- Related articles
- What can PCI-E 3.0 bring us?
- EoS & EoL Announcement for the Cisco FourX CFP to Four SFP+ Converter Module
- The difference between QSFP+ and CSFP
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C4500X-F-32SFP+ Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-4000-4GS8GP4G-E Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SRW2048-K9-UK Switch
- What is media converter in network?
- All Cisco MGBLX1's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matrix)
- What Is Multiport Network Card
- What Is Network Card PCI Express x1?

Over the past few decades, communication network has undergone a milestone development, software defined network (SDN) is a new network structure which sprang up in recent years, it uses OpenFlow technology to separate control planes and data planes from network equipment, thereby to achieve flexible control of network traffic, and provide an excellent platform for core network and application innovation. So, what on earth is software defined network (SDN)? What is the difference between software defined network (SDN) and traditional network? This article will give satisfied answers to these questions.
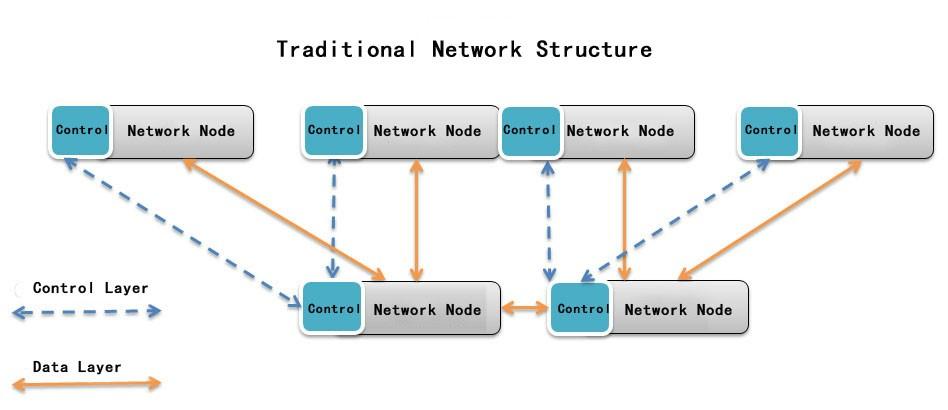
Brief introduction to traditional network structure
In traditional network structure, in order to connect the various terminal services of different services, various devices in the network are also forced to support both interfaces and protocols from both hardware and software. Data planes of the network equipment have to identify the types of each received data, and according to the results to find its corresponding forwarding rules and then forward it. At the control planes of equipment need to separately handle the protocol for each type of service to coordinate and control the forwarding behavior at the data planes. So that to form a stack of multiple business logic network in a physical network. As a result, with the growing number of service types, business logic network becomes increasingly, software and hardware is also becoming more complex, resulting in a decrease in the forwarding efficiency of the network and an increase in the development time of new services.
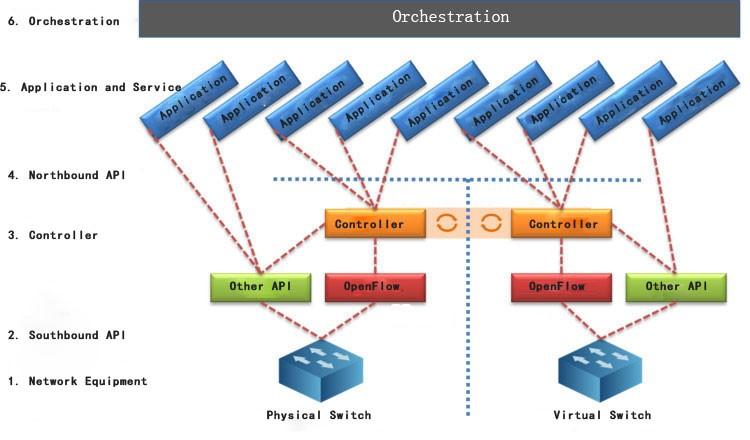
Brief introduction to software defined network (SDN)
 Architecture.jpg)
The components of SDN
Conclusion





















































