- Related articles
- All Cisco CWDM-SFP-1510's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- What is Mini PCI Express Network Card?
- Difference between GLC-T and SFP-GE-T
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3560V2-48TS-S Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960+24LC-L Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C4500X-F-32SFP+ Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco N9K-C93180YC-EX Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3750V2-48TS-S Switch
- Market Trends for Optical Interconnection Hardware in 2023
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco IE-3010-24TC Switch

PCI Express is a new generation of bus interface. In the spring of 2001, Intel is put forward to a new generation of technology to replace the PCI bus and the inner connection of a variety of chip, and is called the third generation I/O bus technology. At the end of 2001, Intel, AMD, DELL, IBM, more than 20 industry leading companies started drafting the specification of the new technology, and completed in 2002, officially named the PCI Express.
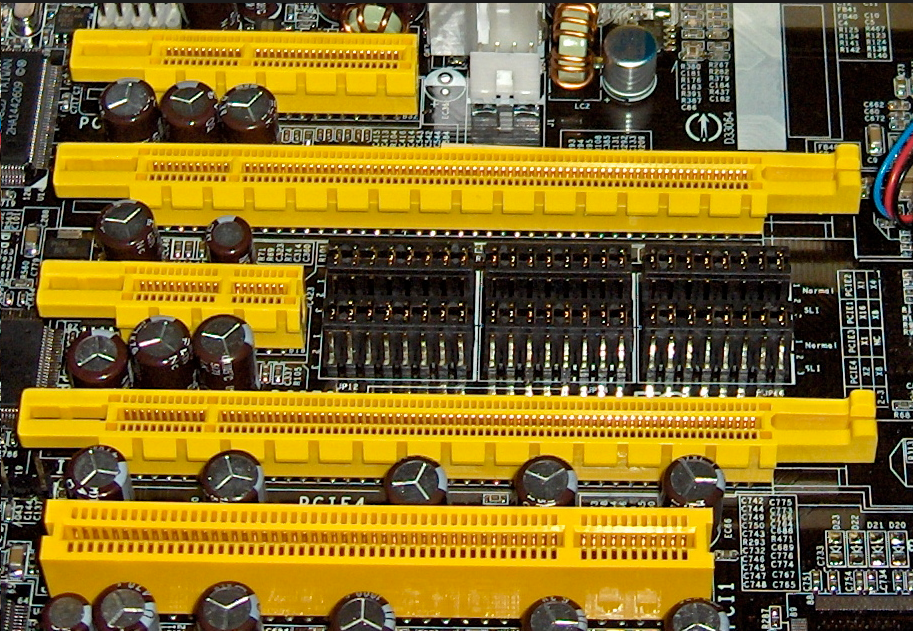
There are so many people feel confused about the different specifications of this brand-new bus interface, cannot fully understand the difference between them. For solving the problem, this article will detailed introduce the definition, parameters, compatibility and some related concepts of PIC-e. We hope that it will be helpful for readers.
Definition of PCI Express:
PCI Express(Peripheral Component Interconnect Express)(officially abbreviated as PCIe) is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standards, designed to replace the old PCI, PCI - X and the AGP bus standard. Compared to the older standards, PCIe has many improvements, including a higher maximum throughput of the system bus, the lower the number of I/O pins and a smaller physical footprint area, better bus equipment performance scale, more detailed error detection and reporting system (senior error reporting, AER) and local hot pluggable function. The latest revision of PCIe standard provides hardware support for the I/O virtualization
Modes of PCI Express:
PCI Express has several different modes, classified by transmission lanes: PCI Express x1, PCI Express x4, PCI Express x8, PCI Express x16. Please check the detailed parameters table.
|
Transmission lanes |
Total number of feet Pin |
Pin number of the main interface area |
Total length |
Length of the main interface area |
Bus width |
Working clock |
Transmission rate |
|
X1 |
36 |
14 |
25 mm |
7.65 mm |
8 Bits |
2.5 GHz |
512 MiB/s(Duplex) |
|
X4 |
64 |
42 |
39 mm |
21.65 mm |
8 Bits |
2.5 GHz |
2.0 GiB/s(Duplex) |
|
X8 |
98 |
76 |
56 mm |
38.65 mm |
8 Bits |
2.5 GHz |
4.0 GiB/s(Duplex) |
|
X16 |
164 |
142 |
89 mm |
71.65 mm |
8 Bits |
2.5 GHz |
8.0 GiB/s(Duplex) |
Difference between PCI Express x1, x4, x8, x16:
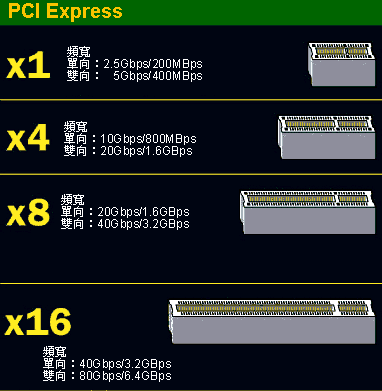
PCI Express Compatibility:
What is PCI Express slot?
Summary:





































































