- Related articles
- EoS and EoL News for the Cisco 10GBASE DWDM XENPAK Modules
- The Things You Need to Know about 40GBASE-KR4 Ethernet Standards
- All Cisco ONS-SI-2G-I1's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matr
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-24TD-E Switch
- What can PCI-E 3.0 bring us?
- GBIC Module, Main Function & Key Features
- All Cisco DWDM-XFP-44.53's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- All Cisco QSFP-40G-SR4-S’s Information ( Overview, Features, Datasheet PDF, Price, Specifi
- How to Configure the Dual Ethernet Adapter?
- All Cisco QSFP-100G-LR4-S's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility m

What is fiber optic cable?
Briefly, fiber optical cable is explained as a cable that contains single or multiple optic fibers in a protective and insulated jacket. It carries light to transmit the digital data through the optic fibers which are individually coated with plastic layer and contained in a glass tube. Namely, fiber optical cable is a data transmission medium.
But to know well about fiber optic cable, it’s necessary to know far more than the definition of fiber optic cable. In practical application, fiber optic cable is commonly used for long distance telecommunication, it brings people and enterprises great convenience and improvement in communication, which plays an increasingly important role in our daily life, so learning more about fiber optic cable is helpful for every single one when we enjoy the benefits it brings.
What is fiber optic cable made of?
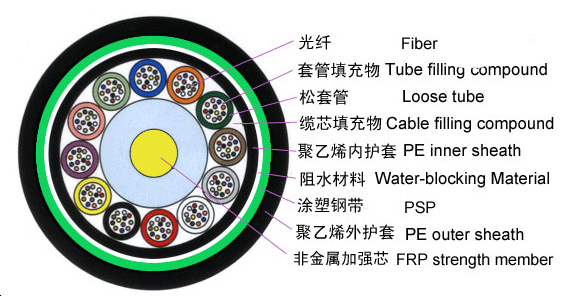
The structure of fiber optic cable includes three main parts: cable cores, strengthening components and protective covers and layers.
Cable core is made of single or multiple optic fibers, with two kinds of structure :loose cover and tight cover.
Strengthening components are generally made by metal wires or non-metal fibers, are used to strength the supportable load when cable laying.
Protective covers are made of LAP, steel (or wire) armor and polyethylene sheath and other components. They are used to protect the cable core with the functions of flame retardant, moisture, pressure, corrosion resistance.
How does fiber optic cable work?
In fiber optic cable, data transmission counts on light transmission. Light travels down a fiber optic cable by bouncing repeatedly off the glass tube due to internal reflection. Each tiny photon bounces down the tube like a bobsleigh going down an ice run, which forms a beam of light traveling in a clear glass tube, this is the light transmission.
To better understand how fiber optic cable works, it is advised to imagine a long soft plastic pipe whose internal surface is coated with glass or mirror, and you are walking in the pipe and looking for the end of pipe where your friend is, and your friend turns on the a flashlight and shines the light into the pipe. At the time the light will constantly bounces from the inside of the glass surface even though the pipe may be bent until it reaches to the destination, then you will see the light at the other end. And if your friend turns the flashlight on and off in a rule that stands for words which both of you know, you could communicate through the light. This is the essence of fiber optic cable working.
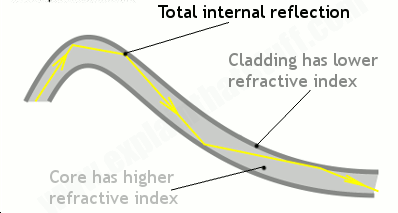
How fiber optics works
Fiber optics transmits data in the form of light particles, or photons, that pulse through a fiber optic cable. The glass fiber core and the cladding each have a different refractive index that bends incoming light at a certain angle.
When light signals are sent through the fiber optic cable, they reflect off the core and cladding in a series of zig-zag bounces, following a process called total internal reflection. The light signals do not travel at the speed of light because of the denser glass layers, instead traveling about 30% slower than the speed of light.
To renew, or boost, the signal throughout its journey, fiber optics transmission sometimes requires repeaters at distant intervals. These repeaters regenerate the optical signal by converting it to an electrical signal, processing that electrical signal and retransmitting the optical signal.
Fiber optic cables are now able to support up to 10 Gbps signals. Typically, as the bandwidth capacity of a fiber optic cable increases, the more expensive it becomes.
Fiber-optic internet
Fios -- the most awarded network for internet service satisfaction over the past 10 years.
Now that you know how fiber optics work, let’s talk about the many benefits of fiber-optic speed.
When you’re on a FTTH network, you’ll experience significantly faster upload and download speeds, more bandwidth for multiple devices at home and a reliable connection. And that’s exactly what you’ll get with Verizon Fios, the 100% fiber-optic network.
Fios Gigabit Connection in select areas offers speeds of up to 940 Mbps download and 880 Mbps upload. You’ll enjoy HD streaming, gaming, video conferencing and so much more on up 100 devices at a time –virtually lag-free. No wonder Fios has been rated #1 by industry leaders time and again. Shop for Verizon Fios and see if fiber internet is available in your area.
Capacity and market
In September 2012, NTT Japan demonstrated a single fiber cable that was able to transfer 1 petabitper second (1015bits/s) over a distance of 50 kilometers.
Although larger cables are available,the highest strand-count single-mode fiber cable commonly manufactured is the 864-count, consisting of 36 ribbons each containing 24 strands of fiber.
In some cases, only a small fraction of the fibers in a cable may actually be in use. Companies can lease or sell the unused fiber to other providers who are looking for service in or through an area. Depending on specific local regulations, companies may overbuild their networks for the specific purpose of having a large network of dark fiberfor sale, reducing the overall need for trenching and municipal permitting.Alternatively, they may deliberately under-invest to prevent their rivals from profiting from their investment.
Conclusion
This article is to make it easy to understand better the fiber optic cable with accessible words and pictures instead of some technical terms. Knowing well fiber optic cable is helpful when we do business with our customers so as to provide satisfied services.