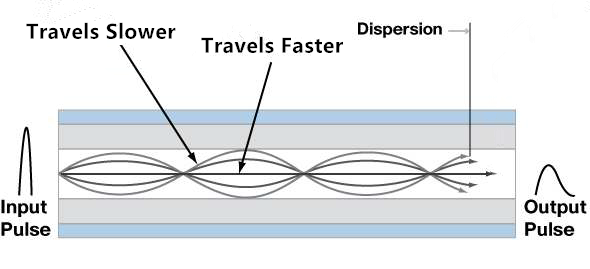
When signal is transmitted in a fiber optic cable, dispersion can not be avoided to happen. There are two types of dispersion named chromatic dispersion and modal dispersion. Both of them are caused because of the type of fiber. Basically, chromatic dispersion is that signal distributes over time as a result of different speeds of light beams. Modal dispersion is signal distributes over time as a result of different transmission modes.
Transmission by multimode fiber is mainly affected by modal dispersion. As signals are transmitted in multiple modes, they can not arrive at a time so that there must be an earlier one and a later one, which caused the optical dispersion happen and affect the transmission performance of multimode fiber.
Splices and Connectors
This factor is actually equal with the signal loss mentioned above. Signal loss would happen as optical signal travels through a splice or connector. While splices or connectors are necessary parts in most fiber optic system. In this case the most important consideration is the loss per kilometer. If less loss the fiber generates per kilometer, longer distance the fiber optic system can support.
Frequency of Transmission
Different types of fiber optic transceivers provide different transmission frequencies so that the transmission distance of an optical signal is affected. Normally, when fiber optic signal is transmitted at a higher frequency, the whole fiber optic system would support a longer distance.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is also affecting the transmission distance that fiber optic system supports. The higher the bandwidth is required in a fiber optic transmission system, the more limited the transmission distance would get.
Conclusion
Transmission distance is always taken into account when deploying fiber-optic network, especially for outdoor network deployment. the literal supportive distances of many optical components are not the exact distances they can support practically, knowing the factors affecting transmission distance must be beneficial for a correct design of network and selection of related fiber optical components.





































































