- Related articles
- All Cisco ONS-SI-GE-ZX's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-X9464PX= Switch
- Used in 10GBASE-ER Standard optical transceiver models
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N3K-C3172PQ-10GE= Switch
- What the IEEE Designation for the Gigabit Ethernet Standard is?
- All Cisco 15454-GBIC-LX's information (Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- 1 GBE SFP SX (1000BASE SX) fiber transceiver
- The datasheet of Cisco SFP-10G-SR
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960X-24TS-L Switch
- Applicable to 1000BASE-LH Standard optical transceiver models

Definition of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable
Ribbon fiber optic cable is the type of the fiber cable commonly contains 12 optical fibers and has a loose tube at the central part. In most cases, ribbon fiber optic cables are found in two types which include; dry tube and gel-filled ribbon cable. Ribbon fiber optic cable has facilitated great change in the fiber industry.
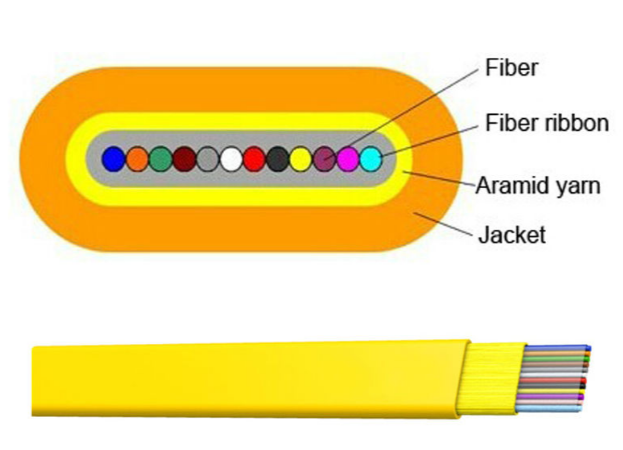
Description of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable
For cables over 144 fibers, a 65% time savings can be recognized by doing ribbon splicing versus single fiber splicing. It typically takes 20-30 minutes to splice 12 individual fiber compared to 7-10 minutes to splice a 12 fiber ribbon. These numbers assume the cable and fibers have been prepped and ready for splicing. This is a 65% reduction. In general terms, a ribbon cable is slightly higher in price versus a loose tube cable, depending on the number of fibers. The savings from mass fusion splicing more than makes up for the incremental cable cost.
Ribbon fibers can be spliced to a loose tube cable. It is a common practice to take 12 loose fibers and build a ribbon for mass fusion splicing. It is also common practice to remove the over coating from a ribbon and splice single fibers together. The term used for the coating that holds the 12 fibers into a rectangular shape in a ribbon cable is Matrix or Acrylic The over coating is used to describe the clear coating that holds the 12 fibers into a flat rectangular shape. The matrix coating easily removed so you can get to the individual fiber. Ribbon matrix over coating is easily removed at the end of the ribbon or in the middle of a ribbon. Normally ribbon matrix over coating peels away easily and cleanly, leaving no residue on the fibers
Advantages of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable
Savings: A ribbon cable allows 12 fibers to be spliced together at 1 time, thus reducing labor time and saving money.
A ribbon cable allows for more fiber to be placed in a smaller cable diameter.
Restoration time is much quicker with a ribbon cable, should a cable cut occur
Makeup of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable
The ribbon cable contains the same types of fiber as a Loose Tube cable
A ribbon fiber cable is typically constructed with the same type of fiber(s) used in a loose tube cable.
The fibers in a ribbon cable are the same colors as fiber used in a Loose Tube cable. A single ribbon contains all 12 standard colors of fiber as used in a Loose Tube cable.
Each ribbon has its own unique print identification. The words Blue, Orange, Green, Brown ( etc ) are printed on each individual ribbon.
Application of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable
Ribbon cables can be installed in aerial, duct, and direct buried applications
Ribbon fiber cables are suitable for aerial lashed, duct, or direct buried applications.
Ribbon cables are available in gel-filled tubes and dry tubes.
Manufactures produce both gel-filled and dry tube ribbon cables.
Conclusion
Ribbon fiber optic cable has facilitated great change in the many economies. This is because many people are now being employed by companies to produce the ribbon fiber optic cables. Consequently, this type of fiber cable gives value to your money because it offers top performance.





















































